A billion-year history of Earth's interior shows it's more mobile than we thought
- Written by Nicolas Flament, Senior Lecturer, University of Wollongong
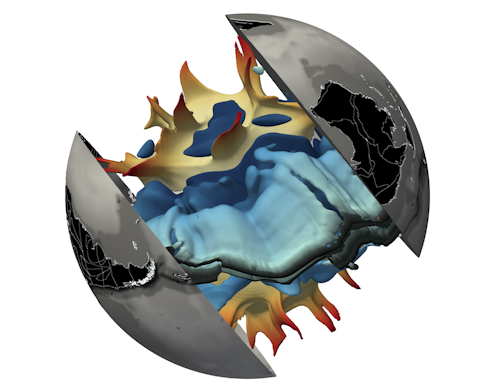
Deep in the Earth beneath us lie two blobs the size of continents. One is under Africa, the other under the Pacific Ocean.
The blobs have their roots 2,900km below the surface, almost halfway to the centre of the Earth. They are thought to be the birthplace of rising columns of hot rock called “deep mantle plumes” that reach Earth’s surface.
When these plumes first reach the surface, giant volcanic eruptions occur – the kind that contributed to the extinction of the dinosaurs 65.5 million years ago. The blobs may also control the eruption of a kind of rock called kimberlite, which brings diamonds from depths 120-150km (and in some cases up to around 800km) to Earth’s surface.
Scientists have known the blobs existed for a long time, but how they have behaved over Earth’s history has been an open question. In new research, we modelled a billion years of geological history and discovered the blobs gather together and break apart[1] much like continents and supercontinents.
A model for Earth blob evolution
The blobs are in the mantle, the thick layer of hot rock between Earth’s crust and its core. The mantle is solid but slowly flows over long timescales. We know the blobs are there because they slow down waves caused by earthquakes, which suggests the blobs are hotter than their surroundings.
Scientists generally agree the blobs are linked to the movement of tectonic plates at Earth’s surface. However, how the blobs have changed over the course of Earth’s history has puzzled them.
One school of thought has been that the present blobs have acted as anchors, locked in place for hundreds of millions of years while other rock moves around them. However, we know tectonic plates and mantle plumes move over time, and research suggests the shape of the blobs is changing[2].
Our new research[3] shows Earth’s blobs have changed shape and location far more than previously thought. In fact, over history they have assembled and broken up in the same way that continents and supercontinents have at Earth’s surface.
We used Australia’s National Computational Infrastructure[4] to run advanced computer simulations of how Earth’s mantle has flowed over a billion years.
These models are based on reconstructing the movements of tectonic plates[5]. When plates push into one another, the ocean floor is pushed down between them in a process known as subduction. The cold rock from the ocean floor sinks deeper and deeper into the mantle, and once it reaches a depth of about 2,000km it pushes the hot blobs aside.
The past 200 million years of Earth’s interior. Hot structures are in yellow to red (darker is shallower) and cold structures in blue (darker is deeper).We found that just like continents, the blobs can assemble – forming “superblobs” as in the current configuration – and break up over time.
A key aspect of our models is that although the blobs change position and shape over time, they still fit the pattern of volcanic and kimberlite eruptions recorded at Earth’s surface. This pattern was previously a key argument for the blobs as unmoving “anchors”.
Strikingly, our models reveal the African blob assembled as recently as 60 million years ago – in stark contrast to previous suggestions the blob could have existed in roughly its present form for nearly ten times as long[6].
Remaining questions about the blobs
How did the blobs originate? What exactly are they made of? We still don’t know.
The blobs may be denser than the surrounding mantle, and as such they could consist of material separated out from the rest of the mantle early in Earth’s history[7]. This could explain why the mineral composition of the Earth is different from that expected from models based on the composition of meteorites.
Alternatively, the density of the blobs could be explained by the accumulation of dense oceanic material from slabs of rock pushed down by tectonic plate movement.
Regardless of this debate, our work shows sinking slabs are more likely to transport fragments of continents to the African blob than to the Pacific blob. Interestingly, this result is consistent with recent work suggesting the source of mantle plumes rising from the African blob contains continental material, whereas plumes rising from the Pacific blob do not.
Tracking the blobs to find minerals and diamonds
While our work addresses fundamental questions about the evolution of our planet, it also has practical applications.
Our models provide a framework to more accurately target the location of minerals associated with mantle upwelling. This includes diamonds brought up to the surface by kimberlites that seem to be associated with the blobs.
Magmatic sulfide deposits, which are the world’s primary reserve of nickel, are also associated with mantle plumes. By helping target minerals such as nickel (an essential ingredient of lithium-ion batteries and other renewable energy technologies) our models can contribute to the transition to a low-emission economy.
References
- ^ the blobs gather together and break apart (www.nature.com)
- ^ the shape of the blobs is changing (agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- ^ Our new research (www.nature.com)
- ^ National Computational Infrastructure (nci.org.au)
- ^ reconstructing the movements of tectonic plates (theconversation.com)
- ^ for nearly ten times as long (www.pnas.org)
- ^ early in Earth’s history (www.nature.com)

















