'fool's gold' contains a newly discovered type of real gold
- Written by Denis Fougerouse, Research Fellow, School of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Curtin University
The mineral pyrite was historically nicknamed fool’s gold[1] because of its deceptive resemblance to the precious metal. The term was often used during the California gold rush in the 1840s because inexperienced prospectors would claim discoveries of gold, but in reality it would be pyrite, composed of worthless iron disulfide (FeS₂).
Ironically, pyrite crystals can contain small amounts of real gold, although it is notoriously hard to extract. Gold hiding within pyrite is sometimes referred to as “invisible gold”, because it is not observable with standard microscopes, but instead requires sophisticated scientific instruments.
It wasn’t until the 1980s when researchers discovered[2] that gold in pyrite can come in different forms – either as particles of gold, or as an alloy, in which the pyrite and gold are finely mixed.
In our new research, published in Geology[3], my colleagues and I discovered a third, previously unrecognised way that gold can lurk inside pyrite. When the pyrite crystal is forming under extreme temperature or pressure, it can develop tiny imperfections in its crystal structure that can be “decorated” with gold atoms.
What are these ‘crystal defects’?
The atoms within a crystal are arranged in a characteristic pattern called an atomic lattice. But when a mineral crystal such as pyrite is growing inside a rock, this lattice pattern can develop imperfections. Like many minerals, pyrite is tough and hard at Earth’s surface, but can become more twisty and stretchy when forming deep in the Earth, which is also where gold deposits form.
When crystals stretch or twist, the bonds between neighbouring atoms are broken and remade, forming billions of tiny imperfections called “dislocations”, each roughly 100,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair, or 100 times smaller than a virus particle.
The chemistry of these atomic-scale imperfections is notoriously difficult to study because they are so small, so any impurities are present in absolutely minuscule quantities. Detecting them requires a specialised instrument called an atom probe[4].
An atom probe can analyse materials at extremely high resolution, but its main advantage over other methods is that it allows us to build a 3D map showing the precise locations of impurities within a crystal — something that was never possible before.
Our research reveals that dislocations within pyrite crystals can be “decorated” with gold atoms. This is particularly common where the crystals have been twisted during their history; here, gold can be present at concentrations several times higher than in the rest of the crystal.
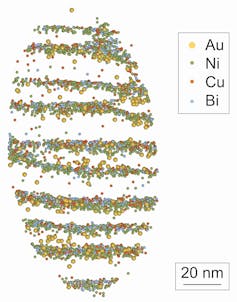 Gold (Au) atoms hiding within a pyrite crystal, alongside other imperfections including nickel, copper and bismuth. Scale bar indicates 20 nanometres.
Author provided
Gold (Au) atoms hiding within a pyrite crystal, alongside other imperfections including nickel, copper and bismuth. Scale bar indicates 20 nanometres.
Author provided
A potential goldmine
Why should anyone care about something so tiny? Well, it gives interesting insights into how mineral deposits form, and is also a potential boon for the gold mining industry.
Previously, it was suspected that gold in anomalously rich pyrite crystals was in fact made of gold particles formed during a multi-step process, suggesting the pyrite and gold crystallised at different times and then became clumped together. But our discovery that gold can decorate these crystal imperfections suggests that even pyrite crystals with relatively high gold content can form in a single process.
Read more: Eureka! X-ray vision can find hidden gold[5]
Our discovery may also help gold miners more efficiently extract gold from pyrite, potentially reducing greenhouse emissions. To extract the gold, the mineral is usually oxidised in large reactors, which uses considerable amounts of energy.
Dislocation sites within crystals could potentially offer an enhanced partial leaching or a target for bacteria to attack and break down the crystal, releasing the gold in a process known as “bio-leaching”, thus potentially reducing energy consumption necessary for extraction. This idea is still untested, but definitely merits investigation.
If it helps pave the way for more sustainable gold-mining methods, then perhaps fool’s gold isn’t so foolish after all.
Perhaps pyrite still lives up to its historic reputation of “fool’s gold” until better, more environmentally sustainable ore processing techniques are developed.
References
- ^ fool’s gold (www.britannica.com)
- ^ researchers discovered (www.researchgate.net)
- ^ published in Geology (pubs.geoscienceworld.org)
- ^ atom probe (youtube.com)
- ^ Eureka! X-ray vision can find hidden gold (theconversation.com)
- ^ How gold rushes helped make the modern world (theconversation.com)

















