Latrobe and Hunter regions both have coal stations, but one has far worse mercury pollution
- Written by Larissa Schneider, DECRA fellow, Australian National University
We know coal-fired power stations can generate high levels of carbon dioxide, but did you know they can be a major source of mercury[1] emissions as well?
Our new research[2] compared the level of mercury pollution in the Hunter Valley in New South Wales and the Latrobe Valley in Victoria.
And we found power stations in the Latrobe Valley emit around 10 times more mercury than power stations in the Hunter Valley. Indeed, the mercury level in the Latrobe Valley environment is 14 times higher than what’s typically natural for the region.
So why is there such a stark difference between states? Well, it has a lot to do with regulations.
Following a NSW requirement[3] for power stations to install pollution control technology, mercury levels in the environment dropped. In Victoria, on the other hand, coal-fired power stations continue to operate without some of the air pollution controls NSW and other developed countries have mandated.
To minimise the safety risks that come with excessive mercury pollution, coal-fired power stations in all Australian jurisdictions should adopt the best available technologies to reduce mercury emissions.
A dangerous neurotoxin
Mercury is a neurotoxin[4], which means it can damage the nervous system, brain and other organs when a person or animal is exposed to unsafe levels.
Coal naturally contains mercury. So when power stations burn coal, mercury is released to the atmosphere and is then deposited back onto the Earth’s surface. When a high level of mercury ends up in bodies of water, such as lakes and rivers, it can be transferred to fish and other aquatic organisms, exposing people and larger animals to mercury that feed on these fish.
Read more: The death of coal-fired power is inevitable — yet the government still has no plan to help its workforce[5]
Mercury does not readily degrade or leave aquatic environments such as lakes and rivers. It’s a persistent toxic element — once present in water, it’s there to stay.
The amount of mercury emitted depends on the type of coal burnt (black or brown) and the type of pollution control devices the power stations use.
The Latrobe Valley stations in Victoria burn brown coal, which has more mercury than the black coal typically found in NSW. Despite this, Victorian regulations have historically not placed specific limits on mercury emissions.
In contrast, NSW power plants are required to use “bag filters”[6], a technology that’s used to trap mercury (and other) particles before they enter the atmosphere.
While bag filters alone fall short of the world’s best practices, they can still be effective. In fact, after bag filters were retrofitted[7] to Hunter Valley’s Liddell power station in the early 1990s, mercury deposition in the surrounding environment halved.
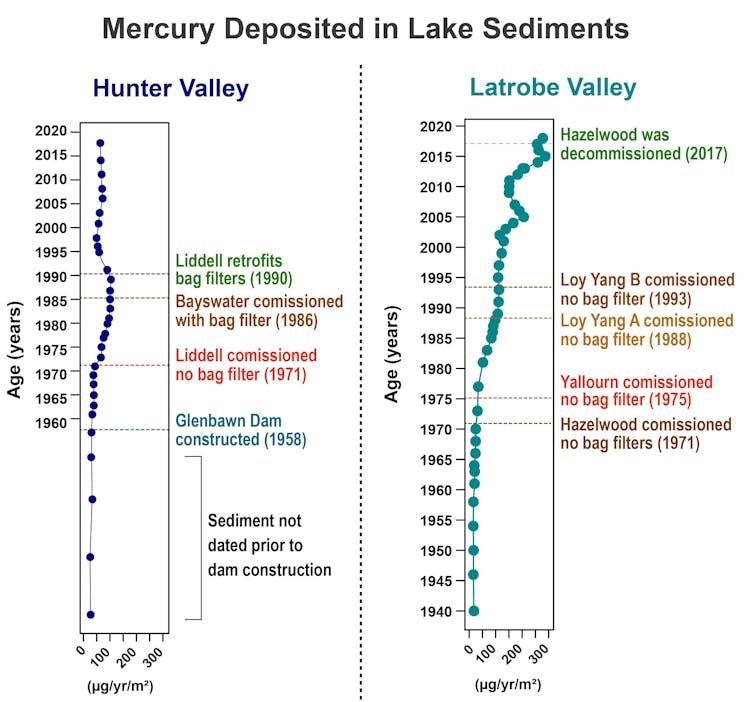 Mercury deposited in sediments of Lake Glenbawn (left) in the Hunter Valley and Traralgon Railway Reservoir (right) in the Latrobe Valley.
Mercury deposited in sediments of Lake Glenbawn (left) in the Hunter Valley and Traralgon Railway Reservoir (right) in the Latrobe Valley.
The best available technology to control mercury emissions[8] from coal-fired power plants is a combination of “wet flue-gas desulfurization” (which removes mercury in its gaseous form) and bag filters (which removes mercury bound to particles).
This is what’s been adopted across North America and parts of Europe. It not only filters out mercury, but also removes sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and other toxic air compounds.
Using lake sediments to see into the past
Lake sediments can capture mercury deposited from the atmosphere and from surrounding areas. Sediments that contain this mercury accumulate at the bottom of lakes over time — the deeper the sediment, the further back in time we can analyse.
We took sediment samples from lakes in the Latrobe and Hunter valleys, and dated them back to 1940 to get a historical record of mercury deposition.
This information can help us understand how much naturally occurring mercury there was before coal-fired power stations were built, and therefore show us the impact of burning coal.
 Lake Narracan: one of the lakes we sampled sediments from, near a coal-fired power station in Latrobe Valley.
Larissa Schneider, Author provided
Lake Narracan: one of the lakes we sampled sediments from, near a coal-fired power station in Latrobe Valley.
Larissa Schneider, Author provided
From these records, we found the adoption of bag filters in the Hunter Valley corresponded with mercury depositions declining in NSW from the 1990s.
In contrast, in Victoria, where there’s been no such requirement, mercury emissions and depositions have continued to increase since Hazelwood power station was completed in 1971[9].
What do we do about it?
In March, the Victorian government announced changes[10] to the regulatory licence conditions for brown coal-fired power stations. Although mercury emissions allowances have been included for the first time, they’re arguably still too high, and there’s no requirement to install specific pollution control technologies.
There’s a risk this approach won’t reduce mercury emissions from existing levels. Victoria should instead consider more ambitious regulations that encourage the adoption of best practice technology to help protect local communities and the environment.
 Loy Yang power station, Victoria’s largest, burns brown coal which contains more mercury.
Shutterstock
Loy Yang power station, Victoria’s largest, burns brown coal which contains more mercury.
Shutterstock
Another vital step toward protecting human health and the environment from mercury is for the federal government to ratify the Minamata Convention on Mercury[11], an international treaty to protect human health and the environment from mercury.
Despite signing the convention in 2013[12], the Australian government is yet to ratify it, which is required to make it legally binding in Australia.
Ratifying the convention will oblige state and federal governments to develop and implement a strategy to reduce mercury emissions, including from coal-fired power stations across Australia. And this strategy should include rolling out effective technologies — our research shows it can make a big difference.
The authors acknowledge Lauri Myllyvirta from the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air for her contributions to this article.
Read more: Hazelwood power station: from modernist icon to greenhouse pariah[13]
References
- ^ source of mercury (www.epa.gov)
- ^ new research (www.sciencedirect.com)
- ^ a NSW requirement (www.epa.nsw.gov.au)
- ^ Mercury is a neurotoxin (www.epa.gov)
- ^ The death of coal-fired power is inevitable — yet the government still has no plan to help its workforce (theconversation.com)
- ^ NSW power plants are required to use “bag filters” (www.epa.nsw.gov.au)
- ^ after bag filters were retrofitted (www.sciencedirect.com)
- ^ best available technology to control mercury emissions (www.mercuryconvention.org)
- ^ completed in 1971 (theconversation.com)
- ^ announced changes (www.epa.vic.gov.au)
- ^ Minamata Convention on Mercury (www.mercuryconvention.org)
- ^ signing the convention in 2013 (www.environment.gov.au)
- ^ Hazelwood power station: from modernist icon to greenhouse pariah (theconversation.com)

















