Bushfire smoke eats up the ozone protecting us from dangerous radiation. The damage will increase as the world heats up
- Written by Ian Rae, Honorary Professorial Fellow, School of Chemistry, The University of Melbourne
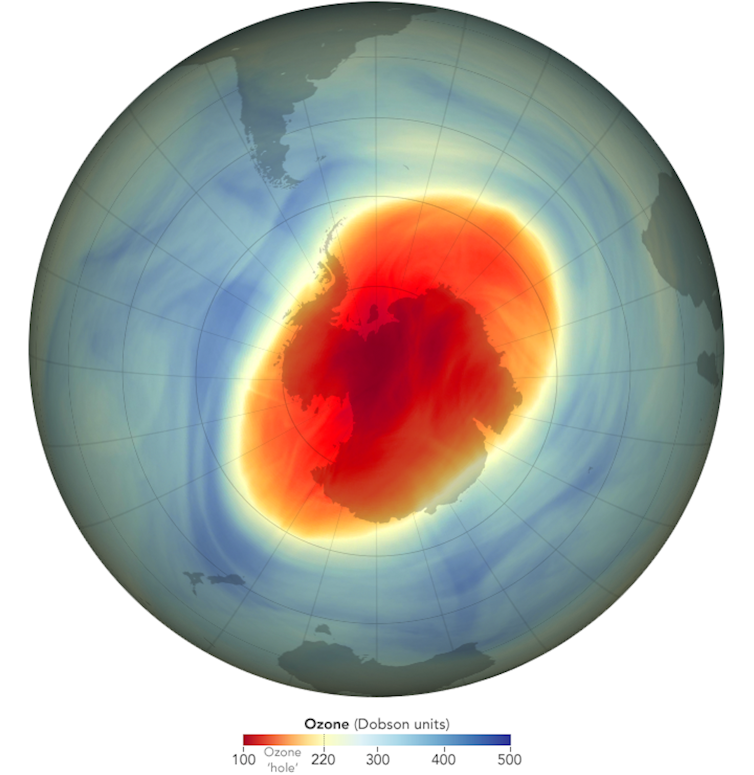
Can bushfire smoke reduce the concentration of ozone in the stratosphere? A decade ago, we might have been sceptical. But there’s a growing body of research showing a clear link.
Last year, MIT expert Susan Solomon and colleagues published a groundbreaking study showing the 900,000 tonnes of bushfire smoke and particles emitted during Australia’s 2019–20 Black Summer did, in fact, thin out the ozone umbrella that protects us[1].
Ozone floats around 20–25 kilometres above our heads, acting like airborne sunscreen. Its concentration is tiny – up to 15 parts per million – but it is highly effective at blocking damaging ultraviolet-B rays from the sun. Without this layer, many plants would die, while humans and other animals would be afflicted with skin cancers.
The Black Summer fires burned so much forest and scrub across the country they produced massive pyrocumulus clouds[2]. The fires were making their own weather, sending plumes of smoke into the higher reaches of our atmosphere, where smoke particles interacted with ozone. That single Australian summer of fire took out 1% of the atmosphere’s ozone – damage that will take a decade[3] to fix.
Now, Solomon’s researchers have found out how smoke actually does it. In their new research[4], they detail the chemistry involved. This research is important, as we enter what’s been dubbed the Pyrocene – the age of fire[5] – with bushfires already growing[6] in size and intensity as the world heats up.
So how does smoke break ozone?
Australians became all too familiar with the sight and smell of bushfire smoke over the Black Summer. But what’s in it?
Particles in bushfire smoke are carbonaceous, consisting of burnt and partly burnt vegetable material alongside sulfates – compounds which can be pumped into the atmosphere by volcanoes, fossil fuel burning, or bushfires.
The problem is, these carbonaceous particles bind well to substances like hydrogen chloride which comes from the chemical compounds found in living plants. Other compounds with chlorine are also involved in the smoke, such as the reactive chlorine nitrate and hypochlorous acid.
Read more: Bushfire smoke is everywhere in our cities. Here's exactly what you are inhaling[7]
The tiny smoke particles act as transport, carrying these substances containing chlorine up higher and higher to the stratosphere. Once there, chlorine sets about destroying ozone[8], molecule by molecule. Each chlorine atom can take apart hundreds of ozone molecules, meaning a small amount can have a disproportionate impact.
To find this out, Solomon and her colleagues relied heavily on models of the atmospheric chemistry. Their results agreed well with experimental observations made by satellite. So, although the chemical interactions have not been fully shown, the overall picture is probably correct.
You might remember it was chlorine atoms at the heart of our fears about the hole in the ozone layer. Almost 50 years ago, scientists discovered our protective ozone layer was thinning – and connected it to the chlorine-dense chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) used in spray cans and refrigerators.
The area of greatest loss was dubbed the “ozone hole”, which still appears over Antarctica each year in spring in smaller form.
The way we responded to the loss of stratospheric ozone is remarkable, in retrospect. In 1987, nations agreed to the Montreal Protocol, banning CFC manufacture and use. It worked, and concentrations of ozone are now recovering by around 1% a year. That figure is about what was lost during the Black Summer.
What does this mean for the future?
It means the ozone layer will be slowly degraded by wildfire smoke. Fires burn in both northern and southern hemispheres, and their smoke is swept around the globe by natural processes. That means we’re likely to see falling ozone concentrations in new places rather than just around the South Pole. Affected areas would include the mid-latitudes around the equator, where billions of people live.
Ozone does replenish itself. It’s continuously formed and destroyed in the stratosphere. The net balance of these competing processes has – until now – been a steady but small concentration of ozone. This layer makes life possible by absorbing the worst of the ultraviolet light pouring down from the sun and giving us a measure of protection from skin-damaging radiation.
A hotter world is one with more fire[10] in it, affecting areas like Siberian tundra, Californian mountains and Kenyan grasslands.
This research is yet another warning about the perils of unmitigated climate change. Bushfire smoke could undo the good work of the Montreal Protocol.
In retrospect, achieving this protocol seems relatively straightforward: ban one class of chemicals. To stop bushfire smoke eating away at our ozone umbrella means reversing climate change. And that is something we are struggling to do.
Read more: Repairing ozone layer is also reducing CO₂ in the atmosphere – new study[11]
References
- ^ protects us (www.dcceew.gov.au)
- ^ pyrocumulus clouds (en.wikipedia.org)
- ^ a decade (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ new research (doi.org)
- ^ age of fire (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ already growing (theconversation.com)
- ^ Bushfire smoke is everywhere in our cities. Here's exactly what you are inhaling (theconversation.com)
- ^ destroying ozone (www.epa.gov)
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
- ^ more fire (www.carbonbrief.org)
- ^ Repairing ozone layer is also reducing CO₂ in the atmosphere – new study (theconversation.com)

















