Why the volcanic eruption in Tonga was so violent, and what to expect next
- Written by Shane Cronin, Professor of Earth Sciences, University of Auckland
The Kingdom of Tonga doesn’t often attract global attention, but a violent eruption of an underwater volcano[1] on January 15 has spread shock waves, quite literally, around half the world.
The volcano is usually not much to look at. It consists of two small uninhabited islands, Hunga-Ha’apai and Hunga-Tonga, poking about 100m above sea level 65km north of Tonga’s capital Nuku‘alofa. But hiding below the waves is a massive volcano, around 1800m high and 20km wide.
A massive underwater volcano lies next to the Hunga-Ha’apai and Hunga-Tonga islands. Author providedThe Hunga-Tonga-Hunga-Ha'apai volcano has erupted regularly over the past few decades. During events in 2009 and 2014/15 hot jets of magma and steam exploded through the waves. But these eruptions were small, dwarfed in scale by the January 2022 events.
Our research[2] into these earlier eruptions suggests this is one of the massive explosions the volcano is capable of producing roughly every thousand years.
Why are the volcano’s eruptions so highly explosive, given that sea water should cool the magma down?
If magma rises into sea water slowly, even at temperatures of about 1200℃, a thin film of steam forms between the magma and water. This provides a layer of insulation to allow the outer surface of the magma to cool.
But this process doesn’t work when magma is blasted out of the ground full of volcanic gas. When magma enters the water rapidly, any steam layers are quickly disrupted, bringing hot magma in direct contact with cold water.
Volcano researchers call this “fuel-coolant interaction” and it is akin to weapons-grade chemical explosions. Extremely violent blasts tear the magma apart. A chain reaction begins, with new magma fragments exposing fresh hot interior surfaces to water, and the explosions repeat, ultimately jetting out volcanic particles and causing blasts with supersonic speeds.
Read more: The 'pulse' of a volcano can be used to help predict its next eruption[3]
Two scales of Hunga eruptions
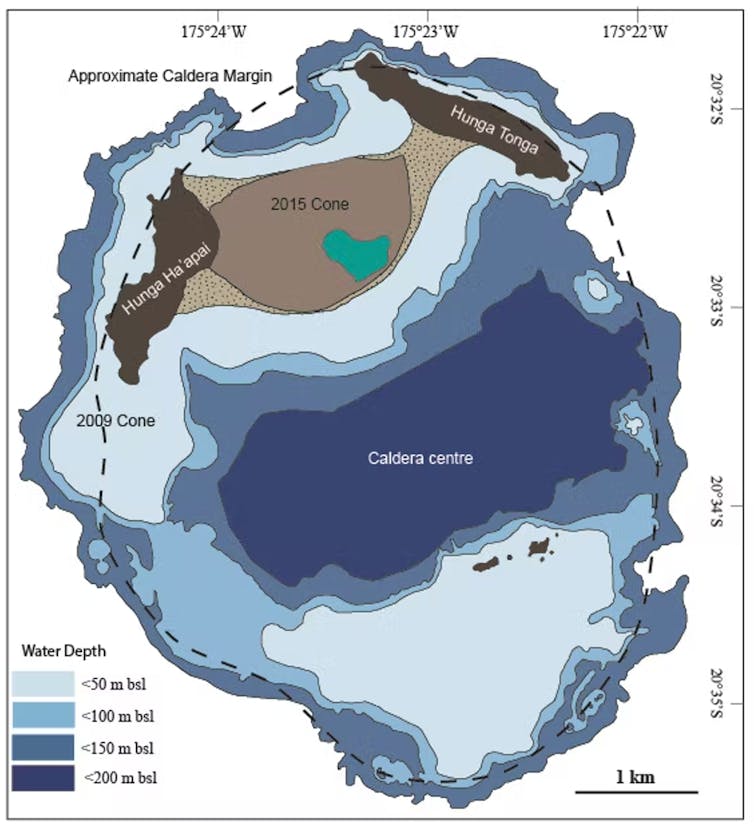
The 2014/15 eruption created a volcanic cone, joining the two old Hunga islands to create a combined island about 5km long. We visited in 2016, and discovered these historical eruptions were merely curtain raisers to the main event[4].
Mapping the sea floor, we discovered a hidden “caldera” 150m below the waves.
The caldera is a crater-like depression around 5km across. Small eruptions (such as in 2009 and 2014/15) occur mainly at the edge of the caldera, but very big ones come from the caldera itself. These big eruptions are so large the top of the erupting magma collapses inward, deepening the caldera.
Looking at the chemistry of past eruptions, we now think the small eruptions represent the magma system slowly recharging itself to prepare for a big event.
We found evidence of two huge past eruptions from the Hunga caldera in deposits on the old islands. We matched these chemically to volcanic ash deposits on the largest inhabited island of Tongatapu, 65km away, and then used radiocarbon dates to show that big caldera eruptions occur about ever 1000 years, with the last one at AD1100.
With this knowledge, the eruption on January 15 seems to be right on schedule for a “big one”.
Read more: Why White Island erupted and why there was no warning[5]
What we can expect to happen now
We’re still in the middle of this major eruptive sequence and many aspects remain unclear, partly because the island is currently obscured by ash clouds.
The two earlier eruptions on December 20 2021 and January 13 2022 were of moderate size. They produced clouds of up to 17km elevation and added new land to the 2014/15 combined island.
The latest eruption has stepped up the scale in terms of violence. The ash plume is already about 20km high. Most remarkably, it spread out almost concentrically over a distance of about 130km from the volcano, creating a plume with a 260km diameter, before it was distorted by the wind.

This demonstrates a huge explosive power – one that cannot be explained by magma-water interaction alone. It shows instead that large amounts of fresh, gas-charged magma have erupted from the caldera.
The eruption also produced a tsunami throughout Tonga[6] and neighbouring Fiji and Samoa. Shock waves traversed many thousands of kilometres, were seen from space, and recorded in New Zealand some 2000km away. Soon after the eruption started, the sky was blocked out on Tongatapu, with ash beginning to fall.
All these signs suggest the large Hunga caldera has awoken. Tsunami are generated by coupled atmospheric and ocean shock waves during an explosions, but they are also readily caused by submarine landslides and caldera collapses.
It remains unclear if this is the climax of the eruption. It represents a major magma pressure release, which may settle the system.
A warning, however, lies in geological deposits from the volcano’s previous eruptions. These complex sequences show each of the 1000-year major caldera eruption episodes involved many separate explosion events.
Hence we could be in for several weeks or even years of major volcanic unrest from the Hunga-Tonga-Hunga-Ha'apai volcano. For the sake of the people of Tonga I hope not.
References
- ^ violent eruption of an underwater volcano (www.rnz.co.nz)
- ^ research (eos.org)
- ^ The 'pulse' of a volcano can be used to help predict its next eruption (theconversation.com)
- ^ curtain raisers to the main event (eos.org)
- ^ Why White Island erupted and why there was no warning (theconversation.com)
- ^ tsunami throughout Tonga (www.theguardian.com)

















