Athlete activism or corporate woke washing? Getting it right in the age of Black Lives Matter is a tough game
- Written by Jessica Vredenburg, Senior Lecturer (Assistant Professor) in Marketing, Auckland University of Technology
So-called brand activism is evolving fast. When Colin Kaepernick first knelt during the US national anthem in 2016, professional football turned its back on him[1]. Now, consumer and sports fan expectations are forcing brands to see activism as good for business[2].
According to a recent Nielsen survey[3], 72% of sports fans believe athletes are an important influence in the Black Lives Matter (BLM) movement. A whopping 59% expect athletes to engage personally with BLM activism.
In short, if brands aren’t taking a stand (or a knee), consumers notice.[4]
Sporting codes have woken up to the benefits of strategically targeting a younger, more racially-diverse demographic. As National Hockey League (NHL) executive vice president for social impact Kim Davis put it[5]:
People understand that doing the right thing is also right for the business.
After the shooting of Jacob Blake[6] by Kenosha police, however, that activism ramped up. Players from most major professional sports protested by refusing to play[7] at all.
Brand activism cuts both ways
It began with local NBA team the Milwaukee Bucks, whose own player Sterling Brown had been brutally beaten by police in 2018[8]. Having refused to take the court for a playoff game, the team’s actions were picked up[9] by social media and the no-play protest spread to other sports.
The backlash and praise were immediate, with the Bucks becoming the most mentioned[10] brand on social media that week.
Read more: Woke washing: what happens when marketing communications don't match corporate practice[11]
There were asymmetric effects[12] for the team brand: a clear drop in brand sentiment from those who disagreed with their stand, and a surge of brand love driven by the backlash.
Whereas brands might once have avoided controversy, there is now a clear case[13] for taking a stand — as the NHL discovered when it continued to play while other sports “went dark”. The backlash[14] from fans and players alike forced the cancellation of two days’ play.
Similarly, the Association of Tennis Professionals (ATP) took a stand by not playing for one day after player Naomi Osaka threatened not to compete[15] in the Western & Southern Open semifinals in Cincinnati. She explained:
Before I am an athlete, I am a black woman. And as a black woman I feel as though there are much more important matters at hand that need immediate attention, rather than watching me play tennis.
Osaka went on to win the US Open, and was praised[16] for donning protective face masks with the names of seven black people killed by police. There was also criticism that a one-day break in play, without further commitment, did little to further the BLM cause.
Read more: Brands may support Black Lives Matter, but advertising still needs to decolonise[17]
But accusations of virtue signalling and woke washing[18] put the ATP between a rock and a hard place. If tennis officials hadn’t engaged in some way with the moment, they risked being called out for insensitivity (as were the NHL and some cricket teams[19]).
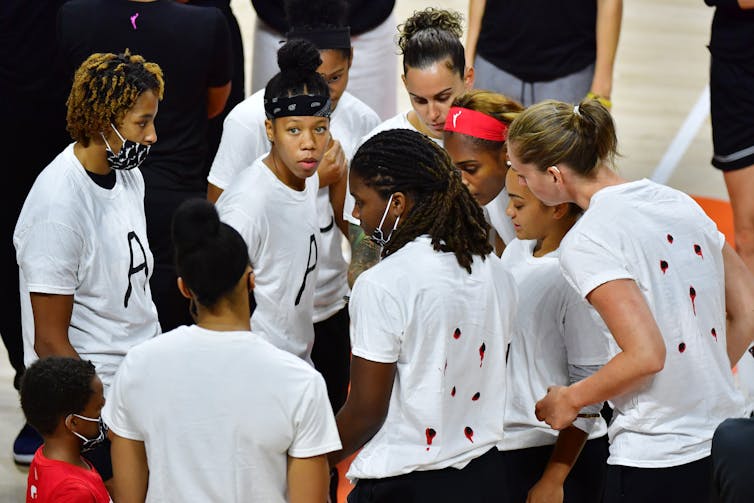 Members of the Washington Mystics wearing T-shirts printed with bullet holes to protest the shooting of Jacob Blake in Kenosha, Wisconsin.
GettyImages
Members of the Washington Mystics wearing T-shirts printed with bullet holes to protest the shooting of Jacob Blake in Kenosha, Wisconsin.
GettyImages
In business we trust
It may not be surprising that brand activism[20] is increasingly being driven by consumers[21] demanding they take a stand (and condemning those who don’t), as some studies now show businesses are more trusted than government[22].
We may be reaching a point where it is more surprising to consumers when brands don’t take a stand on social issues than when they do.
In 2018, consumers responded extremely positively[23] to Nike’s now-iconic Black Lives Matter campaign with Colin Kaepernick. Now the brand has an established pro-social reputation, however, the response to recent anti-racism action has been more muted.
Nike’s You Can’t Stop Us[24] campaign and its declaration[25] of Juneteenth as an annual paid company holiday have been met with a positive but noticeably milder reaction from consumers.
Read more: Black Lives Matter, LGBTQ rights, Trump: The risks and rewards of corporate activism[26]
Surprise is no longer a strategy
Nike was just one of many brands[27] to declare Juneteenth a holiday in the US (along with Google, Lyft, The New York Times, JCPenney, the NFL, Tumblr and Postmates). As our research[28] suggests, such acts are simply not as surprising in 2020 as they once were.
As brand activism becomes more widespread, consumers’ appreciation of it also becomes more sophisticated — to the point where it is a key component[29] of brand loyalty.
However, while consumers expect brands to take a stand, many also believe social issues are used too often as a marketing ploy[30].
The challenge for brands is clear: practice what you preach, make a real difference, pay more than lip service to causes. Staying relevant has never been harder.
References
- ^ professional football turned its back on him (www.bbc.com)
- ^ good for business (www.bloomberg.com)
- ^ Nielsen survey (www.nielsen.com)
- ^ consumers notice. (edition.cnn.com)
- ^ put it (www.nytimes.com)
- ^ shooting of Jacob Blake (edition.cnn.com)
- ^ refusing to play (edition.cnn.com)
- ^ brutally beaten by police in 2018 (www.sbnation.com)
- ^ picked up (izea.com)
- ^ most mentioned (izea.com)
- ^ Woke washing: what happens when marketing communications don't match corporate practice (theconversation.com)
- ^ asymmetric effects (theundefeated.com)
- ^ clear case (www.sciencedirect.com)
- ^ backlash (www.citynews1130.com)
- ^ threatened not to compete (www.insider.com)
- ^ praised (www.timeslive.co.za)
- ^ Brands may support Black Lives Matter, but advertising still needs to decolonise (theconversation.com)
- ^ woke washing (journals.sagepub.com)
- ^ some cricket teams (news.sky.com)
- ^ brand activism (journals.sagepub.com)
- ^ driven by consumers (sproutsocial.com)
- ^ more trusted than government (www.edelman.com)
- ^ extremely positively (www.washingtonpost.com)
- ^ You Can’t Stop Us (edition.cnn.com)
- ^ declaration (edition.cnn.com)
- ^ Black Lives Matter, LGBTQ rights, Trump: The risks and rewards of corporate activism (theconversation.com)
- ^ many brands (www.miamiherald.com)
- ^ research (journals.sagepub.com)
- ^ key component (hbr.org)
- ^ marketing ploy (www.edelman.com)
Authors: Jessica Vredenburg, Senior Lecturer (Assistant Professor) in Marketing, Auckland University of Technology













