Why does gravity pull us down and not up?
- Written by Mario Borunda, Associate Professor of Physics, Oklahoma State University
 Curious Kids[1] is a series for children of all ages. If you have a question you’d like an expert to answer, send it to curiouskidsus@theconversation.com[2].
Why does gravity pull us down and not up? - Gracie, age 9, Brookline, Massachusetts
Gravity is the reason things with mass or energy are attracted to each other. It is why apples fall toward the ground and planets orbit stars.
Magnets attract some types of metals, but they can also push other magnets away. So how come you feel only the pull of gravity?
In 1915, Albert Einstein figured out the answer when he published his theory of general relativity[3]. The reason gravity pulls you toward the ground is that all objects with mass, like our Earth, actually bend and curve the fabric of the universe, called spacetime[4]. That curvature is what you feel as gravity.
What is spacetime?
Before getting into the complicated world of gravity, you need to understand spacetime.
Spacetime is exactly what it sounds like: the three dimensions of space – length, width and height – combined with the fourth dimension – time. Using some very brilliant math, Einstein was the first person to realize that the laws of physics work in a universe where space and time are merged together[5].
What this means is that space and time are connected – if you move really fast through space, time slows down for you compared to someone who is moving slowly. This is why astronauts – who are moving very fast in space – age a tiny bit more slowly than people on Earth[6].
Curious Kids[1] is a series for children of all ages. If you have a question you’d like an expert to answer, send it to curiouskidsus@theconversation.com[2].
Why does gravity pull us down and not up? - Gracie, age 9, Brookline, Massachusetts
Gravity is the reason things with mass or energy are attracted to each other. It is why apples fall toward the ground and planets orbit stars.
Magnets attract some types of metals, but they can also push other magnets away. So how come you feel only the pull of gravity?
In 1915, Albert Einstein figured out the answer when he published his theory of general relativity[3]. The reason gravity pulls you toward the ground is that all objects with mass, like our Earth, actually bend and curve the fabric of the universe, called spacetime[4]. That curvature is what you feel as gravity.
What is spacetime?
Before getting into the complicated world of gravity, you need to understand spacetime.
Spacetime is exactly what it sounds like: the three dimensions of space – length, width and height – combined with the fourth dimension – time. Using some very brilliant math, Einstein was the first person to realize that the laws of physics work in a universe where space and time are merged together[5].
What this means is that space and time are connected – if you move really fast through space, time slows down for you compared to someone who is moving slowly. This is why astronauts – who are moving very fast in space – age a tiny bit more slowly than people on Earth[6].
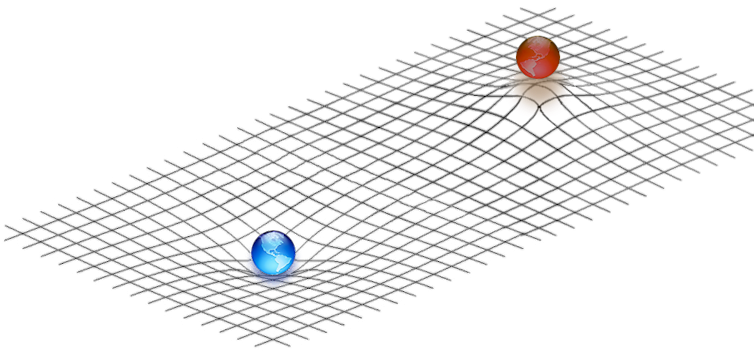 Earth curves spacetime so that you fall toward Earth instead of away from it.
Tokamak/WikimediaCommons, CC BY-SA[7][8]
Matter makes gravity wells, not gravity hills
Remember, gravity is the idea that objects in the universe are attracted to each other because spacetime is bent and curved. When Einstein came up with general relativity, he showed that all stuff in the universe can curve spacetime – in physics terms that stuff is mass and energy.
Earth curves spacetime so that you fall toward Earth instead of away from it.
Tokamak/WikimediaCommons, CC BY-SA[7][8]
Matter makes gravity wells, not gravity hills
Remember, gravity is the idea that objects in the universe are attracted to each other because spacetime is bent and curved. When Einstein came up with general relativity, he showed that all stuff in the universe can curve spacetime – in physics terms that stuff is mass and energy.
 Gravity works similarly to how objects will roll toward your feet if you stand on a trampoline.
MoMo Productions/Stone via Getty Images[9]
Since your brain usually thinks about the world in three dimensions, it is really hard to think about the four dimensions of spacetime as a single idea. So to make it easier to visualize, imagine the surface of a trampoline. If there is nothing on it, it is flat. But if you stand on the trampoline, it stretches around your feet and creates a valley with you at the center. If there is a ball on the trampoline, it would roll toward your feet.
This is a two-dimensional example of how spacetime works. Your mass stretched the trampoline, creating what is called a gravity well that the ball rolls into. This is very similar to how the gravity of a heavy object – like the Earth – pulls things like you and me toward it.
To make things even weirder, since space and time are connected, time is also stretched by heavy objects[10]!
In the movie ‘Interstellar,’ the characters go to a planet close to a black hole, and while they are there, they age slower than everyone else.The heavier you are, the steeper the sides of the trampoline well. That is why really massive things in the universe – like the Sun or black holes – have stronger gravity than Earth.
So why does gravity pull you down and not push you away?
Imagine someone went under the trampoline and pushed up. The ball would roll away! This would be a gravity hill, not a gravity well. As far as scientists know, matter – or stuff – always makes gravity wells and not gravity hills. Scientists can imagine things made of exotic matter or energy that would cause gravity to push you off into space, but so far, no one has found anything that could cause gravity to push you away from Earth.
Hello, curious kids! Do you have a question you’d like an expert to answer? Ask an adult to send your question to CuriousKidsUS@theconversation.com[11]. Please tell us your name, age and the city where you live.
And since curiosity has no age limit – adults, let us know what you’re wondering, too. We won’t be able to answer every question, but we will do our best.
Gravity works similarly to how objects will roll toward your feet if you stand on a trampoline.
MoMo Productions/Stone via Getty Images[9]
Since your brain usually thinks about the world in three dimensions, it is really hard to think about the four dimensions of spacetime as a single idea. So to make it easier to visualize, imagine the surface of a trampoline. If there is nothing on it, it is flat. But if you stand on the trampoline, it stretches around your feet and creates a valley with you at the center. If there is a ball on the trampoline, it would roll toward your feet.
This is a two-dimensional example of how spacetime works. Your mass stretched the trampoline, creating what is called a gravity well that the ball rolls into. This is very similar to how the gravity of a heavy object – like the Earth – pulls things like you and me toward it.
To make things even weirder, since space and time are connected, time is also stretched by heavy objects[10]!
In the movie ‘Interstellar,’ the characters go to a planet close to a black hole, and while they are there, they age slower than everyone else.The heavier you are, the steeper the sides of the trampoline well. That is why really massive things in the universe – like the Sun or black holes – have stronger gravity than Earth.
So why does gravity pull you down and not push you away?
Imagine someone went under the trampoline and pushed up. The ball would roll away! This would be a gravity hill, not a gravity well. As far as scientists know, matter – or stuff – always makes gravity wells and not gravity hills. Scientists can imagine things made of exotic matter or energy that would cause gravity to push you off into space, but so far, no one has found anything that could cause gravity to push you away from Earth.
Hello, curious kids! Do you have a question you’d like an expert to answer? Ask an adult to send your question to CuriousKidsUS@theconversation.com[11]. Please tell us your name, age and the city where you live.
And since curiosity has no age limit – adults, let us know what you’re wondering, too. We won’t be able to answer every question, but we will do our best.
References
- ^ Curious Kids (theconversation.com)
- ^ curiouskidsus@theconversation.com (theconversation.com)
- ^ theory of general relativity (www.space.com)
- ^ called spacetime (www.livescience.com)
- ^ space and time are merged together (einstein.stanford.edu)
- ^ age a tiny bit more slowly than people on Earth (www.space.com)
- ^ Tokamak/WikimediaCommons (commons.wikimedia.org)
- ^ CC BY-SA (creativecommons.org)
- ^ MoMo Productions/Stone via Getty Images (www.gettyimages.com)
- ^ time is also stretched by heavy objects (en.wikipedia.org)
- ^ CuriousKidsUS@theconversation.com (theconversation.com)
Read more https://theconversation.com/why-does-gravity-pull-us-down-and-not-up-162141
















