Move over mānuka – here are 5 other delicious native NZ honeys to try this summer
- Written by Megan Grainger, Senior Lecturer in Analytical Chemistry, University of Waikato
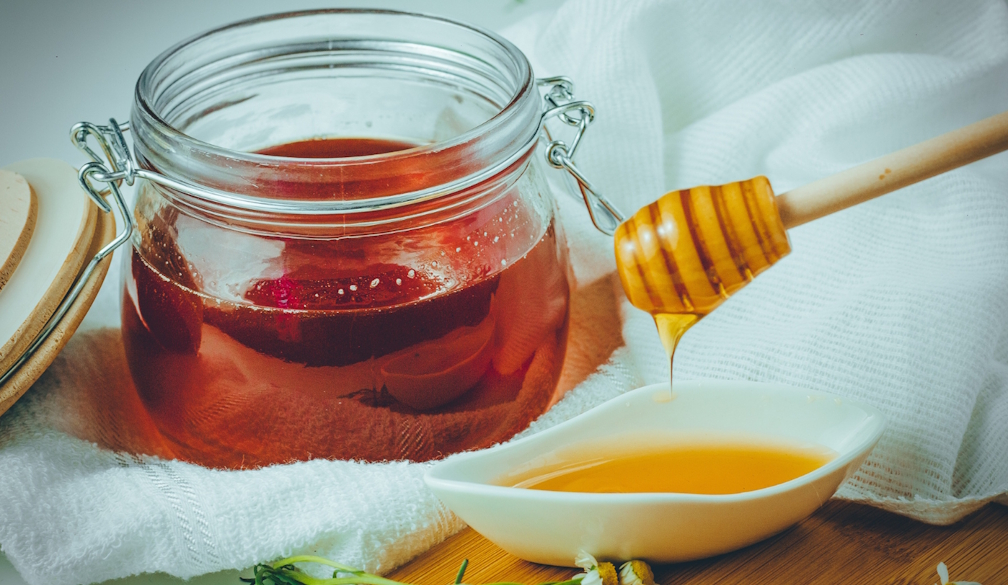

As I write, the summer landscape is bright with pōhutukawa flowers. Sitting in the shade of the “New Zealand Christmas tree”, I can hear bees humming as they move between flowers collecting nectar.
Pulling the picnic basket near, I cut a slice of fresh bread and cover it in white honey – made from that very pōhutukawa nectar. This is indeed the taste of summer – sweet, like butterscotch with a hint of salt.
But pōhutukawa honey, like other native varieties, tends to live in the shadow of its famous cousin, mānuka. That’s a shame, because the options, and the potential for more industry growth, are certainly there.
To continue driving the industry forward, we need to be thinking about those lesser-known New Zealand native honeys. At the moment, however, these are often mixed as “bush honey”, since there isn’t a large market for their individual sale.
All honey is primarily glucose and fructose, but the flavour profile comes from other compounds found in nectar that remain once it is converted into honey by bees. The combination of compounds varies between species, giving rise to some delectable flavours.
Not so long ago, consumers only had a choice of red or white wine. Now there are multiple varieties, each suited to their own occasion. Honey, too, can spread its variety around a bit more.
Liquid gold rush
New Zealand mānuka honey is still highly sought-after, of course. Its unique non-peroxide antibacterial activity[1] was discovered in the 1980s by biochemist Peter Molan. It wasn’t until 2008 that the compound responsible, methylglyoxal[2], was identified. This allowed honey to be graded by its antibacterial activity – and the price of mānuka dramatically increased.
Mānuka honey is now a household name and valuable brand. It’s used medically, as well as on toast, and even been endorsed by celebrities such as Novak Djokovic and Ariana Grande. The most expensive jar[3] ever sold went for NZ$4,964 for 230 grams at Harrods in London in 2021.
In 2022, 76% of the $583 million generated by the New Zealand apiculture (beekeeping) sector was from mānuka honey exports. Many beekeepers chased the mānuka flowering season while honey prices were high and honey was easy to sell, with 918,026 beehives registered in 2019.
But hive numbers are now down 34.5% and it appears the liquid gold rush might be over. A large honey surplus and weaker consumer demand are tipping the supply and demand balance in the wrong direction for now.
Putting all the eggs in one basket – or all bees on one flowering crop – is a risk for beekeepers. And these days, extreme weather events during summer can add to the uncertainty.
Heavy rains in some places last summer resulted in a 45% decrease[4] in honey production compared to the previous year. The mānuka tree flowers for a short period, and such events can affect the volume of honey harvested and hence annual revenue.
Sweet variety
Apiculture New Zealand[5] wants to future-proof the industry[6] and believes the honey sector can more than double by 2030, mostly due to increasing mānuka exports. This will take time as the supply-demand scale is rebalanced.
Diversification can be another strategy. Nectar-producing native plants produce a wide range of honey flavours, all worthy choices for the consumer.
In fact, other varieties can compete successfully with mānuka internationally, and a rewarewa honey was awarded “world’s best tasting honey[7]” at the 2021 Black Jar Honey Contest[8] in the United States.
Rewarewa has a rich, malty flavour. But it is also reported to have anti-bacterial, anti-fungal[9] and anti-inflammatory[10] properties. While this is promising news, there are currently only a few studies based on limited samples.
Further research on honeys from various geographical locations and seasons is needed. But this takes time, money and resources. In the meantime, we can just enjoy one of the world’s oldest foods for its taste. Here are five New Zealand native honeys to keep an eye out for:
-
tāwari has been described as tasting like white chocolate melting off the tongue, and is superb on pancakes or ice cream
-
kāmahi is sweet with a buttery finish, and is a match with camembert or goat’s feta
-
kānuka is described as earthy with a toffee-like finish
-
rata is mild and rich, not too sweet, with a fruity taste and hint of salt
-
pōhutukawa is salty-sweet, a touch of butterscotch with a sprinkle of salt.
Increasing the profile of more native honeys would benefit the apiculture industry, build resilience into beekeeping businesses, diversify exports over time, and help maintain ecological biodiversity – which is important for our native fauna.
This summer, why not head to a farmer’s market, or even jump online from your deckchair, and support New Zealand’s smaller beekeepers by trying some of these native honeys. You may just find your next favourite to add to that charcuterie board or drizzle on your ice cream.
References
- ^ non-peroxide antibacterial activity (www.sciencedirect.com)
- ^ methylglyoxal (www.sciencedirect.com)
- ^ expensive jar (www.nzherald.co.nz)
- ^ 45% decrease (www.mpi.govt.nz)
- ^ Apiculture New Zealand (apinz.org.nz)
- ^ future-proof the industry (apinz.org.nz)
- ^ world’s best tasting honey (www.manawahoney.co.uk)
- ^ Black Jar Honey Contest (centerforhoneybeeresearch.org)
- ^ anti-bacterial, anti-fungal (www.tandfonline.com)
- ^ anti-inflammatory (journals.sagepub.com)