A national insurance crisis looms. The Morrison government's $10 billion 'pool' plan won't fix it
- Written by Antonia Settle, Academic (McKenzie Postdoctoral Research Fellow), The University of Melbourne
As climate change intensifies extreme weather events, home and building insurance premiums have been rising, particularly in Northern Australia.
As premiums rise, more people are choosing drop their insurance coverage, risking financial disaster when the next natural disaster hits.
The consequences of this are so dire that the Morrison government has committed A$10 billion to a “reinsurance pool” to bring home insurance premiums down in northern Australia.
It’s an attractive policy option — simple and quick. Though it exposes the government to potentially huge costs, these won’t need to be paid until the next big disaster hits.
But it’s not the kind of policy we need. Analysis by myself and colleagues at the Melbourne Institute indicates it won’t be sufficient to stop record numbers of households — and not just in northern Australia — forgoing home insurance due to rising premiums.
The policy needed, for northern Australia now and the rest of the country in the coming years, must also mitigate the damage of fires, floods and cyclones to homes.
The coming crisis
As extreme weather events become more frequent and more ferocious, Australian households are making bigger claims more often.
This means higher costs for insurers. From the 1980s to the 2010s, insurers paid out about A$1.3 billion a year (adjusted for inflation) on claims for damage from natural disasters. Over the past 10 years, payouts doubled to an average annual cost of A$2.6 billion.
 CC BY[1]
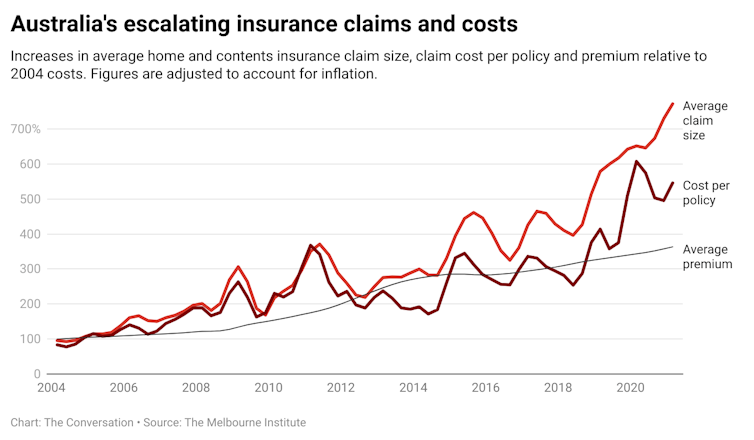
Higher payouts by insurers means higher insurance premiums for households. The average home insurance premium for all Australians now costs almost four times as much[2] as it did in 2004, according to Insurance Council of Australia data. These patterns are only going to intensify.
Our research[3] indicates many more households will drop their insurance coverage than experts have previously anticipated.
Those who decide premiums are no longer worth the money are more likely to be lower-risk customers. With a smaller pool of customers who are higher risk, insurers push premiums up further, prompting yet more households to opt out. This Fewer vicious circle will accelerate as costs climb with greater impacts from climate change.
So an insurance and social crisis looms, with financially devastating consequences for the uninsured.
No easy policy fixes
So what can policy makers do?
One option would be for the government to directly subsidise households’ insurance costs, similar to how it subsidises child-care costs.
Read more:
Underinsurance is entrenching poverty as the vulnerable are hit hardest by disasters[4]
The federal government has instead opted for an indirect subsidy, by stepping into the “reinsurance” market.
Reinsurers are like wholesalers, providing insurance to retail insurance companies. By providing reinsurance at a cheaper cost than commercial reinsurers, the government can bring household premiums down.
The downside is it exposes the government to the risk of huge costs when insurers draw on that reinsurance to pay out households in the event of a disaster. That risk will rise as the climate warms. So in the long run it simply shifts risks and costs to the public purse.
The idea of a government providing a reinsurance pool has been rejected by the industry, regulators and consumer groups because it exposes the government to potentially massive costs without having any impact on the root of the problem.
The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission said in its Northern Australia insurance inquiry[5] (finalised in December 2020):
We do not consider government reinsurance pools or government insurers are well-suited to address affordability concerns in a targeted way.
It went on to conclude:
Improving the resilience of properties and communities to natural hazards will have significant benefits now and into the future, including through lower insurance claims costs. Greater consideration of the likely benefits (and costs) of mitigation and other resilience measures is required.
CC BY[1]
Higher payouts by insurers means higher insurance premiums for households. The average home insurance premium for all Australians now costs almost four times as much[2] as it did in 2004, according to Insurance Council of Australia data. These patterns are only going to intensify.
Our research[3] indicates many more households will drop their insurance coverage than experts have previously anticipated.
Those who decide premiums are no longer worth the money are more likely to be lower-risk customers. With a smaller pool of customers who are higher risk, insurers push premiums up further, prompting yet more households to opt out. This Fewer vicious circle will accelerate as costs climb with greater impacts from climate change.
So an insurance and social crisis looms, with financially devastating consequences for the uninsured.
No easy policy fixes
So what can policy makers do?
One option would be for the government to directly subsidise households’ insurance costs, similar to how it subsidises child-care costs.
Read more:
Underinsurance is entrenching poverty as the vulnerable are hit hardest by disasters[4]
The federal government has instead opted for an indirect subsidy, by stepping into the “reinsurance” market.
Reinsurers are like wholesalers, providing insurance to retail insurance companies. By providing reinsurance at a cheaper cost than commercial reinsurers, the government can bring household premiums down.
The downside is it exposes the government to the risk of huge costs when insurers draw on that reinsurance to pay out households in the event of a disaster. That risk will rise as the climate warms. So in the long run it simply shifts risks and costs to the public purse.
The idea of a government providing a reinsurance pool has been rejected by the industry, regulators and consumer groups because it exposes the government to potentially massive costs without having any impact on the root of the problem.
The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission said in its Northern Australia insurance inquiry[5] (finalised in December 2020):
We do not consider government reinsurance pools or government insurers are well-suited to address affordability concerns in a targeted way.
It went on to conclude:
Improving the resilience of properties and communities to natural hazards will have significant benefits now and into the future, including through lower insurance claims costs. Greater consideration of the likely benefits (and costs) of mitigation and other resilience measures is required.
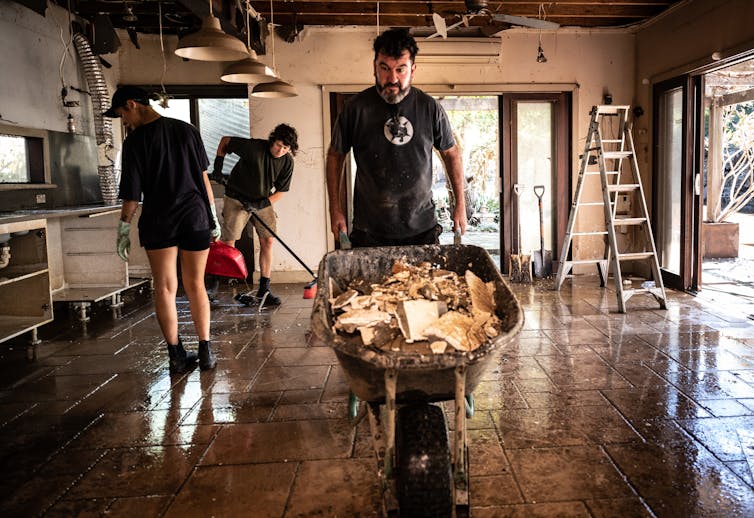 Ben Sullivan and friends clear debris from his flood-damaged home in Windsor, about an hour’s drive noth-west of central Sydney, on March 26,2021.
James Gourley/AAP
Mitigation activities
By mitigation the commission report means reducing the effects of extreme weather events. (Climate scientists tend to refer to this as adaptation, while mitigation is reducing global warming by cutting greenhouse gas emissions.)
The federal budget did commit A$600 million to a national mitigation program[6] but this nowhere near as bold as needed.
Mitigation requires work at multiple levels.
Some efforts involve limiting the severity of disasters. Strategic fuel reduction, for example, can make bush fires less extreme.
Other efforts involve limiting the effect of disasters on the built environment. A key change is reforming land use regulations to stop more housing development on flood plains.
We can also do more to limit the damage that extreme weather events have on buildings. Construction codes have been improving to make the design and materials used in new houses more resistant to fire and heavy winds, but more can be done.
Read more:
It can't all be insured: counting the hidden economic impact of floods and bushfires[7]
Investment at all levels
Our best hope to bring premiums down and help the households that need it most is comprehensive mitigation combined with targeted direct subsidies for low-income households, as the Northern Australia insurance inquiry recommended[8].
This requires a multi-pronged policy package looking far beyond the next electoral cycle. It must support investment in mitigation by all levels of government as well as households. But unless this is done the insurance crisis is only only going to intensify.
This story is part of a series The Conversation is running on the nexus between disaster, disadvantage and resilience. It is supported by a philanthropic grant from the Paul Ramsay foundation. You can read the rest of the stories here[9].
Ben Sullivan and friends clear debris from his flood-damaged home in Windsor, about an hour’s drive noth-west of central Sydney, on March 26,2021.
James Gourley/AAP
Mitigation activities
By mitigation the commission report means reducing the effects of extreme weather events. (Climate scientists tend to refer to this as adaptation, while mitigation is reducing global warming by cutting greenhouse gas emissions.)
The federal budget did commit A$600 million to a national mitigation program[6] but this nowhere near as bold as needed.
Mitigation requires work at multiple levels.
Some efforts involve limiting the severity of disasters. Strategic fuel reduction, for example, can make bush fires less extreme.
Other efforts involve limiting the effect of disasters on the built environment. A key change is reforming land use regulations to stop more housing development on flood plains.
We can also do more to limit the damage that extreme weather events have on buildings. Construction codes have been improving to make the design and materials used in new houses more resistant to fire and heavy winds, but more can be done.
Read more:
It can't all be insured: counting the hidden economic impact of floods and bushfires[7]
Investment at all levels
Our best hope to bring premiums down and help the households that need it most is comprehensive mitigation combined with targeted direct subsidies for low-income households, as the Northern Australia insurance inquiry recommended[8].
This requires a multi-pronged policy package looking far beyond the next electoral cycle. It must support investment in mitigation by all levels of government as well as households. But unless this is done the insurance crisis is only only going to intensify.
This story is part of a series The Conversation is running on the nexus between disaster, disadvantage and resilience. It is supported by a philanthropic grant from the Paul Ramsay foundation. You can read the rest of the stories here[9].
References
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
- ^ four times as much (insurancecouncil.com.au)
- ^ research (melbourneinstitute.unimelb.edu.au)
- ^ Underinsurance is entrenching poverty as the vulnerable are hit hardest by disasters (theconversation.com)
- ^ Northern Australia insurance inquiry (www.accc.gov.au)
- ^ national mitigation program (www.pm.gov.au)
- ^ It can't all be insured: counting the hidden economic impact of floods and bushfires (theconversation.com)
- ^ Northern Australia insurance inquiry recommended (www.accc.gov.au)
- ^ here (theconversation.com)
















