The way Australia produces food is unique. Our updated dietary guidelines have to recognise this
- Written by David Masters, Adjunct Professor in Agriculture and Environment, The University of Western Australia

You might know Australia’s dietary guidelines[1] from the famous infographics[2] showing the types and quantities of foods we should eat to have a healthy diet.
Last updated 12 years ago, the National Health and Medical Research Council is now revising them to consider not only how food affects our health but also how sustainable our foods are. At least 37 other countries[3] have already added sustainability to their dietary guidelines.
Many countries use global load indicators to assess the environmental impact of specific foods, based on the planetary boundaries[4] within which humanity can safely operate. While useful to compare between countries, these indicators don’t match Australia’s environmental risks and priorities.
Unlike many other countries, locally produced food represents around 90%[5] of what Australians eat. The environmental footprint of these foods is shaped almost entirely by the country’s unique landscapes, climates and farming systems.
Our recent research[6] suggests forthcoming guidelines need to take local conditions into account. If global load indicators are the sole way to measure impact, the guidelines won’t capture Australia’s specific environmental challenges in producing food.
Local indicators matter
Global load indicators include greenhouse gas emissions, how much land is used per kilo of food, water use, land and water pollution and biodiversity loss.
This is how we get common figures such as the statistic that it takes 1,670 litres of water to produce 1 kilogram of rice[7].
While global measures are useful in comparing between countries and products, they don’t always match local environmental risks and priorities.
For example, using 1,670L of water to produce a kilo of rice in the contested and controlled Murray Darling Basin will have a different impact compared to using the same volume in Western Australia’s Kununurra irrigation system, where water is more abundant and has fewer alternative uses. Growing a kilo of rice in Italy will differ again.
If we want dietary guidelines to encourage real improvements on farm and in rural landscapes, environmental indicators must reflect the challenges rural stakeholders actually face.
Consumer preferences have already shifted several food production systems. Rising demand for free-range eggs[8] and grass-fed beef has changed how farmers operate. It’s important to get this right.
One size does not fit all
Australia’s agricultural lands are diverse.
By area, more than 80% of our farmland falls in the rangelands[9]. Here, cattle and sheep graze with minimal human intervention on vast tropical savannas, woodlands, shrublands and grasslands. Low rainfall and poor soils mean livestock are kept at low densities. Other food production options haven’t proved viable.
If we used global load indicators, food from rangelands would be assessed as having a high environmental impact due to large land use, lots of potentially polluting nutrients (dung and urine) and use of rainfall to grow forage vegetation.
But the main environmental issues for Australia’s rangelands are different, including methane emissions from livestock, land degradation[10], invasive weeds such as buffel grass[11] and biodiversity loss[12].
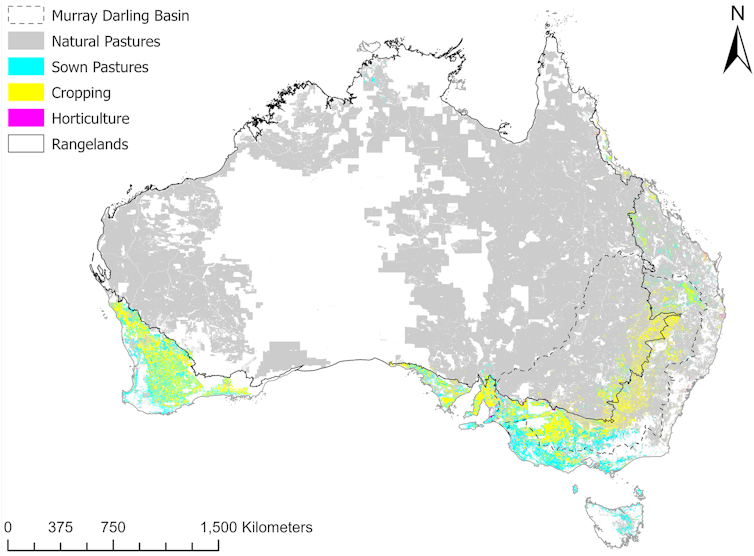
Australia’s next largest area of agriculture is mixed crop and livestock, found in regions such as the Mallee[15] in Victoria and Western Australia’s Wheatbelt[16]. Most crops and 40% of livestock are produced in these areas, characterised by reliable rainfall patterns and low to medium rainfall of around 250–450 millimetres a year.
Farming here can make soils more acid[17] due to high levels of nitrogen from fertilisers, alongside issues such as dryland salinity, erosion, biodiversity loss and greenhouse gas emissions. These issues have degraded some land so much it can’t sustain[18] farming.
For these two types of agriculture, local indicators work better.
By contrast, the intensive and productive irrigated farms of the Murray–Darling Basin have environmental impacts more aligned to global indicators. Environmental issues here include greenhouse gases, competition for land and water use, nutrient pollution (primarily fertilisers) and biodiversity loss.
Good for your health – and the environment?
While previous Australian studies[19] have assessed the environmental footprint of different foods or focused on a narrow description[20] of environmental impact derived from overseas studies, these haven’t accounted for local environmental priorities or trade-offs.
Trade-offs are common. For instance, plant-based diets may result in lower greenhouse gas emissions but can increase pressure on soil health and biodiversity, as crops are commonly grown as monocultures with high fertiliser and pesticide use.
Common Australian diets mixing plant and animal foods can have a lower impact on biodiversity and soil health but higher greenhouse gas emissions, as mixed diets entail a more diverse range[21] of cultivated plants and animals but rely more on methane-producing livestock.
Recognising and balancing these trade-offs will be essential if Australia’s updated dietary guidelines are to support healthy people and a healthy environment.
What’s next?
Ideally, Australia’s updated dietary guidelines will capture the unique pressures and challenges of producing food locally. This won’t be easy, given impacts will vary across different foods, regions and production systems. But the tools are already available.
Farm software can track every aspect of the production in a local environmental context, making it possible to predict impacts on the natural capital of individual farms – if agreements to share and aggregate data can be negotiated.
Gathering these data will allow local environmental indicators to be embedded in dietary guidelines. If this is done, it will become possible to link recommended diets to sustainability reporting. Farms, retailers and banks are increasingly required to report sustainability metrics, which can be linked to foods.
That means Australians could see the environmental credentials of their food on the labels, based not on global averages – but on how the specific farm is doing.
References
- ^ dietary guidelines (www.eatforhealth.gov.au)
- ^ infographics (www.eatforhealth.gov.au)
- ^ 37 other countries (www.eatforhealth.gov.au)
- ^ planetary boundaries (doi.org)
- ^ around 90% (www.agriculture.gov.au)
- ^ recent research (doi.org)
- ^ 1 kilogram of rice (doi.org)
- ^ free-range eggs (www.australianeggs.org.au)
- ^ the rangelands (www.dcceew.gov.au)
- ^ land degradation (doi.org)
- ^ buffel grass (www.landscape.sa.gov.au)
- ^ biodiversity loss (www.rangelandswa.com.au)
- ^ Author provided (www.cambridge.org)
- ^ CC BY-NC-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ Mallee (en.wikipedia.org)
- ^ Wheatbelt (en.wikipedia.org)
- ^ more acid (www.soilquality.org.au)
- ^ can’t sustain (www.epa.wa.gov.au)
- ^ previous Australian studies (doi.org)
- ^ narrow description (doi.org)
- ^ more diverse range (doi.org)
















