New technology can create treatment against drug-resistant bacteria in under a week and adapt to antibiotic resistance
- Written by Kristen Eller, PhD Candidate in Chemical Engineering, University of Colorado Boulder
The Research Brief[1] is a short take about interesting academic work.
The big idea
A new technique my colleagues and I developed[2] that can kill deadly, multidrug-resistant bacteria[3] in real time could be used to generate targeted therapies that replace traditional, increasingly ineffective antibiotics.
Bacteria follow the same basic genetic process[4] that all organisms do: DNA, which contains instructions on how an organism will look and function, is copied into an intermediate form called RNA that can be translated into proteins and other molecules the organism can use.
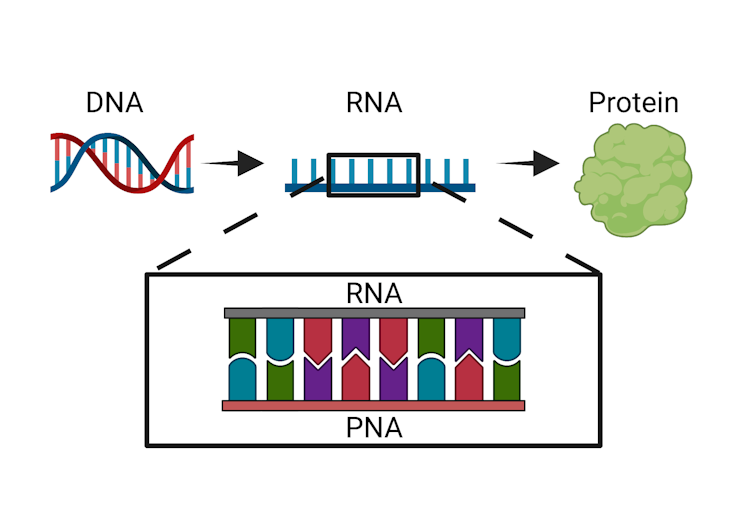 PNAs can be introduced to interrupt the process in which DNA is converted into protein or other useful biological molecules necessary for life.
Kristen Eller, CC BY-ND[5]
PNAs can be introduced to interrupt the process in which DNA is converted into protein or other useful biological molecules necessary for life.
Kristen Eller, CC BY-ND[5]
The technique we developed at the Chatterjee Lab[6] at the University of Colorado Boulder uses a synthetic version of RNA called PNA, or peptide nucleic acid[7], to disrupt this basic process in bacteria. Our PNA molecule clings to the bacterial RNA, blocking it from carrying out its job. Because this molecule is a perfect match to bacterial RNA, it binds very tightly to the RNA and resists degradation. This means that it can not only escape the bacteria’s error detection processes but also prevent that RNA from being translated into proteins and other useful biological molecules. This impediment can be lethal to the bacteria.
Our study, which we recently published in Communications Biology, demonstrates the therapeutic potential of a technique that can design, synthesize and test PNA treatments in under a week.
Most antibiotics aren’t specific enough to target only infectious bacteria without also destroying the body’s good bacteria[8]. Our technology, however, uses noninfectious versions of multidrug-resistant bacteria to create highly specific molecules. By targeting just the pathogen of interest, these PNA therapeutics may avoid the harm that current antibiotics pose to the body’s good bacteria.
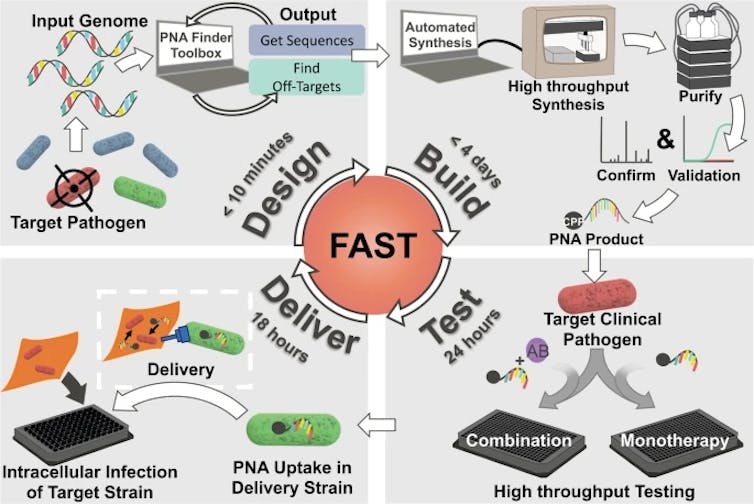 The Facile Accelerated Specific Therapeutic (FAST) platform can produce therapies against multidrug-resistant bacteria in under a week.
Kristen Eller, CC BY-ND[9][10]
The Facile Accelerated Specific Therapeutic (FAST) platform can produce therapies against multidrug-resistant bacteria in under a week.
Kristen Eller, CC BY-ND[9][10]
Why it matters
Bacteria’s adaptation to survive current antibiotics, or antibiotic resistance[11], is on the rise.
Medicine’s current arsenal of treatments mostly consist of naturally occurring antibiotics that were isolated more than 30 years ago[12]. Discovery of new antibiotics in nature has stagnated while bacteria continue to evolve and evade current treatments. And even if scientists were to find a new natural antibiotic, research shows that bacteria will begin to develop resistance within as little as 10 years[13], leaving us in the same predicament as before.
New types of therapies need to be considered for a post-antibiotic era[14], a time when our arsenal of antibiotics is no longer effective. By using a system that can target specific bacteria and be continuously modified based on emerging resistance patterns, doctors would no longer have to rely on chance discoveries. Treatments can adapt with bacteria.
What still isn’t known
Although we explore multiple characteristics that determine which RNA sequences are the best targets, more research is necessary to identify the most effective PNA therapeutics against multidrug-resistant bacteria. As our study only tested our new strategy on cell cultures in the lab, we’ll also need to see how it works in living animals to maximize the effectiveness of this kind of treatment.
What’s next
Our team is currently testing the technology in different animal models against different types of infections. We are also exploring other PNA delivery options, including adapting our bacterial delivery system to probiotic strains so it can integrate with the existing healthy bacteria population in the body.
With further development, our goal is to adapt the platform to target diseases that also use the same basic genetic processes as bacteria, such as viral infections or cancer.
[Get the best of The Conversation, every weekend. Sign up for our weekly newsletter[15].]
References
- ^ Research Brief (theconversation.com)
- ^ new technique my colleagues and I developed (doi.org)
- ^ multidrug-resistant bacteria (doi.org)
- ^ same basic genetic process (www.yourgenome.org)
- ^ CC BY-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ Chatterjee Lab (www.colorado.edu)
- ^ PNA, or peptide nucleic acid (www.atdbio.com)
- ^ without also destroying the body’s good bacteria (doi.org)
- ^ Kristen Eller (doi.org)
- ^ CC BY-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ antibiotic resistance (www.cdc.gov)
- ^ more than 30 years ago (sitn.hms.harvard.edu)
- ^ as little as 10 years (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- ^ post-antibiotic era (www.cdc.gov)
- ^ Sign up for our weekly newsletter (theconversation.com)

















