Consent laws aren't the reason for low sexual assault conviction rates — it's how society views rape itself
- Written by Simon Bronitt, Head of School and Dean Professor of Law, University of Sydney
Public debate about our rape laws in recent weeks has fixated, yet again, on the concept of consent and whether our current definition in the law is “fit for purpose”.
Over the past three decades, Australia’s states and territories have set out to modernise the definition of consent, albeit with some variability in how it is defined.
South Australia, New South Wales and Northern Territory, for example, have a requirement[1] of “free and voluntary agreement” to sexual intercourse, while Victoria and Tasmania have a more pared-down version of “free agreement”.
Queensland and Western Australia have gone their own way, rejecting the idea of consent as “agreement” in favour of a more active interpretation that consent is “freely and voluntarily given”.
These definitions are still being refined and debated. The NSW Greens have, for instance, introduced a bill[2] to extend the current definition to require enthusiastic consent to sex. This is a qualitative threshold that would go far beyond the “free and voluntary” language in the current law.
Last week, NSW Police Commissioner Mick Fuller also proposed[3] using an app to record sexual consent — an idea that was roundly criticised.
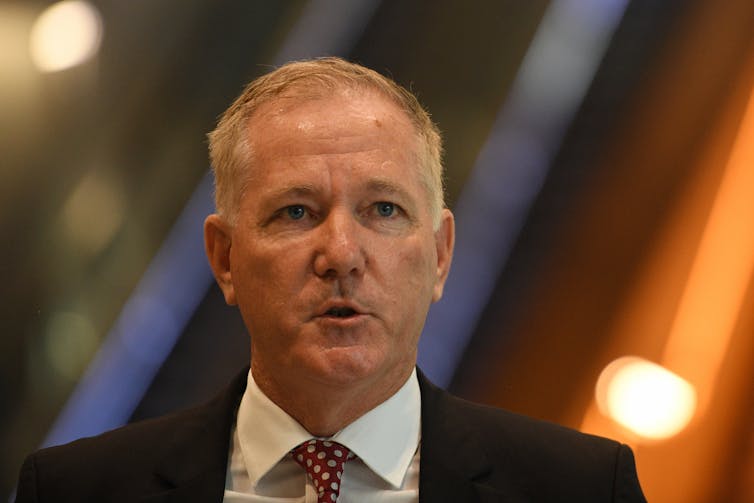 Fuller has conceded his consent app ‘could be a terrible idea’, but the idea was intended to start a debate.
Dean Lewins/AAP
Fuller has conceded his consent app ‘could be a terrible idea’, but the idea was intended to start a debate.
Dean Lewins/AAP
Why consent can’t be contractually given
Advocates for rape law reform argue our current definitions of consent are leading to “staggeringly low[4]” reporting rates of sexual assaults and conviction rates.
According to the national statistics, nearly nine in 10[5] victims of sexual assaults do not go to police.
In NSW, official statistics reveal[6] the number of sexual offences reported to police increased from 3,541 to 4,444 from 2015–19. Of most concern, however, is that only 19% of these incidents proceeded to trial in 2019. (Two-thirds of those charged were found guilty.)
Understanding the attrition of cases is complex. This can turn on the strength of evidence, as well as how police and prosecutors exercise their powers to progress a case at various points in the process.
Read more: Almost 90% of sexual assault victims do not go to police — this is how we can achieve justice for survivors[7]
These statistics are often cited in support of the case for expanding the legal definition of rape. Some law reform advocates and survivors are calling for[8] a broader “affirmative” consent standard, which would require consent to be actively given by actions and/or words before, and continuously throughout, a sexual act.
Encouraging open conversations about consent before and during sexual activity is important, as awkward as this might be for some people. Though it may seem “unromantic” — as Fuller noted[9] last week — this type of communication provides safety and assurance for both parties.
The NSW police commissioner’s idea that consent could be structured and recorded via an app, however, has raised the ire of many commentators.
Some critics argue this approach to consent is apt to mislead. It promotes a contractual understanding of sexual relations - an “offer and acceptance” model, in which one person actively initiates sex with an offer and terms that can be revised, accepted or rejected by the other person.
Read more: Apps against sexual violence have been tried before. They don't work[10]
Indeed, the idea of a “consent app” is deeply problematic. It is reminiscent of the paper-based consent forms[11] that floated about some university campuses (with free condoms) in the 1990s.
Such written consent forms, on closer scrutiny, had little if any legal or evidential value in sexual assault cases. The key point behind a “positive” definition of consent is that it should be viewed as an active, conscious and above all reflexive exercise.
Consent is given and obtained through communication, not contracts. It cannot be inferred from a written document or an app, negotiated some time before the sexual activity. And it must be remembered that consent must be ongoing and can be withdrawn at any time before and during sex.
Put simply, consent should never be implied or inferred by an offender from apps, Tinder swipes or social media likes.
The proposal for a consent app has little merit, except perhaps to provide a platform for educating people about the law and reminding them about the standards of behaviour expected from people when engaging in sex.
Perceptions of what constitutes ‘real’ rape
From my perspective, there is another core issue that is leading to low reporting and high attrition rates of sexual assault cases — and this can’t be solved by further fiddling with our legal definitions of consent.
This is how our community perceives rape — or what constitutes “real” rape as opposed to consensual intercourse.
The law has an important role in shaping community standards. Over the past three decades, the legislature and courts have worked to embed and reflect more modern concepts of human dignity and respectful decision-making in the law governing sexual activity.
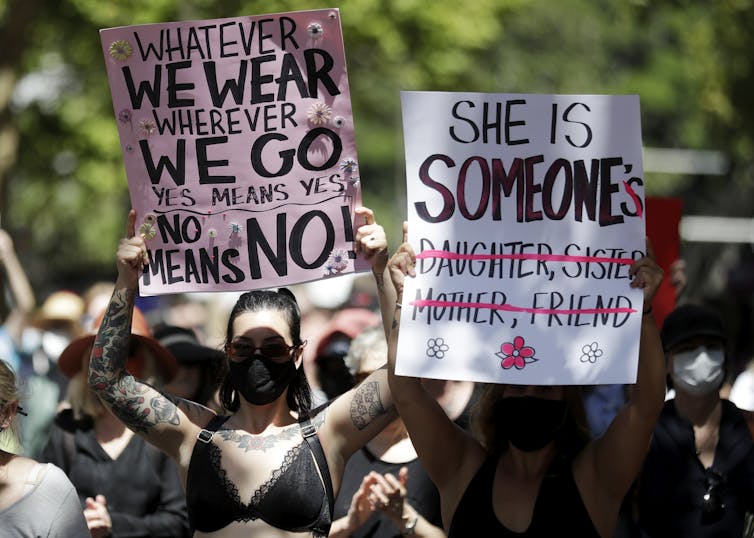 Thousands demanded justice for women at marches across the country earlier this month.
Rick Rycroft/AP
Thousands demanded justice for women at marches across the country earlier this month.
Rick Rycroft/AP
For instance, marital rape gradually came to be criminalised[12] in all Australian states and territories, though the process took many years.
And the legislatures and courts have provided further guidance on the wide range of cases where the victim’s apparent “consent” has been compromised by the effects of intoxication, fraud, mistakes, blackmail, threats or other abuses of power.
The battle at the heart of rape trials rarely relates to issues of identity or whether in fact sexual activity took place. Rather, cases often turn on the differing perceptions of the people involved about what took place (what is referred to as “he said, she said[13]”).
And this is where community attitudes toward gender, sexuality and race invariably come into play.
Read more: 'Cultural misogyny' and why men's aggression to women is so often expressed through sex[14]
When it comes to consent, for example, juries must decide whether the prosecution has proven beyond a reasonable doubt there was no free and voluntary consent. And the perceptions of juries are influenced by these wider societal beliefs and attitudes.
In the end, the “law’s truth” about consent, as legal feminist Carol Smart pointed out[15] more than three decades ago, is decided in the context of how the police, prosecutors, defence team, courts and wider community view what constitutes a “real rape” (or not).
Countering these entrenched biases and myths about “real rape” is needed to improve sexual assault reporting and conviction rates.
We can do this by reviewing our laws and procedures governing rape investigations, improving our judicial and lawyer education, and providing better jury directions on consent in “plain English”.
This is the best way forward to tackle what is, and will remain, a complex and often deeply contested aspect of every rape trial.
References
- ^ requirement (www.parliament.nsw.gov.au)
- ^ introduced a bill (greens.org.au)
- ^ proposed (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ staggeringly low (greens.org.au)
- ^ nearly nine in 10 (www.aihw.gov.au)
- ^ reveal (www.bocsar.nsw.gov.au)
- ^ Almost 90% of sexual assault victims do not go to police — this is how we can achieve justice for survivors (theconversation.com)
- ^ calling for (theconversation.com)
- ^ noted (www.news.com.au)
- ^ Apps against sexual violence have been tried before. They don't work (theconversation.com)
- ^ paper-based consent forms (www.nytimes.com)
- ^ criminalised (www.auswhn.org.au)
- ^ he said, she said (www.lexology.com)
- ^ 'Cultural misogyny' and why men's aggression to women is so often expressed through sex (theconversation.com)
- ^ pointed out (www.jstor.org)

















