Today's decisions lock in industry emissions for decades — here's how to get them right
- Written by Alison Reeve, Deputy Program Director, Energy and Climate Change, Grattan Institute
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[1] has made clear there’s little time left to reach net zero emissions and hold the global temperature rise to 1.5C.
If Australia is to do its bit, emissions need to fall across the economy.
The states and territories all have net-zero targets for 2050, and the prime minister says the national target is also net zero emissions, preferably by 2050.
2050 feels a long way off. It’s ten election cycles for prime ministers, seven for state premiers. Does that mean there’s plenty of time to come up with mechanisms to get us there?
Unfortunately, no. Here’s why.
For net zero, 2050 is sooner than you think
Around 30% of Australia’s emissions come from the industrial sector — from facilities such as coal mines, liquefied natural gas platforms, steel smelters, and zinc processing plants.
These facilities have long operating lives — up to 30 to 40 years, sometimes more.
This means facilities that start up tomorrow will probably still be operating in 2050. Older facilities have only one replacement cycle between now and 2050.
Companies don’t have ten chances to get on the pathway right. They have one.
Read more: IPCC says Earth will reach temperature rise of about 1.5℃ in around a decade. But limiting any global warming is what matters most[2]
Planning to replace an ageing asset starts well before it is due to end its life, and companies can only consider realistic options.
They can’t assess costs and risks on technologies that are still in the lab.
If low-emissions technologies aren’t available or commercially feasible when decisions are made, what firms do install will lock in decades of future emissions.
Decisions made today will extend beyond 2050
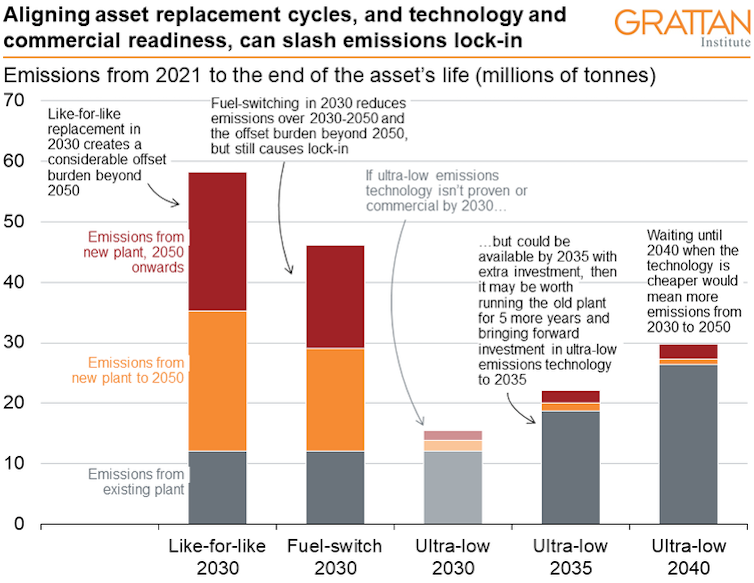
Consider a coal-powered cement plant that will reach the end of its design life in 2030. The owner is considering three options
like-for-like replacement that still uses coal but is slightly more efficient, with costs and risks well understood
a new plant that uses gas as well as coal, whose costs and risks can be forecast with some certainty
an experimental ultra-low-emissions technology, expected to be commercially ready in 2040, with hard to quantify costs and risks, and bigger upfront cost
Taking the third option (waiting) might mean squeezing another 10 years out of an ageing plant, with a risk it might not make the distance.
This chart shows emissions between now and the end of the new plant’s life for each option.
 Grattan analysis of public data for various Australian cement facilities.
Towards Net Zero: practical policies for the industrial sector[3]
Grattan analysis of public data for various Australian cement facilities.
Towards Net Zero: practical policies for the industrial sector[3]
Like-for-like replacement locks in considerable emissions between 2030 and 2050, and the risk of having to buy carbon offsets between 2050 (when Australia moves to next zero) and the end of the plant’s life in 2070.
A changed fuel mix reduces the lock-in and the likely burden of offsets, but they are still material.
Waiting until 2040 (and running the risk that the old plant might not have an extra 10 years life in it) will mean less emissions after 2040 and less liability for carbon offsets, but much more emissions before then.
Read more: Top economists call for measures to speed the switch to electric cars[4]
From an emissions perspective, the best decision may be a halfway house — running the old plant for an extra five years, and installing the new technology before it is fully commercial, if someone else is willing to share the risk.
Without a signal from either a state or federal government the cement plant owner is likely to go with option one or two.
Government can help
Our report, Towards Net Zero: practical policies for the industrial sector[5], outlines three things the federal government can do now to tilt companies’ decisions in favour of something like option three.
First, it can signal that it expects all new facilities to avoid locking in long tails of emissions.
The best way to do this would be to fulfil its 2015 commitment to set best-practice benchmarks[6] for new facilities. They were meant to be in place by 2020[7].
Second, it should set up an Industrial Transformation Future Fund[8] in order to share the risk of new technologies with industry.
Read more: Australia's economy can withstand the proposed EU carbon tariff[9]
Third, it should adjust its safeguard mechanism[10] under which big emitters have report and adhere to emissions intensity standards to require them to start cutting emissions immediately.
This would level the field between new and old facilities. It would mean some older facilities closed earlier than planned, but it would mean they would be replaced by cleaner facilities.
It is important these policies start now. Every decision we make from now on will affect our chance of reaching net zero and escaping catastrophic climate change.
References
- ^ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (theconversation.com)
- ^ IPCC says Earth will reach temperature rise of about 1.5℃ in around a decade. But limiting any global warming is what matters most (theconversation.com)
- ^ Towards Net Zero: practical policies for the industrial sector (grattan.edu.au)
- ^ Top economists call for measures to speed the switch to electric cars (theconversation.com)
- ^ Towards Net Zero: practical policies for the industrial sector (grattan.edu.au)
- ^ benchmarks (cdn.theconversation.com)
- ^ 2020 (cdn.theconversation.com)
- ^ Industrial Transformation Future Fund (grattan.edu.au)
- ^ Australia's economy can withstand the proposed EU carbon tariff (theconversation.com)
- ^ safeguard mechanism (www.cleanenergyregulator.gov.au)
















