2 reasons for its record-shattering rainfall in NYC and the Northeast long after the winds weakened
- Written by Russ Schumacher, Associate Professor of Atmospheric Science and Colorado State Climatologist, Colorado State University
Record downpours from Hurricane Ida overwhelmed cities across the Northeast on Sept. 1, 2021, hitting some with more than 3 inches of rain an hour. Water poured into subway stations in New York and Boston. Streets flooded up to the rooftops of cars in Philadelphia. The storm had already wreaked havoc on the Gulf Coast after hitting Louisiana three days earlier[1] as a Category 4 hurricane.
Ida had weakened well below hurricane strength by the time it reached the Northeast, so how did it still cause so much rain?
Two major factors likely contributed to its extended extreme rainfall.
First, Ida’s tropical moisture interacted with developing warm and cold fronts.
Second, evidence is mounting that, as the climate warms, the amount of precipitation from heavy rainstorms is increasing, especially in the central and eastern U.S.
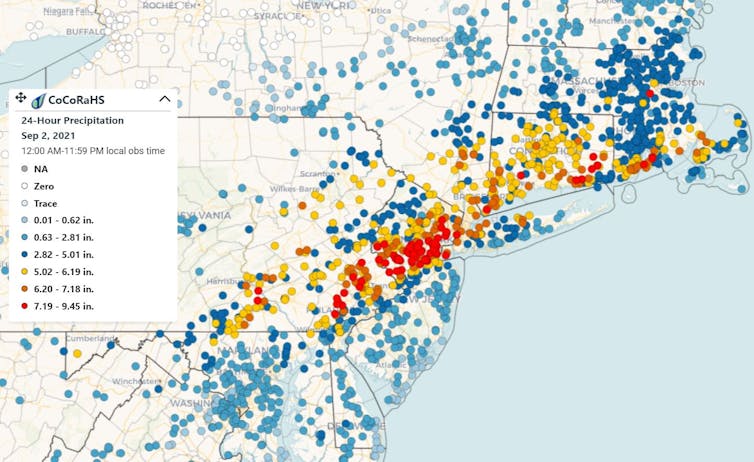 Rainfall totals over 24 hours, Sept. 1-2, 2021.
CoCoRaHS Mapping System, CC BY-ND[2][3]
Rainfall totals over 24 hours, Sept. 1-2, 2021.
CoCoRaHS Mapping System, CC BY-ND[2][3]
From tropical to extratropical
As hurricanes move northward from the tropics, they often transition from their characteristic circular shape to become “extratropical cyclones” with warm and cold fronts extending outward from the low pressure at the center. Even though they no longer have the intense winds that they did in the tropics, they still bring tropical humidity. That moist air is lifted along the fronts, and long-lasting, very heavy rain can result. That was happening as Ida’s remnants moved toward the Northeast.
Weather forecasters saw the disaster coming[4].
Forecasters emphasized the threat of flash flooding well ahead of its arrival, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Weather Prediction Center issued a rare “high risk” of excessive rainfall[5] outlook for parts of the Northeast a day in advance.
The widespread, intense rainfall overwhelmed rivers and drainage systems in the highly populated corridor from Philadelphia to New York and Boston. That led to major flash flooding and more than 45 deaths in the region[6]. Newark, New Jersey, recorded 8.41 inches of rain, their most ever in a single day, shattering the old record by over 1.5 inches. Weather stations in New York City saw rain rates over 3 inches per hour[7]. The extreme rainfall arrived with tornadoes in Maryland and New Jersey.
Warmer climate, heavier rainfall
Extreme rain and flash flooding aren’t new to the Northeast, and they often result from hurricanes or their remnants. The remains of Hurricanes Agnes (1972), Floyd (1999), Irene (2011), Lee (2011) and Sandy (2012), among others, all brought widespread rainfall and flooding through the area.
Yet, heavy downpours are becoming more common in the region as the climate warms.
The reasons are fairly simple: Warmer air can have more water vapor in it. With every 1 degree Celsius (1.8 F) increase in temperature, there can be about 7% more moisture in the air[8]. This is formally known as the Clausius-Clapeyron relation.
Because the amount of rain that a storm produces is closely connected to the amount of water vapor in the air, this means that, all else being equal, heavy downpours are more likely in a warmer climate[9]. It explains why heavy rain occurs year-round in the tropics, whereas it is much more likely in summer than winter in the U.S.
This is also why the intensity of rainfall is expected to increase as the climate warms. When weather patterns that bring together the ingredients for heavy rainfall, like hurricanes, occur in a warmer world, more moisture is available, and more rain falls. Unfortunately, this is not a linear process: A small bit of added moisture can lead to a lot more rain[10].
The latest National Climate Assessment, in 2018, described a trend toward increasing precipitation in the Northeast[11] and also warned that aging infrastructure in the region isn’t prepared to handle the water.
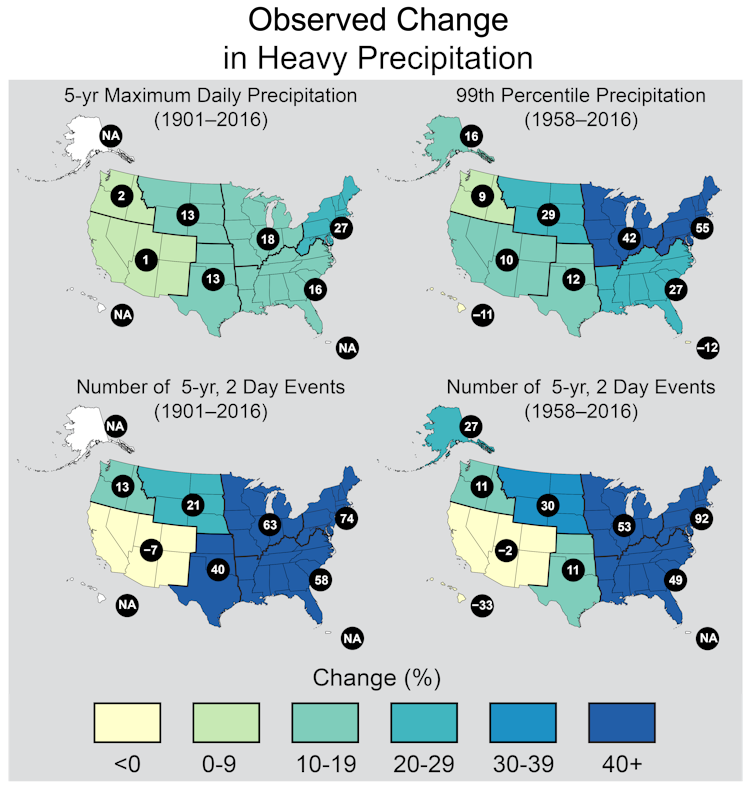 Observed changes in heavy precipitation across the U.S., from the 4th National Climate Assessment. This figure shows four different metrics of heavy precipitation change. For example, the upper right panel shows that in the northeastern U.S., the amount of rain in the heaviest precipitation events increased by 55% from 1958-2016.
4th National Climate Assessment
Observed changes in heavy precipitation across the U.S., from the 4th National Climate Assessment. This figure shows four different metrics of heavy precipitation change. For example, the upper right panel shows that in the northeastern U.S., the amount of rain in the heaviest precipitation events increased by 55% from 1958-2016.
4th National Climate Assessment
Hurricanes are limited to certain areas, but extreme rainfall from other types of storms can occur just about anywhere – think of intense cloudbursts during the summer monsoon in the Desert Southwest, or organized thunderstorm systems like the one that caused deadly flooding in Tennessee[12] in August 2021.
Many communities are already highly vulnerable to the type of extreme precipitation that has been observed historically. Floods have always been a hazard, and intense rainfall can test the infrastructure even in places where it happens often. But as the climate changes, these risks will only increase further.
This article was updated Sept. 2 with the Northeast death toll rising.
[Over 100,000 readers rely on The Conversation’s newsletter to understand the world. Sign up today[13].]
References
- ^ hitting Louisiana three days earlier (theconversation.com)
- ^ CoCoRaHS Mapping System (maps.cocorahs.org)
- ^ CC BY-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ saw the disaster coming (www.nhc.noaa.gov)
- ^ high risk” of excessive rainfall (www.nhc.noaa.gov)
- ^ more than 45 deaths in the region (apnews.com)
- ^ over 3 inches per hour (twitter.com)
- ^ 7% more moisture in the air (www.ipcc.ch)
- ^ heavy downpours are more likely in a warmer climate (www.ipcc.ch)
- ^ small bit of added moisture can lead to a lot more rain (theconversation.com)
- ^ a trend toward increasing precipitation in the Northeast (nca2018.globalchange.gov)
- ^ deadly flooding in Tennessee (apnews.com)
- ^ Sign up today (theconversation.com)

















