Physics Nobel awarded to neural network pioneers who laid foundations for AI
- Written by Aaron J. Snoswell, Research Fellow in AI Accountability, Queensland University of Technology
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics[1] has been awarded to scientists John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton “for foundational discoveries and inventions that enable machine learning with artificial neural networks”.
Inspired by ideas from physics and biology, Hopfield and Hinton developed computer systems that can memorise and learn from patterns in data. Despite never directly collaborating, they built on each other’s work to develop the foundations of the current boom in machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI).
What are neural networks? (And what do they have to do with physics?)
Artificial neural networks are behind much of the AI technology we use today.
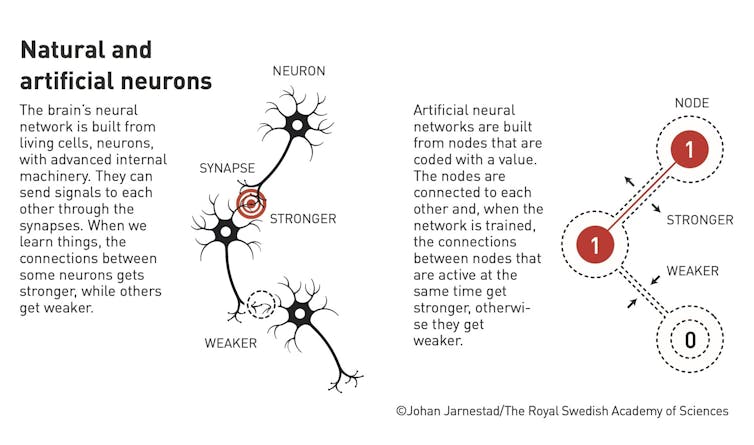
In the same way your brain has neuronal cells linked by synapses, artificial neural networks have digital neurons connected in various configurations. Each individual neuron doesn’t do much. Instead, the magic lies in the pattern and strength of the connections between them.
Neurons in an artificial neural network are “activated” by input signals. These activations cascade from one neuron to the next in ways that can transform and process the input information. As a result, the network can carry out computational tasks such as classification, prediction and making decisions.
















