The Heart of Speed: An In-Depth Look at Racing Engines

Racing engines are the beating heart of motorsport, engineered for speed, performance, and reliability. These powerhouses are finely crafted machines, embodying the pinnacle of automotive engineering. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of racing engines, including their design, performance characteristics, types, and the latest advancements in technology.
Understanding Racing Engines
At their core, racing engines differentiate themselves from standard automotive engines through their focus on maximizing power output and efficiency while minimizing weight and resistance. Racing engines often utilize enhanced materials, advanced fuel formulations, and intricate design features that allow them to endure the demanding conditions of competition racing engines.
Key Characteristics
- High Power Output: Racing engines produce significantly more horsepower compared to standard engines. An average racing engine can exceed 800 horsepower, depending on the racing class and regulations. This power allows cars to reach blistering speeds on the track.
- High Rev Limits: Racing engines are designed to operate at high revolutions per minute (RPM), often exceeding 10,000 RPM in some motorsport categories. This characteristic enables the engine to generate more power over a smaller displacement.
- Lightweight Design: Weight is critical in racing. Engineers utilize lightweight materials such as titanium and carbon fiber in components like pistons, rods, and crankshafts to reduce weight without compromising strength and durability.
- Enhanced Cooling Systems: Racing engines generate significant heat during operation. High-performance cooling systems with specialized radiators and oil coolers are crucial to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating.
- Precision Engineering: Tolerances in racing engines are typically much tighter than in standard road cars. This precision allows for increased performance through enhanced airflow, combustion efficiency, and ultimately, more power.
Types of Racing Engines
Racing engines can be categorized based on their design, fuel type, and racing class. Here are some of the most common types:
- Naturally Aspirated Engines
These engines rely on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chamber. Naturally aspirated engines tend to provide smoother power delivery and are preferred in many categories of racing, including Formula 1 and sports car racing. Tuned for high RPM, these engines maximize airflow and combustion efficiency without the complexity of forced induction.
- Turbocharged Engines
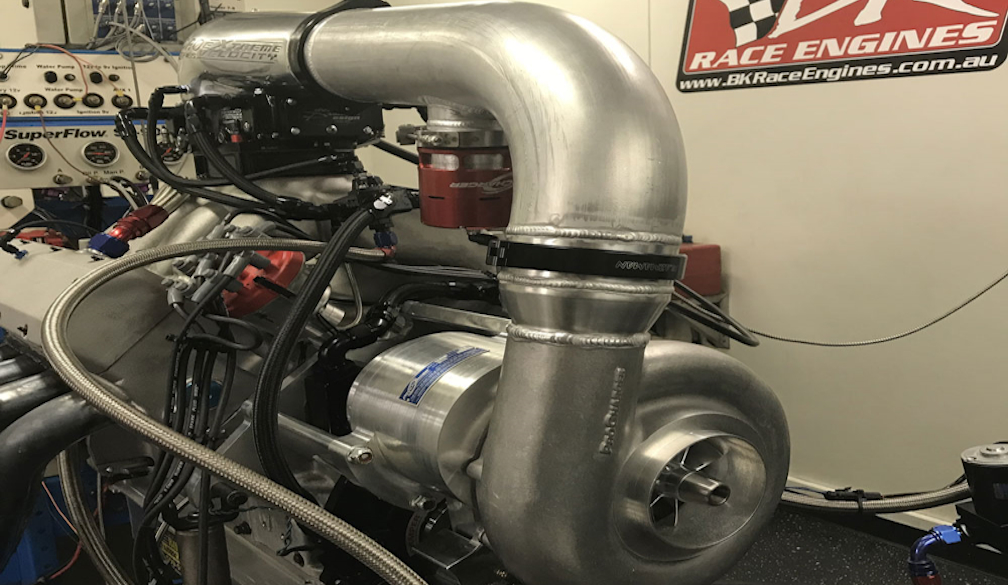
Turbochargers force additional air into the combustion chamber, allowing the engine to burn more fuel and generate more power. This technology is ubiquitous in modern motorsport, including NASCAR and World Rally Championship (WRC). Turbocharged engines can deliver impressive performance despite having smaller displacements, leading to lightweight and efficient powerplants.
- Supercharged Engines
Similar to turbochargers, superchargers compress air entering the engine. However, superchargers are mechanically driven, often resulting in immediate power delivery without any lag as seen in turbo systems. These engines often find their place in drag racing due to their instant throttle response.
- Hybrid Powertrains
The integration of electric motors with traditional internal combustion engines has given rise to hybrid powertrains in motorsport. Formula E and some modern endurance racing events utilize this technology, showcasing the potential for cleaner, more efficient racing while still delivering exceptional performance.
Innovations in Racing Engine Technology
The automotive industry continues to push the envelope in racing engine development, driven by competition and the demand for efficiency. Some of the key innovations include:
- Advanced Materials
The use of composite materials, such as carbon-fiber reinforced polymers and advanced alloys, has revolutionized the weight and durability of engine components. This not only improves performance but also enhances reliability during long races.
- Engine Management Systems
Modern racing engines rely on sophisticated engine management systems that utilize real-time data and algorithms to optimize fuel mapping, ignition timing, and throttle response. These systems are highly programmable, allowing engineers to fine-tune performance for specific tracks and conditions.
- Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
VVT technology adjusts the timing of the intake and exhaust valves, enhancing performance across varied RPM ranges. This versatility allows racing engines to maintain high performance throughout different phases of a race.
- Alternative Fuels and Electrification
As motorsports look to a more sustainable future, alternative fuel sources like biofuels, synthetic fuels, and electric power are becoming increasingly significant. Events like Formula E are pioneering electric racing, proving that sustainability and performance can coexist on the track.
Conclusion
Racing engines represent the culmination of innovation, engineering prowess, and a relentless quest for speed. They are not just machines; they are a testament to human ingenuity and the passion for motorsport. As technology continues to advance, racing engines will undoubtedly evolve, balancing the age-old quest for speed with the modern need for efficiency and sustainability. From the roar of a naturally aspirated V8 to the silent swiftness of an electric racer, the world of racing engines is a fascinating landscape where the limits of possibility are continually pushed. Drivers and teams alike push the envelope in pursuit of victory, making every race a thrilling testament to the art and science of racing engineering.