The climate crisis gives science a new role. Here's how research ethics must change too
- Written by Alexandre Wadih Raffoul, PhD Candidate, Department of Peace and Conflict Studies, Uppsala University
Young people across the world have taken to the streets again, demanding decision-makers at COP26 listen to the science[1]. But if science is to live up to these expectations, a fundamental rethinking of research ethics in light of the climate and ecological crises is needed.
The ongoing planetary crises create new ethical dilemmas for researchers. The three main principles of research ethics[2] – do no harm, integrity, and responsibility – remain relevant to avoid wrongdoing. But these were formulated reactively, in response to scandals in biomedical research[3], and could not anticipate these new challenges.
We are proposing a move from a negative ethics focused on avoiding harm to a positive research ethics. These new ethics are needed to guide the global scientific community in relation to civil society and politics during the climate and ecological crises.
Read more: Why we need engineers who study ethics as much as maths[4]
Do no harm
According to the “do no harm” imperative, researchers have a responsibility to avoid hurting humans or animals directly involved in their research. But what does “do no harm” mean in the midst of climate and ecological crises?
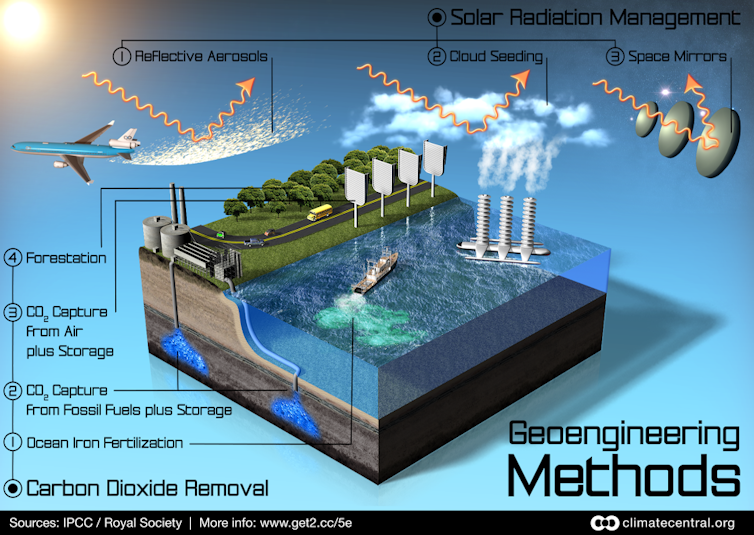
A growing group of scientists question the carbon footprint of academic activities, ranging from flying to conferences[5] to developing artificial intelligence[6]. The long-term and unpredictable consequences of research have also come back into focus. An example is the debate about the high risks[7] of geoengineering[8].
Read more: A global carbon removal industry is coming – experts explain the problems it must overcome[10]
The “do no harm” principle should thus be broadened in two ways:
it should include humans, animals and ecosystems that are traditionally not considered part of the research process, but can be negatively affected by it
it should better account for the long-term, indirect or unintended consequences of research projects or new technologies.
But if averting the climate crisis requires the complete transformation of society within ten years[11], is it enough for research to “do no harm”? Inspired by post-colonial approaches to research ethics[12], we suggest moving beyond this negative principle and towards a positive, regenerative science.
This science would actively contribute to the project of regenerating society and ecosystems[13]. It would be motivated by an analysis of the suffering already taking place and acknowledge historical responsibilities and power relations.
Read more: Four reasons why restoring nature is the most important endeavour of our time[14]
Act with integrity
The principle of integrity asks researchers to follow rigorous protocols, disclose conflicts of interest, refrain from manipulating data, and abstain from plagiarism. But can science be rigorous if it overlooks environmental variables?
Some disciplines ignore the predictions of IPCC reports, as well as indications of mass extinction and ecosystem collapse. They also struggle to reflect the complex and delicate interconnection[15] between humanity and nature in their practical recommendations.
For example, by focusing heavily on GDP growth, mainstream economics portrays our planetary habitat mostly as a resource to use or exploit. The idea of geoengineering also largely rests on an understanding of our life-support systems as a set of disconnected pieces that can be engineered.
Ultimately, “integrity means wholeness[16]”. It implies acknowledging that we are parts of a fragile and interconnected web of life, which we need to preserve.
Researchers should thus account for ecological dimensions in their analyses. They should also interrogate the conception of the humanity-nature relationship that implicitly underpins their work.
Take responsibility
According to the “responsibility” principle, research should be relevant to society and communicated to the public. But in a climate crisis, findings can be so dramatic, their implications for society so huge and controversial, that the word “responsibility” takes a new, heavier meaning.
In this context, some scientists do not dare to speak out, fearing to appear biased. As a result, they fail to influence the public debate[17].
Others are tempted to adjust their research to political demands. An example is the inclusion of unrealistic amounts of “negative carbon emissions” in climate models to satisfy policymakers. This was criticised[18] for unintentionally providing a scientific cover-up for climate inaction.
Read more: Climate scientists: concept of net zero is a dangerous trap[19]
Yet other researchers suggest that focusing mainly on technological innovation[20] can resolve the ecological crises. It’s a discourse that delays action by decreasing the sense of emergency[21] in tackling these crises.
The “responsibility” principle should therefore be enriched in three ways:
scientists should take their own findings seriously and stand up for their societal implications, even when it is uncomfortable to do so
researchers should defend the scientific process itself from the influence of political and economic interests[22][23][24]
scientists should remain humble as to what science can achieve. This means acknowledging the limits to our knowledge of an infinitely complex world, as well as the slow pace and unpredictable consequences of technological development[25].
From words to deeds
The research ethics sketched here need to be further developed. They can then be incorporated into global guidelines for individual researchers, but also for governments, universities and funding agencies.
Academic research will be at the heart of any solution to the climate and ecological crises. Embracing this responsibility and facing these existential threats requires much more from universities than the adoption of sustainability plans.
Read more: Climate change is the most important mission for universities of the 21st century[26]
References
- ^ listen to the science (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ three main principles of research ethics (www.gov.uk)
- ^ in response to scandals in biomedical research (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- ^ Why we need engineers who study ethics as much as maths (theconversation.com)
- ^ flying to conferences (link.springer.com)
- ^ developing artificial intelligence (dl.acm.org)
- ^ high risks (www.carbonbrief.org)
- ^ geoengineering (www.nytimes.com)
- ^ © Climate Central. Used with permission (www.climatecentral.org)
- ^ A global carbon removal industry is coming – experts explain the problems it must overcome (theconversation.com)
- ^ within ten years (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ post-colonial approaches to research ethics (journals.co.za)
- ^ project of regenerating society and ecosystems (theconversation.com)
- ^ Four reasons why restoring nature is the most important endeavour of our time (theconversation.com)
- ^ complex and delicate interconnection (books.google.se)
- ^ integrity means wholeness (philpapers.org)
- ^ fail to influence the public debate (www.yesmagazine.org)
- ^ criticised (theconversation.com)
- ^ Climate scientists: concept of net zero is a dangerous trap (theconversation.com)
- ^ focusing mainly on technological innovation (e360.yale.edu)
- ^ delays action by decreasing the sense of emergency (www.carbonbrief.org)
- ^ defend the scientific process itself (press.princeton.edu)
- ^ influence (www.merchantsofdoubt.org)
- ^ political and economic interests (www.drdavidmichaels.com)
- ^ unpredictable consequences of technological development (books.google.se)
- ^ Climate change is the most important mission for universities of the 21st century (theconversation.com)

















