We created a microscope slide that could improve cancer diagnosis, by revealing the 'colour' of cancer cells
- Written by Brian Abbey, Professor of Physics, La Trobe University
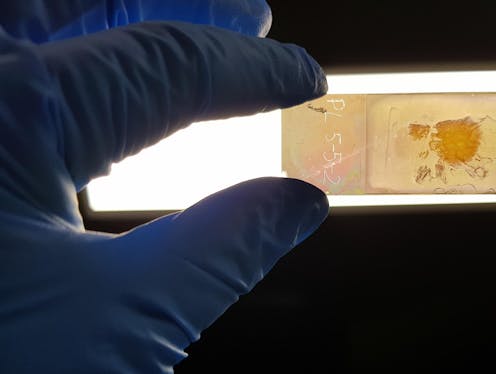
When we look at biological cells under a microscope, they’re usually not very colourful. Normally, to visualise them we have to artificially add colour — typically by staining. By doing so, we can see their shape and arrangement in a tissue and determine whether they’re healthy or not.
Sometimes, though, cell structure alone isn’t enough to accurately identify disease — which can lead to misdiagnosis and potentially fatal consequences for a patient. But what if there was a way to not only see the structure of cells, but also determine whether they are abnormal, simply by looking at their intrinsic colour under a microscope?
This was our team’s goal as we developed a new medical diagnostic tool called the NanoMslide. We modified a standard microscope slide to turn it into a powerful tool for breast cancer detection. Our research[1] is published today in Nature.
Early detection is key
It’s estimated[2] one in eight Australian women will be diagnosed with breast cancer by age 85. As with most cancers, catching the disease early is critical. However, an accurate diagnosis of the earliest stages of breast cancer requires identifying small numbers of diseased cells throughout a tissue, which can be incredibly challenging.
The NanoMslide can manipulate light at the nanoscale, causing cells to “light up” with vivid colour contrast. This makes it easier to recognise potentially cancerous cells (or benign abnormalities) within the tissue.
By providing a way to instantly distinguish which cells could be cancerous, the tool may help to reduce current uncertainty around very early-stage breast cancer detection. With mammogram screening, distinguishing breast abnormalities from early breast cancers upon biopsy is very important, particularly as misdiagnosis rates can be as high as 15%.
Read more: 'Devastated and sad' after 36 years of research — early detection of ovarian cancer doesn't save lives[3]
Major barriers in development
Incorporating nanotechnology into medical diagnostics presents a number of challenges. It took us six years of development to ensure NanoMslide would work effectively. In the end it was a combination of cutting-edge nanofabrication, a significant amount of trial-and-error and a bit of good fortune that led to our breakthrough.
For decades, researchers have known cancer cells tend to interact with light in a way that’s different to healthy cells. This is due to a variety of factors, such as the distribution of protein inside the cell and differences in its overall shape.
The main challenge is these differences can be extremely subtle and can present in a variety of ways. Previous approaches to differentiating cancer cells (without using stains or labels) have tended to use specialised microscopy equipment, or complex techniques.
But these approaches are difficult to incorporate into existing pathology workflows and can require specialist training and knowledge. So we took a radically different approach.
Success with human tissue
Rather than focusing on developing a better microscope, we focused on improving the microscope slide instead.
By developing a special nanofabricated coating, we modified the surface of an ordinary microscope slide and transformed it into one huge sensor. What’s truly remarkable is the structures of the sensor are just a few hundred nanometres across, yet are repeated with amazing precision across an area of tens of centimetres, or more.
Maintaining this level of precision, which is necessary for reliable fabrication at this scale, has taken advances in nanofabrication techniques that have only become commercially available in the past six years.
The sensor is activated by visible light. And when an object such as a tissue or single cell comes into contact with the sensor’s surface, colours are produced. It is this feature which we’ve been able to optimise to allow pathologists to detect cells that are likely cancerous, just by looking at them.
The dyes which are currently used to stain tissues (to visualise cell shape and architecture) normally present as one or two colours. The NanoMslide renders tissues in beautiful full-colour contrast, making it easier to differentiate multiple types of cell on a single slide.
For our study, we tested the slides with expert breast-cancer pathologists, using both a mouse model and patient tissue. By starting with a well-characterised small-animal model, our team of physicists, cancer researchers and breast pathologists was able to develop the technology further.
We eventually reached the point where we could be confident some of the specific colours visible were indicative of cancerous cells. This led to further pathology assessments with patient tissue, where there is more complexity to contend with in terms of diagnosis.
Yet, even in this more challenging setting, the NanoMslide performed strongly. It also outperformed some commercial biomarkers, which are used as an aid for borderline diagnoses (where cancer is difficult to tell apart from benign abnormalities).
Like going from black and white to colour television
Because the technology doesn’t rely on any special function, or specific molecular interactions, it could potentially be applied to other types of cancer — even other types of disease. Another application now being worked on is to examine the results of liquid biopsies, such as cheek swabs, for immediate point-of-care analysis.
In April, we were fortunate to benefit from the opening of a new instrument at the Australian National Fabrication Facility to enable the scaling-up of production. This means NanoMslide can be moved from small-scale to medium-scale manufacture, allowing us to explore a number of different applications, and produce the numbers of slides required for further clinical validation.
The technology could also be hugely beneficial to the growing digital-pathology space, where the vivid colours generated by NanoMslide could help develop next-generation artificial intelligence algorithms to identify signs of disease.
Read more: Curious Kids: Why do people get cancer?[4]
References
- ^ research (www.nature.com)
- ^ estimated (www.canceraustralia.gov.au)
- ^ 'Devastated and sad' after 36 years of research — early detection of ovarian cancer doesn't save lives (theconversation.com)
- ^ Curious Kids: Why do people get cancer? (theconversation.com)

















