endangered animals released into the wild may lack the match-fitness to evade predators
- Written by Natasha Harrison, PhD Candidate, The University of Western Australia
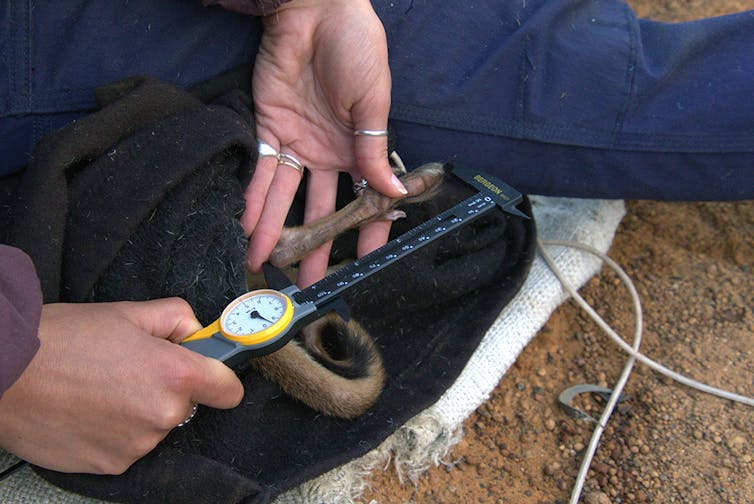
Breeding threatened mammals in fenced, predator-free areas is a common conservation strategy in Australia. The method is designed to protect vulnerable species and breed animals for release into the wild.
But our research[1] – involving a cute, digging mammal known as a woylie – suggests the strategy may put animals at a distinct disadvantage once they’re fending for themselves.
We found animals bred in fenced conservation areas, known as “havens”, lost traits they need to detect and escape predators. It’s likely this made them less able to survive in the wild.
This unintended downside could jeopardise the survival of endangered species such as woylies. It shows we must increase investment in managing wild populations of threatened species, and help animals in havens get accustomed to predators.
Saving our disappearing mammals
Woylies[2] (also known as brush-tailed bettongs) are small marsupials that jump around like kangaroos. They improve soil health through their prolific digging; a single woylie can turn over about five tonnes of soil[3] each year.
These animals were once abundant across much of Australia’s southern and semi-arid areas. They are now endangered, due to habitat loss and being killed by introduced predators such as cats[4] and foxes[5].
Since Europeans arrived in Australia, one in ten[6] native mammals have become extinct. Many more once-abundant species have fallen to critically low numbers.
Given the vulnerability of many mammals to introduced predators, conservation havens have been established around Australia – both inside fences on the mainland, and on offshore islands.
Nationally, more than 120 havens now exist[7]. They protect about 200 threatened mammal populations from introduced predators.
In many ways, havens have been a huge success[8]. Populations of woylies and many other mammals have greatly increased inside havens and at least 13 extinctions have been avoided.[9]
However, havens cover only around 0.1%[10] of the country. For conservation to be effective, animals must be returned to areas where the species once lived, where they can perform their important roles in nature.
But do animals bred in havens have what it takes to survive outside the fence? Our research examined this question.
Read more: The future is fenced for Australian animals[11]
Life outside the fence
We examined ten-years of monitoring data collected from woylie populations inside and outside of a haven in Western Australia, and compared the two groups.
Inside the haven, where there were no predators, competition for food was the biggest pressure. Bold, carefree woylies ate before more cautious individuals which likely discouraged cautious behaviour.
What’s more, in just four generations, woylies born inside havens became successively smaller than previous generations and their feet became shorter.
Why? We suspect it’s because food supply was limited and the animals didn’t need to escape from predators – which meant there was less benefit in being big. At this stage, we don’t know if the changes were the result of natural selection (in other words, survival of the fittest) or what’s known as “phenotypic plasticity[12]” – changes in an organism in response to their environment.
The data showed protected woylies also became less reactive and fearful. It meant humans (and potential predators) could get relatively close to the animals before they fled.
Woylies in havens also had a dampened response to other natural anti-predator responses, such as ejecting young[13] from their pouch to distract predators while they escape. (This may sound brutal, but it’s a survival strategy also used by other marsupials such as quokkas and potoroos.)
The loss of anti-predator traits has also been observed in populations of other species in havens, including the boodie[14], brushtail possum[15] and eastern bettong[16].
Read more: The mystery of the Top End's vanishing wildlife, and the unexpected culprits[17]
What does this all mean?
The study revealed important insights into how quickly animal populations can lose anti-predator defences. This presents a problem for programs that reintroduce species to their former areas.
Havens have stopped rapid population declines and extinctions, and enabled some species – including woylies – to multiply quickly. But our study shows they’re not a silver bullet over the long term.
Other strategies outside havens are needed. Importantly, we must ensure native animals have good quality habitat. This should include sufficient food, and safe places to sleep and hide from predators.
Our study also highlights the value in regular monitoring of threatened species, to allow a robust comparison of anti-predator traits through time.
The findings suggest animals in havens may need to be exposed to low levels of predators to reinstate survival traits. Our future research will investigate this strategy. We will assess how quickly woylies can regain their anti-predator traits and what predator levels woylie populations can withstand.
We hope our findings will help conservation managers develop better ways to protect Australia’s threatened mammal species over the long term – so we can not only prevent extinctions, but restore species to their former roles in nature.
References
- ^ research (doi.org)
- ^ Woylies (www.dcceew.gov.au)
- ^ five tonnes of soil (doi.org)
- ^ cats (doi.org)
- ^ foxes (theconversation.com)
- ^ one in ten (www.bbc.com)
- ^ exist (www.publish.csiro.au)
- ^ huge success (theconversation.com)
- ^ avoided. (www.nespthreatenedspecies.edu.au)
- ^ only around 0.1% (www.nespthreatenedspecies.edu.au)
- ^ The future is fenced for Australian animals (theconversation.com)
- ^ phenotypic plasticity (www.sciencedirect.com)
- ^ ejecting young (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ boodie (doi.org)
- ^ brushtail possum (doi.org)
- ^ eastern bettong (doi.org)
- ^ The mystery of the Top End's vanishing wildlife, and the unexpected culprits (theconversation.com)

















