Restoring land around abandoned oil and gas wells would free up millions of acres of forests, farmlands and grasslands
- Written by Matthew D. Moran, Professor of Biology, Hendrix College
 CC BY-ND[1]
President Joe Biden’s infrastructure plan[2] proposes to spend US$16 billion plugging old oil and gas wells and cleaning up abandoned mines. But there’s no authoritative measure[3] of how many of these sites exist across the nation.
In a recent study, my colleagues and I sought to account for every oil and gas well site in the lower 48 states that was eligible for restoration[4] – meaning that the well no longer was producing oil or gas, and there were no other active wells using that site. We found more than 430,000 old well sites, with associated infrastructure such as access roads, storage areas and fluid tanks. They covered more than 2 million acres – an area larger than Delaware and Rhode Island combined.
These sites are scattered across the country, concentrated mainly in forests, grassland and cropland. They could be put to good use. We estimated the value of crops that could be produced if these lands are restored at over $14 billion over the next 50 years.
We calculated that restoring these lands could remove millions of tons of carbon from the atmosphere as vegetation regrows on them, providing an estimated $7 billion in benefits from reduced greenhouse gas emissions. It also would provide habitat for wildlife and could produce timber for harvesting. And because healthy ecosystems filter air[5] and water[6], returning these lands to a natural state could reduce air pollution and improve drinking water quality.
Retired oil and gas executive Curtis Shuck explains why his nonprofit is working to plug thousands of orphaned wells across the U.S.In recent years, energy production has become the largest consumer of new land[7] in the U.S., outpacing urban and residential development. The oil and gas industry has a particularly large footprint, occupying millions of acres, with big impacts on the environment[8]. Energy development reduces biodiversity, increases carbon emissions, disrupts natural ecological processes and decreases ecosystem services[9] – the numerous benefits that natural landscapes perform for humanity.
While active wells are producing oil and gas, they generate obvious economic benefits, along with direct and indirect costs[10]. Eventually, however, all wells go dry. After that, their economic value is gone and only the costs remain.
Most states and the federal government require energy developers to plug old wells and reclaim the land[11], and to post bonds[12] to help ensure that they do so. Often, however, companies either go bankrupt and abandon sites[13] or assert that idled wells are still producing[14] and maintain their leases indefinitely. Furthermore, the bond amounts are almost never enough[15] to cover the complete costs of plugging wells and restoring the land.
CC BY-ND[1]
President Joe Biden’s infrastructure plan[2] proposes to spend US$16 billion plugging old oil and gas wells and cleaning up abandoned mines. But there’s no authoritative measure[3] of how many of these sites exist across the nation.
In a recent study, my colleagues and I sought to account for every oil and gas well site in the lower 48 states that was eligible for restoration[4] – meaning that the well no longer was producing oil or gas, and there were no other active wells using that site. We found more than 430,000 old well sites, with associated infrastructure such as access roads, storage areas and fluid tanks. They covered more than 2 million acres – an area larger than Delaware and Rhode Island combined.
These sites are scattered across the country, concentrated mainly in forests, grassland and cropland. They could be put to good use. We estimated the value of crops that could be produced if these lands are restored at over $14 billion over the next 50 years.
We calculated that restoring these lands could remove millions of tons of carbon from the atmosphere as vegetation regrows on them, providing an estimated $7 billion in benefits from reduced greenhouse gas emissions. It also would provide habitat for wildlife and could produce timber for harvesting. And because healthy ecosystems filter air[5] and water[6], returning these lands to a natural state could reduce air pollution and improve drinking water quality.
Retired oil and gas executive Curtis Shuck explains why his nonprofit is working to plug thousands of orphaned wells across the U.S.In recent years, energy production has become the largest consumer of new land[7] in the U.S., outpacing urban and residential development. The oil and gas industry has a particularly large footprint, occupying millions of acres, with big impacts on the environment[8]. Energy development reduces biodiversity, increases carbon emissions, disrupts natural ecological processes and decreases ecosystem services[9] – the numerous benefits that natural landscapes perform for humanity.
While active wells are producing oil and gas, they generate obvious economic benefits, along with direct and indirect costs[10]. Eventually, however, all wells go dry. After that, their economic value is gone and only the costs remain.
Most states and the federal government require energy developers to plug old wells and reclaim the land[11], and to post bonds[12] to help ensure that they do so. Often, however, companies either go bankrupt and abandon sites[13] or assert that idled wells are still producing[14] and maintain their leases indefinitely. Furthermore, the bond amounts are almost never enough[15] to cover the complete costs of plugging wells and restoring the land.
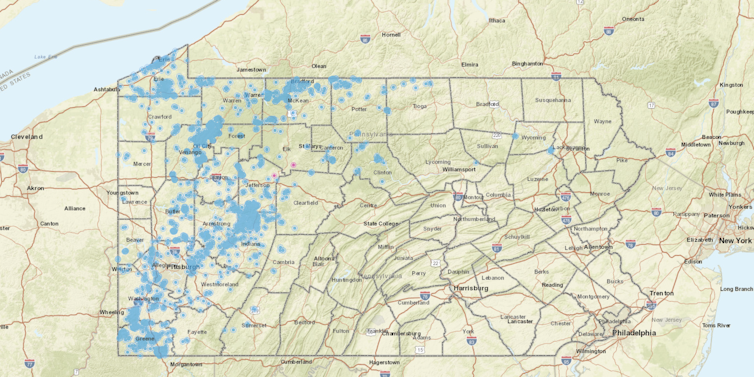 Pennsylvania officials have identified thousands of abandoned oil and gas wells in the state (marked in blue) with no identifiable responsible party to complete plugging them.
Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection[16]
Abandoned wells can sit idle for many years. Many leak methane[17], a potent greenhouse gas, or other contaminants[18], damaging surrounding landscapes[19] and threatening water supplies.
Restoring these sites starts with plugging the well to remove contamination hazards. Next, companies remove all infrastructure, such as well pads and roads. They replace topsoil, plant native plants – which may need extra care to become established over several years – and restore the site’s natural drainage patterns.
Thousands more active oil and gas wells[20] will stop producing in the coming years. Energy companies installed over 150,000 wells on 500,000 acres of land[21] during the initial oil and gas “fracking” boom from 2004 to 2015. These wells and older ones cover millions more acres of land that may someday become rural brownfields scattered across the American landscape.
How far would $16 billion go toward remediating inactive oil and gas sites? We estimated that the land around all currently nonproducing wells in the lower 48 states could be restored for about $7 billion, with additional costs for plugging wells.
We had only a few publicly available examples[22] of actual[23] restoration costs[24] to develop our estimate, and costs likely vary widely[25] across different types of ecosystems. But we carried out a detailed assessment and found that in every scenario we studied, the economic benefits from restored lands would be much greater than the costs.
In my view, this investment would produce returns that include crop production, better human health, cleaner air and water, and a more beautiful and ecologically sound landscape.
[Get the best of The Conversation, every weekend. Sign up for our weekly newsletter[26].]
Pennsylvania officials have identified thousands of abandoned oil and gas wells in the state (marked in blue) with no identifiable responsible party to complete plugging them.
Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection[16]
Abandoned wells can sit idle for many years. Many leak methane[17], a potent greenhouse gas, or other contaminants[18], damaging surrounding landscapes[19] and threatening water supplies.
Restoring these sites starts with plugging the well to remove contamination hazards. Next, companies remove all infrastructure, such as well pads and roads. They replace topsoil, plant native plants – which may need extra care to become established over several years – and restore the site’s natural drainage patterns.
Thousands more active oil and gas wells[20] will stop producing in the coming years. Energy companies installed over 150,000 wells on 500,000 acres of land[21] during the initial oil and gas “fracking” boom from 2004 to 2015. These wells and older ones cover millions more acres of land that may someday become rural brownfields scattered across the American landscape.
How far would $16 billion go toward remediating inactive oil and gas sites? We estimated that the land around all currently nonproducing wells in the lower 48 states could be restored for about $7 billion, with additional costs for plugging wells.
We had only a few publicly available examples[22] of actual[23] restoration costs[24] to develop our estimate, and costs likely vary widely[25] across different types of ecosystems. But we carried out a detailed assessment and found that in every scenario we studied, the economic benefits from restored lands would be much greater than the costs.
In my view, this investment would produce returns that include crop production, better human health, cleaner air and water, and a more beautiful and ecologically sound landscape.
[Get the best of The Conversation, every weekend. Sign up for our weekly newsletter[26].]
References
- ^ CC BY-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ infrastructure plan (www.whitehouse.gov)
- ^ no authoritative measure (www.pewtrusts.org)
- ^ eligible for restoration (doi.org)
- ^ air (doi.org)
- ^ water (doi.org)
- ^ largest consumer of new land (doi.org)
- ^ big impacts on the environment (doi.org)
- ^ ecosystem services (doi.org)
- ^ costs (www.nap.edu)
- ^ plug old wells and reclaim the land (www.fws.gov)
- ^ post bonds (www.gao.gov)
- ^ go bankrupt and abandon sites (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ assert that idled wells are still producing (www.hh-law.com)
- ^ are almost never enough (doi.org)
- ^ Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (gis.dep.pa.gov)
- ^ leak methane (doi.org)
- ^ other contaminants (www.reuters.com)
- ^ landscapes (doi.org)
- ^ Thousands more active oil and gas wells (www.eia.gov)
- ^ 150,000 wells on 500,000 acres of land (doi.org)
- ^ examples (wyofile.com)
- ^ actual (www.gao.gov)
- ^ restoration costs (oerb.com)
- ^ likely vary widely (www.gao.gov)
- ^ Sign up for our weekly newsletter (theconversation.com)

















