How do nuclear-powered submarines work? A nuclear scientist explains
- Written by AJ Mitchell, Research fellow, Australian National University
The Australian government has just declared an historic defence agreement[1] with the United States and United Kingdom that will see a new fleet of nuclear-powered submarines patrol our shores and surrounding waters.
Research into nuclear-based propulsion of marine vessels began in the 1940s with the dawn of the “nuclear age”. Since then, only six nations have owned and operated nuclear submarines: China, France, India, Russia, the UK and the US.
Considering Australia has just torn up a A$90 billion contract to construct a new arsenal of conventional submarines, yesterday’s announcement will probably come as a surprise to many.
Read more: Australia to build nuclear submarines in a new partnership with the US and UK[2]
So what is “nuclear” about a nuclear submarine? The first thing to say is that a nuclear-powered submarine is not a nuclear weapon.
On the surface, they look like any other submarine. The key difference lies in the way they are powered.
In the early days of atomic research, scientists rapidly realised the huge amounts of energy released by “splitting the atom” can be harnessed to generate electricity. Nuclear reactors inside power stations have been powering homes and industry across the world for 70 years. Similarly, each nuclear submarine draws power from its own miniature onboard nuclear reactor.
 Prime Minister Scott Morrison announced the new submarine fleet as part of a new trilateral security pact with the United Kingdom and United States.
Mick Tsikas/AAP Image
Prime Minister Scott Morrison announced the new submarine fleet as part of a new trilateral security pact with the United Kingdom and United States.
Mick Tsikas/AAP Image
At the heart of every atom is an atomic nucleus, made of protons and neutrons. The number of protons defines what chemical element that atom belongs to; nuclei with the same number of protons but varying numbers of neutrons are called isotopes of that element.
Some very heavy nuclei are highly susceptible to a process known as nuclear fission, whereby they split into two lighter nuclei with a total mass less than the original nucleus. The remainder is converted to energy.
The amount of energy released is immense, as we can see from Einstein’s famous equation, E = mc², which tells us the energy is equal to the change in mass multiplied by the square of the speed of light!
Reactors in a nuclear-powered submarine are typically fuelled with uranium. Natural uranium mined from the ground consists mainly of an isotope called uranium-238, mixed with small amounts (0.7%) of the key isotope uranium-235.
For the reactor to work, the uranium fuel has to be “enriched” to contain the desired proportion of uranium-235. For submarines, this is typically about 50%. The degree of fuel enrichment is a crucial factor in maintaining a chain reaction that gives a consistent, safe level of energy output.
Inside the reactor, uranium-235 is bombarded with neutrons, causing some of the nuclei to undergo nuclear fission. In turn, more neutrons are released and the process continues in a so-called “nuclear chain reaction”. The energy is given off as heat, which can be used to drive turbines that generate electricity for the submarine.
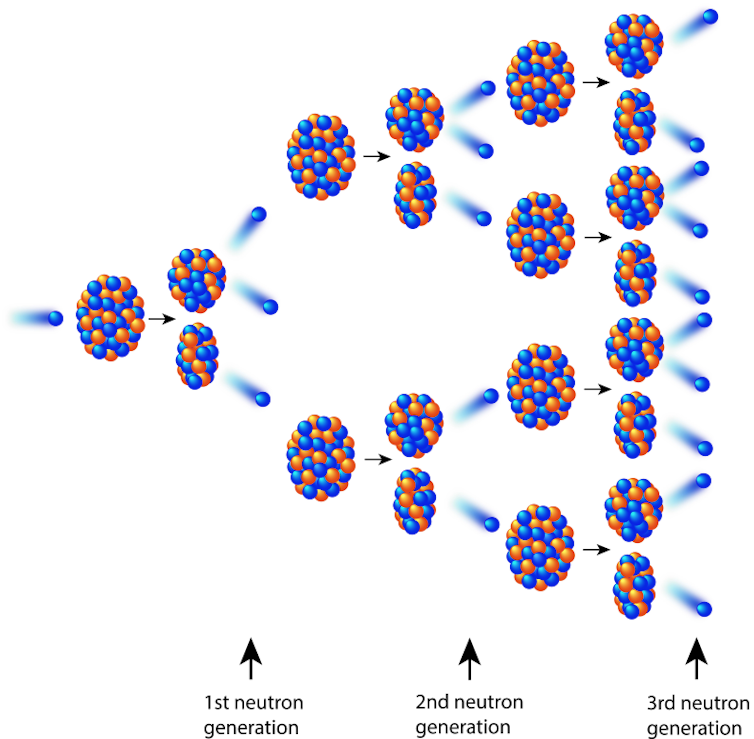 Conceptual diagram of a nuclear fission chain reaction.
ANU, Author provided
Conceptual diagram of a nuclear fission chain reaction.
ANU, Author provided
What are the pros and cons of going nuclear?
One huge advantage of nuclear-powered submarines is they do not require refuelling. When one of them enters into service, it will be commissioned with enough uranium fuel to last more than 30 years.
The high efficiency of nuclear power also enables these submarines to operate at high speed for longer periods than conventional diesel-electric submarines. What’s more, unlike conventional fuel combustion, nuclear reactions do not require air. That means nuclear submarines can stay submerged at deep depths for months at a time, giving them better stealth capabilities and allowing for longer, more remote deployments.
The downside is the eye-watering cost. Each nuclear submarine typically costs several billion dollars to build, and requires a highly skilled workforce with expertise in nuclear science. With its dedicated training programs offered by world-class universities and government agencies, Australia is well situated to meet the increasing demands in this space, and will also benefit from existing UK and US expertise through the new trilateral security pact.
At this stage, details on where the fuel would be sourced are unclear. While Australia has an ample supply of uranium in the ground, it lacks the capacity to enrich or fabricate the reactor fuel, which could be sourced from overseas.
What will happen to the spent fuel? The 2015 Nuclear Fuel Cycle Royal Commission[3] found commercial viability for long-term radioactive waste storage and disposal facilities in South Australia. Whether this eventuates will doubtless be subject to deliberations at local and federal government levels for years to come.
Read more: Why nuclear submarines are a smart military move for Australia — and could deter China further[4]
Popular misconceptions
I’ll say it again. This is not a call by Australia to deploy nuclear weapons in our waters. For uranium to be designated “weapons grade”, it needs to be enriched to upwards of 90% uranium-235 - the fuel for a nuclear-powered submarine doesn’t come close.
In any case, Australia has never produced a nuclear weapon, and it is a party to nuclear nonproliferation treaties and international export control regimes, including the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons and Non-Proliferation and Disarmament Initiative[5].
The tactical advantage of submarines comes from their stealth and ability to pinpoint targets secretly without detection.
Maintaining safety, for both crew and the natural environment, is crucial onboard any sea vessel. Hollywood movies such as K19: The Widowmaker[6], in which a nuclear submarine malfunctions on its maiden voyage, play on our emotions and our instinctive fear of nuclear radiation.
But advances in modern safety controls and procedures mean reactor accidents in submarines are hopefully now consigned to the past.
The strategic and geopolitical outcomes of this policy decision are yet to be seen. But one thing is already clear: Australia’s latest foreign policy venture is also a firm embrace of nuclear science.
References
- ^ historic defence agreement (theconversation.com)
- ^ Australia to build nuclear submarines in a new partnership with the US and UK (theconversation.com)
- ^ Nuclear Fuel Cycle Royal Commission (nuclearrc.sa.gov.au)
- ^ Why nuclear submarines are a smart military move for Australia — and could deter China further (theconversation.com)
- ^ Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons and Non-Proliferation and Disarmament Initiative (www.dfat.gov.au)
- ^ K19: The Widowmaker (www.imdb.com)

















