how human trash in Australian bird nests changed over 195 years
- Written by Kathy Ann Townsend, Senior Lecturer in Animal Ecology, University of the Sunshine Coast
Environmental scientists see flora, fauna and phenomena the rest of us rarely do. In this series, we’ve invited them to share their unique photos from the field[1].
When we opened a box supplied by museum curators, our research team audibly gasped. Inside was a huge Australian magpie nest from 2018.
It was more than a metre wide and made up of the strangest assortment of items, including wire coat hangers, headphones, saw blades and plastic 3D glasses — a mix of detritus reflecting our modern lifestyle.
This was one of almost 900 Australian nest specimens dating back over 195 years that we inspected for our recent, world-first study[2].
We estimate that today, around 30% of Australian bird nests incorporate human-made materials (primarily plastics). We also noted a steady increase in nest parasites over this period.
It’s clear the types of debris the birds use has reflected changes in society over time. They highlight the unexpected and far-reaching ways Australians impact their environment, and put birds in danger.
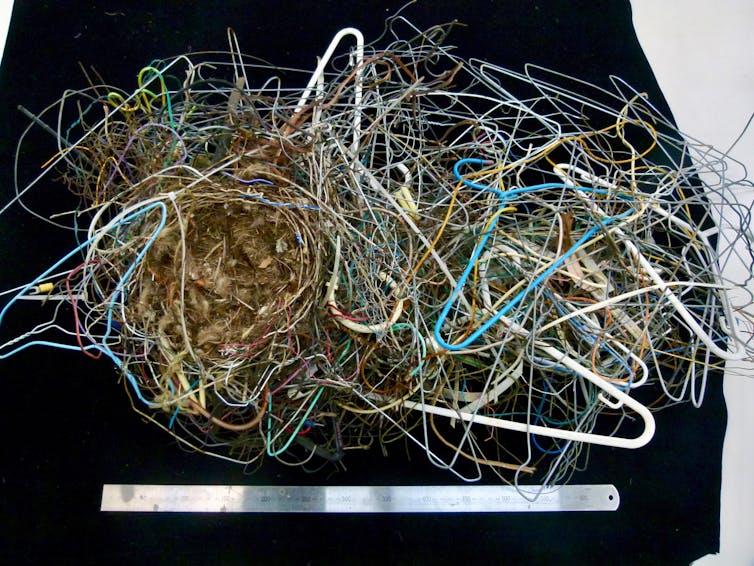 The full magpie nest from 2018 that was collected outside a construction site.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
The full magpie nest from 2018 that was collected outside a construction site.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
The first synthetic item
Birds and humans have been sharing spaces and habitats throughout history.
It’s well known birds incorporate material from their environment into their nests, making them ideal indicators of environmental changes and human activity. It’s also well known, particularly among scientists, that museum collections can provide unique insight into environmental changes through time and space.
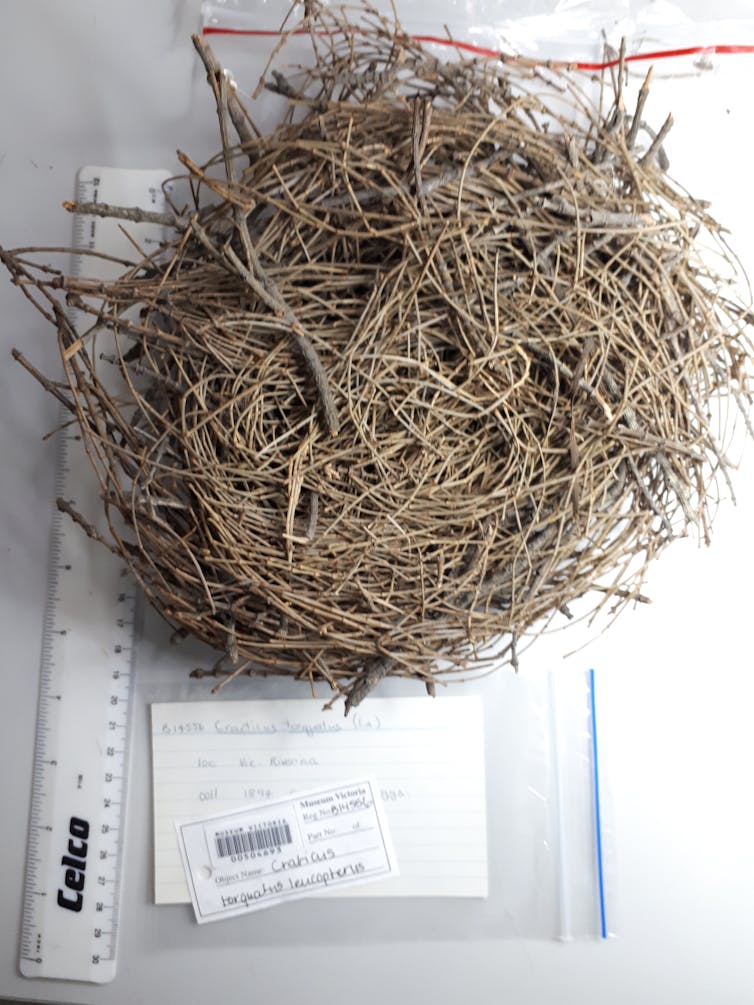 Compare the magpie nest above to this natural butcherbird nest from 1894. Butcherbirds are in the same family as magpies.
Dominique Potvin, Author provided
Compare the magpie nest above to this natural butcherbird nest from 1894. Butcherbirds are in the same family as magpies.
Dominique Potvin, Author provided
With this in mind, our international team investigated Australian museum bird nest specimens collected between 1823 and 2018. Sourced from Museums Victoria and CSIRO’s Crace Site[3] in Canberra, we inspected a total of 892 nests from 224 different bird species.
Australian birds generate an amazing array of nest types. Rufous fantails, for example, build delicately woven structures made of fine grass and spiderwebs, while welcome swallows and white-winged choughs create nests out of mud, which dry incredibly hard and can be used year after year.
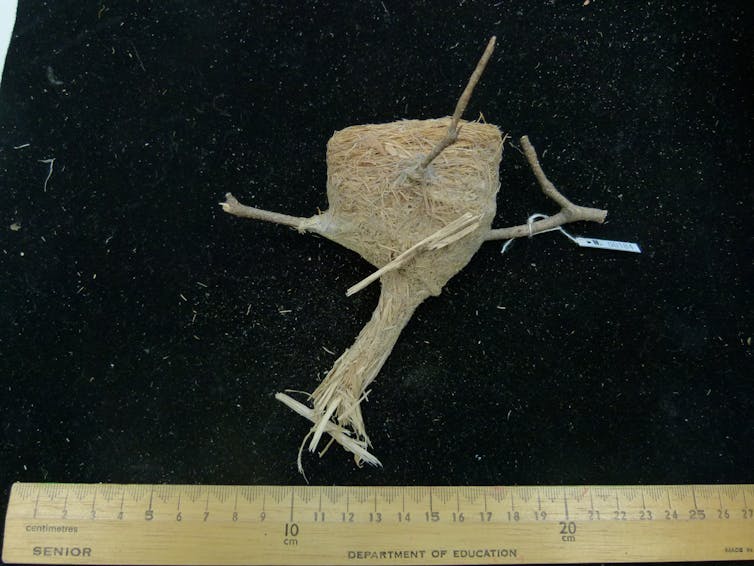 A woven egg cup nest from 1870, made of grass and spiderwebs, by the rufous fantail.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
A woven egg cup nest from 1870, made of grass and spiderwebs, by the rufous fantail.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
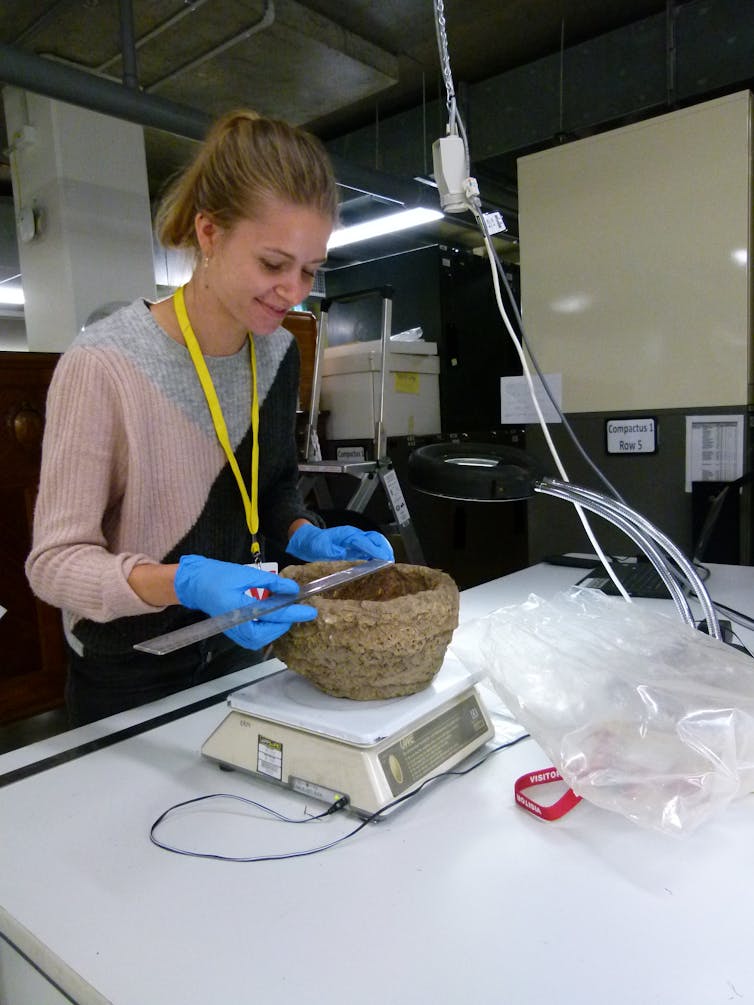 Fabiola Opitz, a member of our research team, measuring mudnest collected circ. 1933 of a whitewinged chough. These mudnests can last for years.
Dominique Potvin, Author provided
Fabiola Opitz, a member of our research team, measuring mudnest collected circ. 1933 of a whitewinged chough. These mudnests can last for years.
Dominique Potvin, Author provided
Before the 1950s, human-made debris found in the nests consisted of degradable items such as cotton thread and paper.
This changed in 1956, when we found the first synthetic item in a bird nest from Melbourne: a piece of polyester string. This appearance correlates with the increased availability[4] of plastic polymers across Australian society, seven years after the end of the second world war.
Australian magpies earn their name
We also determined, based on collection date and using historical maps, whether the nests came from natural, rural or urban landscapes. And it turns out the nest’s location, when it was built, and the species that made it largely determined whether human-made materials were present.
 The nest of a noisy miner found on the Sunshine Coast, Queensland, in 2020 with plastic string.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
The nest of a noisy miner found on the Sunshine Coast, Queensland, in 2020 with plastic string.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
Our study found nests built close to urban areas or farmland after the 1950s by birds from the families Craticidae (Australian magpies and butcherbirds), Passeridae (old world or “true” sparrows) and Pycnonotidae (bulbuls) had significantly more human-made debris.
Familiar to many an urban bird enthusiast, these species tend to adapt quickly to new environments. The incorporation of human materials in nests is likely one example of this behavioural flexibility.
The research team also had access to ten bowerbird bowers from the family Ptilonorhynchidae, spanning more than 100 years. Male bowerbirds[5] are known for creating elaborate structures, decorated with a range of colourful items to attract a mate.
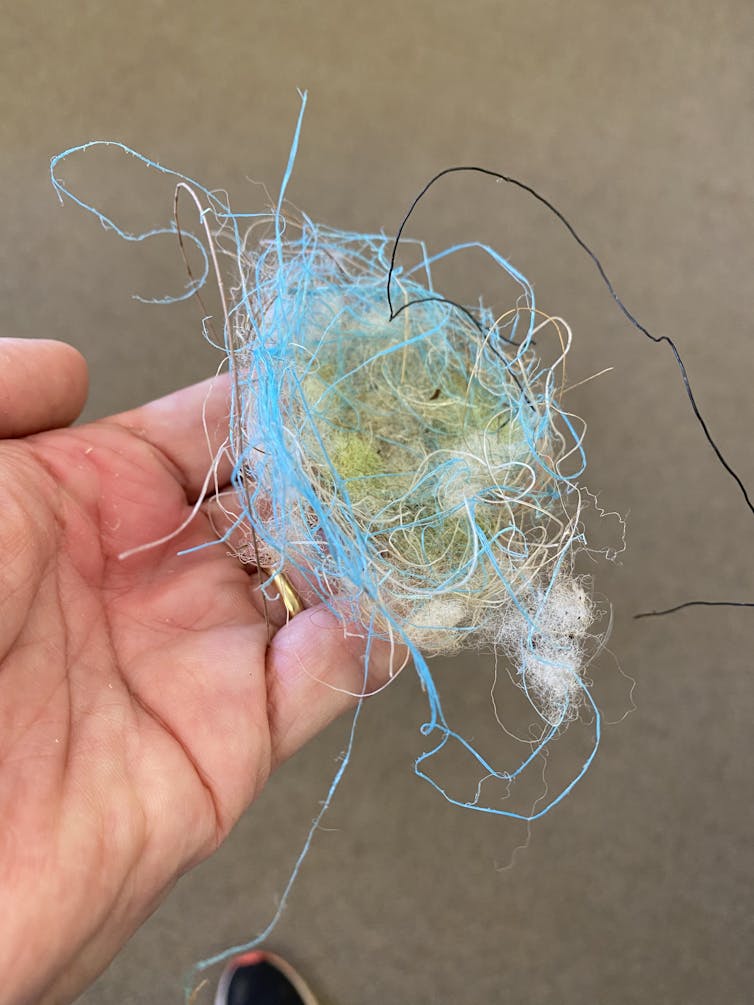 A silvereye or gerygong nest from 2019.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
A silvereye or gerygong nest from 2019.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
In the 1890s, the birds decorated their bowers with natural items such as flowers and berries. Newspaper scraps were the only human-produced items we identified.
This changed dramatically 100 years later, where the most sought-after items included brightly coloured plastics, such as straws, pen lids and bottle caps.
A satin bowerbird collecting blue junk. Video: BBC Wildlife.But there are tragic consequences
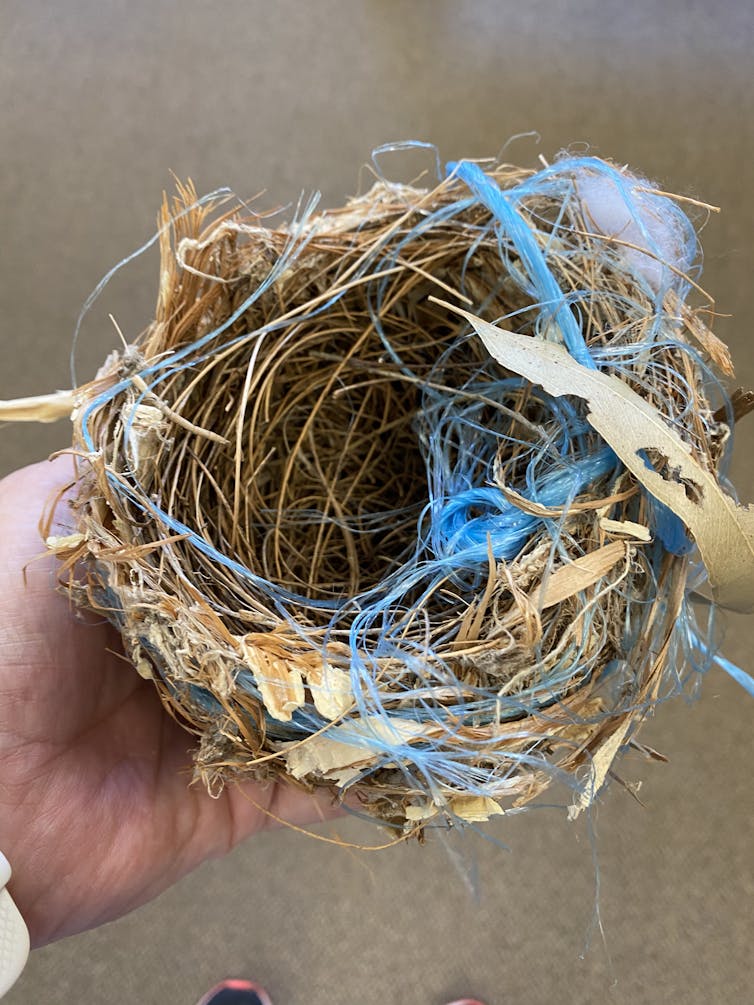
When birds weave non-biodegradable materials — such as fishing line and polymer rope — into their nests, it increases the risk of entanglement, amputation and even accumulation of plastics in the gut of nestlings.
For example, we found evidence of one pallid cuckoo juvenile dying in 1981 after it was entangled in plastic twine used by its adoptive bell miner parents.
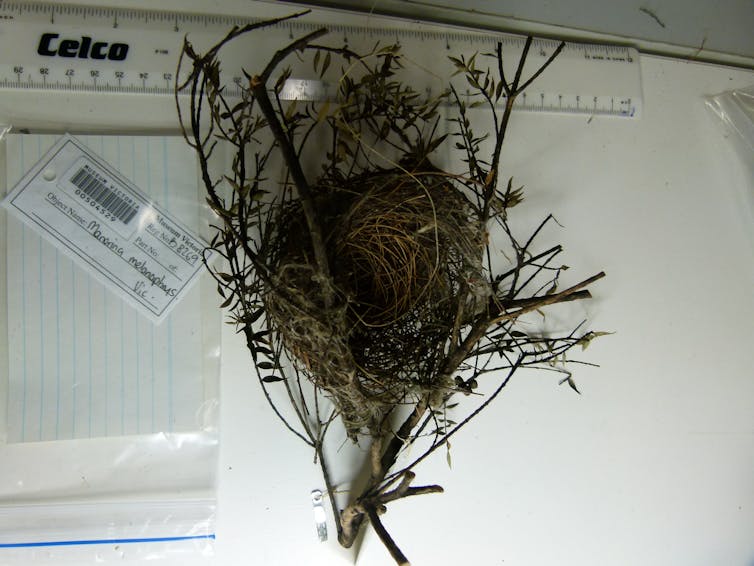 This is the bell miner nest with twine that caused the cuckoo chick to die, according to the museum notes.
Dominique Potvin, Author provided
This is the bell miner nest with twine that caused the cuckoo chick to die, according to the museum notes.
Dominique Potvin, Author provided
Plastic was not the only issue. We found the prevalence of nest parasites that attack the young chicks also increased by about 25% over the last 195 years.
Nest parasites can kill huge numbers of nestlings. Recent research into the forty-spotted pardalote in Tasmania, a threatened species, has shown nest parasites[6] kill up to 81% of its nestlings.
What has caused this increase isn’t clear. However, the team determined it wasn’t directly linked to urban or rural habitat type, or the presence of human-made materials in the nest. This goes against the findings of other studies[7], which show a decrease of parasites in nests that incorporated items such as cigarettes.
Interestingly, we did find eucalyptus leaves might deter parasites, as nests that incorporated them were less likely to show evidence of parasitism.
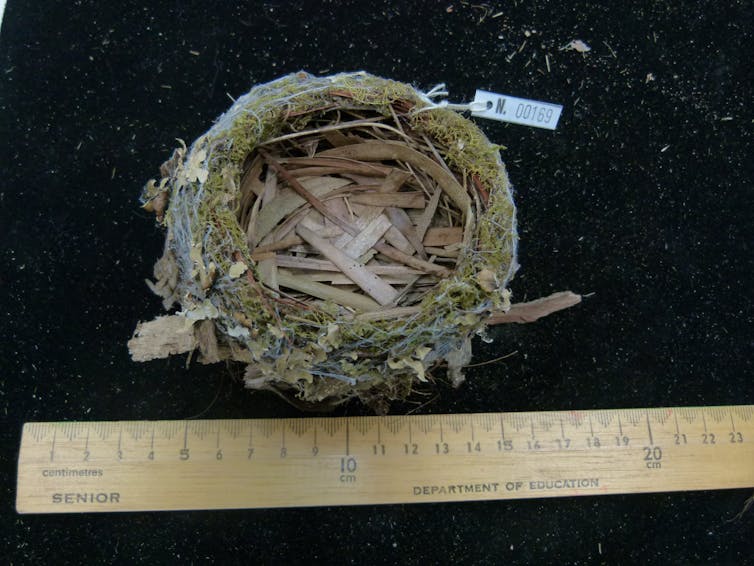 An eastern yellow robin nest from 2003, with eucalyptus leaves, lichen, spider webs and no parasites. Eastern yellow robins are specialist nest builders that don’t tend to stray from using specific natural items.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
An eastern yellow robin nest from 2003, with eucalyptus leaves, lichen, spider webs and no parasites. Eastern yellow robins are specialist nest builders that don’t tend to stray from using specific natural items.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
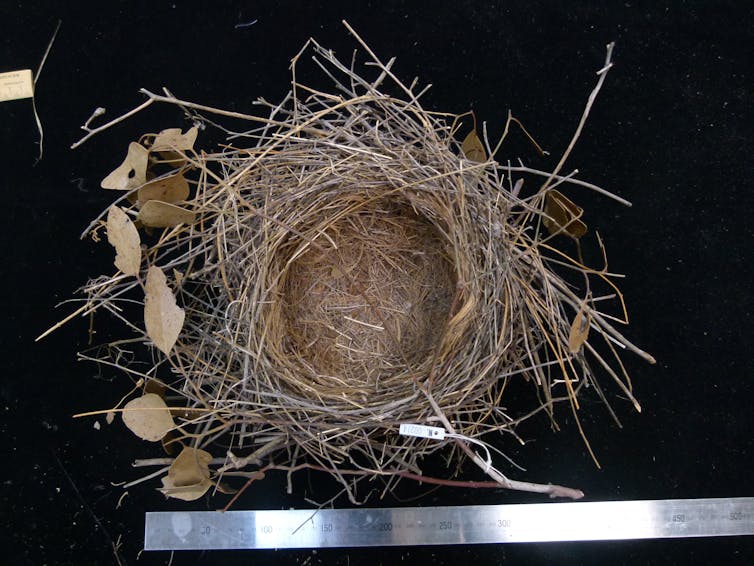 This nest from 1932 is from an Australian magpie, using eucalyptus leaves.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
This nest from 1932 is from an Australian magpie, using eucalyptus leaves.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
It may be, therefore, that sticking with certain natural materials is not only better for the safety of nest inhabitants, but also may have an added effect of pest control.
Stop littering, please
While most are aware of how plastics harm sea life, our study is one of the first to show the impact goes further to harm animals living in our own backyard. If the trend continues, the future for Australian birds looks bleak.
However, we can all do something about it.
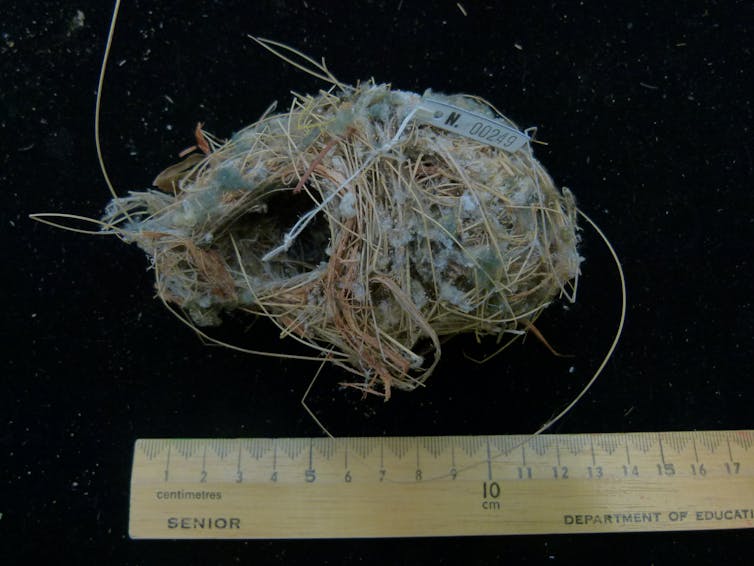 A weebill or mistletoe bird’s woven nest from 1941, with tufts of spider webs and plant fluff.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
A weebill or mistletoe bird’s woven nest from 1941, with tufts of spider webs and plant fluff.
Kathy Townsend, Author provided
It is as simple as being responsible for our rubbish and supporting proposed legislation[8] and campaigns[9] for moving away from single-use plastics.
The team had access to nests from 224 different species, which equates to only about a quarter of Australia’s total of 830 bird species.
There is still plenty more to discover.
Read more: Birds on beaches are under attack from dogs, photographers and four-wheel drives. Here's how you can help them[10]
References
- ^ photos from the field (theconversation.com)
- ^ our recent, world-first study (link.springer.com)
- ^ Crace Site (www.csiro.au)
- ^ increased availability (www.sciencehistory.org)
- ^ Male bowerbirds (theconversation.com)
- ^ parasites (zslpublications.onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- ^ studies (link.springer.com)
- ^ legislation (www.environment.gov.au)
- ^ campaigns (theconversation.com)
- ^ Birds on beaches are under attack from dogs, photographers and four-wheel drives. Here's how you can help them (theconversation.com)

















