Senate's vote to ban slave-made imports shows the weakness of Australia's Modern Slavery Act
- Written by Kyla Raby, PhD Candidate researching the role of consumers in eradicating modern slavery in supply chains, University of South Australia
When the Australian government introduced its Modern Slavery Bill to parliament in 2018, it heralded it as the start of a “race to the top”.
But it has turned out to be less a race than a meander.
The bill required companies with annual revenues greater than $100 million to report on action they take to ensure their supply chains are free of slave labour. The premise was that transparency and accountability were enough to drive reform.
“Business feedback indicates the primary driver for compliance will be investor pressure and reputational costs and benefits,” a government spokeswoman said at the time[1]. “This will drive compliance more effectively than legislated penalties and encourage a business-led race to the top”.
That bill was passed in December 2018[2]. But so far, according to research published last month[3] by the Australian Council of Superannuation Investors, most companies are engaged in a “race to the middle”, disclosing only the minimum and not wishing to reveal more than their key peers.
Could more be done?
Yes — but the possibilities and pitfalls are shown by a private member’s bill that passed the Senate this week.
Proposed by South Australian independent senator Rex Patrick, the Customs Amendment (Banning Goods Produced By Forced Labour) Bill 2021[4] would amend federal customs regulations to prohibit the import of any goods made using forced labour.
It passed the Senate on Monday with support from the Labor Party, the Greens and One Nation senators. But Coalition senators voted against the bill. This was despite it reflecting the recommendations of a inquiry chaired by Liberal senator Eric Abetz, who said Patrick’s bill[5] was “worthy of consideration and support, in principle”.
Without government support the bill won’t pass the House of Representatives to become law. Nonetheless, it is worth considering why senators as disparate as the Greens and One Nation have backed it. Despite the Modern Slavery Act[6], there’s much more to be done before Australians can be confident the goods they buy are free of slave labour.
The call for a stronger approach
Patrick began with less expansive ambitions, introducing a bill[7] in December 2020 to ban the import of goods from China produced by Uyghur forced labour.
This was in response to mounting evidence of the Chinese government’s detention of more than a million Uyghurs (and other ethnic minorities) in the western province of Xinjiang, forcing them to work making goods sold by Western companies.
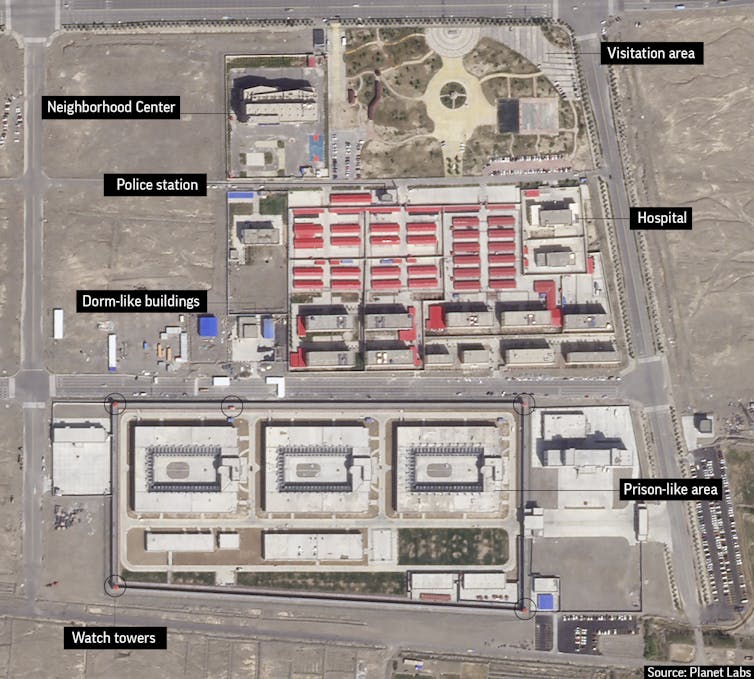 A 2018 satellite image shows detention camps built near the Kunshan Industrial Park in China’s Xinjiang region.
Planet Labs/AP,
A 2018 satellite image shows detention camps built near the Kunshan Industrial Park in China’s Xinjiang region.
Planet Labs/AP,
Patrick’s bill was referred to the Senate Standing Committee on Foreign Affairs, Defence and Trade, chaired Abetz. After considering about 60 submissions, in June the committee recommended (among other things) amending the Customs Act and other legislation “to prohibit the import of any goods made wholly or in part with forced labour, regardless of geographic origin”.
Read more: Four Corners’ forced labour exposé shows why you might be wearing slave-made clothes[8]
The committee endorses without reservation the objectives of the bill. The state-sponsored forced labour to which the Uyghur people are being subjected by the Chinese dictatorship is a grave human rights violation. It is incumbent on the government to take steps to ensure that Australian businesses and consumers are not in any way complicit in these egregious abuses.
Slavery is all around us
Patrick’s revised bill reflects this sentiment.
While the Chinese government may be detaining up to a million Uyghurs, the anti-slavery organisation Walk Free Foundation[10] estimates globally about 4 million people are forced to work by state authorities, with further 21 million people exploited in private supply chains.
The foundation estimates each year goods worth more than US$350 billion (about $A480 billion)[11] imported into G20 countries are at at-risk of having been produced, at least in part, by forced labour.
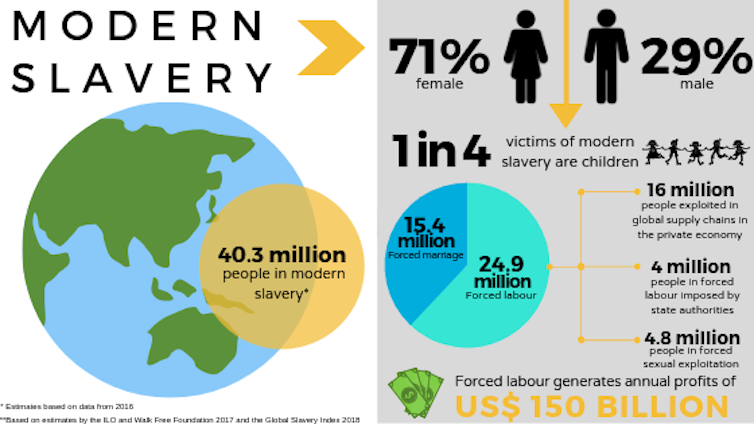 Anti-Slavery Australia
No country or industry is untouched. The estimate for imports into Australia is US$12 billion (about A$16.5 billion) a year. It’s highly likely at some stage you’ve bought something that has been made with exploited labour.
It might have been clothing made in China[12]. Or it might have tinned tuna from Thailand[13], cotton milled in India[14]. Or chocolate made from cacao farmed West Africa[15].
Australia’s Modern Slavery Act has been part of international moves to make companies accountable for the conditions of workers in the global supply chains from which they profit. This law requires reporting entities to submit an annual “Modern Slavery Statement” to a public register[16].
The law, however, has been criticised for lacking any real bite. There’s no real penalty for noncompliance. Instead it relies on the fear of being “named and shamed” — and as the research from the Australian Council of Superannuation Investors suggests, this doesn’t seem enough.
How did the government respond?
So why didn’t the government support Patrick’s bill?
In the words of Abetz, speaking in the Senate on Monday, “my heart says yes to this bill but my head says not yet”.
The government’s hesitancy is understandable. If passed, the law will require every Australian company — not just the big ones — to prove that any goods it imports are slave-free. That’s a huge leap from what is currently required.
Some large corporations are already struggling with how to adhere to the spirit and less strenuous requirements of the Modern Slavery Act. Many small- and medium-sized enterprises and not-for-profits may also not have the expertise or resources to comply.
But even if this particular bill isn’t right, the issues with Australia’s current response to modern slavery cannot be ignored. The enslavement of human beings shouldn’t be an issue where a progressive, but painfully slow, approach is accepted.
Senator Patrick’s bill may not become law. But it has helped shine a light on the deficiencies with the current law and shown there is broad community support for stronger action.
As the famous abolitionist William Wilberforce said: “You may choose to look the other way, but you can never say again that you did not know.”
Anti-Slavery Australia
No country or industry is untouched. The estimate for imports into Australia is US$12 billion (about A$16.5 billion) a year. It’s highly likely at some stage you’ve bought something that has been made with exploited labour.
It might have been clothing made in China[12]. Or it might have tinned tuna from Thailand[13], cotton milled in India[14]. Or chocolate made from cacao farmed West Africa[15].
Australia’s Modern Slavery Act has been part of international moves to make companies accountable for the conditions of workers in the global supply chains from which they profit. This law requires reporting entities to submit an annual “Modern Slavery Statement” to a public register[16].
The law, however, has been criticised for lacking any real bite. There’s no real penalty for noncompliance. Instead it relies on the fear of being “named and shamed” — and as the research from the Australian Council of Superannuation Investors suggests, this doesn’t seem enough.
How did the government respond?
So why didn’t the government support Patrick’s bill?
In the words of Abetz, speaking in the Senate on Monday, “my heart says yes to this bill but my head says not yet”.
The government’s hesitancy is understandable. If passed, the law will require every Australian company — not just the big ones — to prove that any goods it imports are slave-free. That’s a huge leap from what is currently required.
Some large corporations are already struggling with how to adhere to the spirit and less strenuous requirements of the Modern Slavery Act. Many small- and medium-sized enterprises and not-for-profits may also not have the expertise or resources to comply.
But even if this particular bill isn’t right, the issues with Australia’s current response to modern slavery cannot be ignored. The enslavement of human beings shouldn’t be an issue where a progressive, but painfully slow, approach is accepted.
Senator Patrick’s bill may not become law. But it has helped shine a light on the deficiencies with the current law and shown there is broad community support for stronger action.
As the famous abolitionist William Wilberforce said: “You may choose to look the other way, but you can never say again that you did not know.”
References
- ^ said at the time (probonoaustralia.com.au)
- ^ in December 2018 (theconversation.com)
- ^ published last month (acsi.org.au)
- ^ Customs Amendment (Banning Goods Produced By Forced Labour) Bill 2021 (www.aph.gov.au)
- ^ said Patrick’s bill (parlinfo.aph.gov.au)
- ^ Modern Slavery Act (www.legislation.gov.au)
- ^ a bill (www.aph.gov.au)
- ^ Four Corners’ forced labour exposé shows why you might be wearing slave-made clothes (theconversation.com)
- ^ inquiry report stated (www.aph.gov.au)
- ^ Walk Free Foundation (www.walkfree.org)
- ^ more than US$350 billion (about $A480 billion) (downloads.globalslaveryindex.org)
- ^ clothing made in China (theconversation.com)
- ^ tinned tuna from Thailand (theconversation.com)
- ^ cotton milled in India (theconversation.com)
- ^ cacao farmed West Africa (theconversation.com)
- ^ public register (modernslaveryregister.gov.au)
Authors: Kyla Raby, PhD Candidate researching the role of consumers in eradicating modern slavery in supply chains, University of South Australia