California is planning floating wind farms offshore to boost its power supply – here's how they work
- Written by Matthew Lackner, Professor of Mechanical Engineering, University of Massachusetts Amherst
Northern California has some of the strongest offshore winds in the U.S., with immense potential to produce clean energy[1]. But it has a problem. Its continental shelf drops off quickly, making building traditional wind turbines directly on the seafloor costly if not impossible.
Once water gets more than about 200 feet deep – roughly the height of an 18-story building – these “monopile” structures are pretty much out of the question.
A solution has emerged that’s being tested in several locations around the world: making wind turbines that float. In fact, in California, where drought is putting pressure[2] on the hydropower supply and fires have threatened[3] electricity imports from the Pacific Northwest, the state is moving forward on plans[4] to develop the nation’s first floating offshore wind farms as we speak.
So how do they work?
Three main ways to float a turbine
A floating wind turbine works just like other wind turbines[5] – wind pushes on the blades, causing the rotor to turn, which drives a generator that creates electricity. But instead of having its tower embedded directly into the ground or the sea floor, a floating wind turbine sits on a platform with mooring lines, such as chains or ropes, that connect to anchors in the seabed below.
These mooring lines hold the turbine in place against the wind and keep it connected to the cable that sends its electricity back to shore.
Most of the stability is provided by the floating platform itself. The trick is to design the platform so the turbine doesn’t tip too far in strong winds or storms.
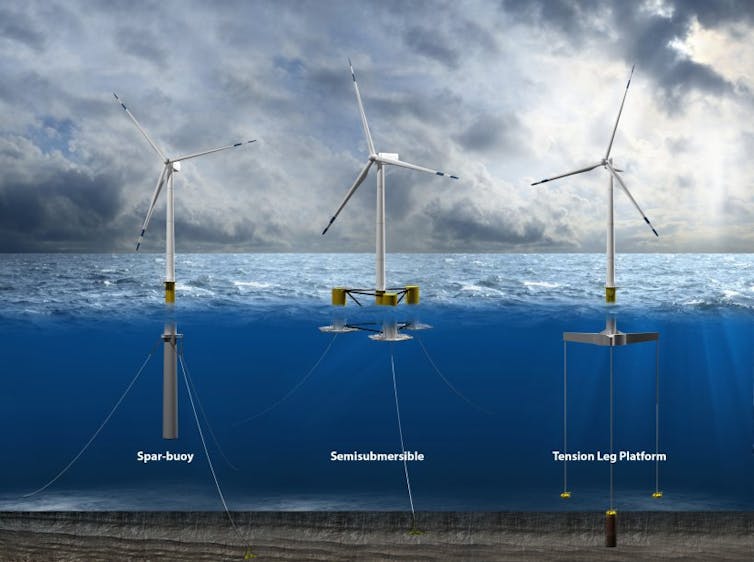 Three of the common types of floating wind turbine platform.
Josh Bauer/NREL[6]
Three of the common types of floating wind turbine platform.
Josh Bauer/NREL[6]
There are three main types of platforms:
A spar buoy platform is a long hollow cylinder that extends downwards from the turbine tower. It floats vertically in deep water, weighted with ballast in the bottom of the cylinder to lower its center of gravity. It’s then anchored in place, but with slack lines that allow it to move with the water to avoid damage. Spar buoys have been used by the oil and gas industry[7] for years for offshore operations.
Semi-submersible platforms have large floating hulls that spread out from the tower, also anchored to prevent drifting. Designers have been experimenting with multiple turbines[8] on some of these hulls.
Tension leg platforms have smaller platforms with taut lines running straight to the floor below. These are lighter but more vulnerable[9] to earthquakes or tsunamis because they rely more on the mooring lines and anchors for stability.
Each platform must support the weight of the turbine and remain stable while the turbine operates. It can do this in part because the hollow platform, often made of large steel or concrete structures, provides buoyancy to support the turbine. Since some can be fully assembled in port and towed out for installation, they might be far cheaper[10] than fixed-bottom structures, which requires specialty boats[11] for installation on site.
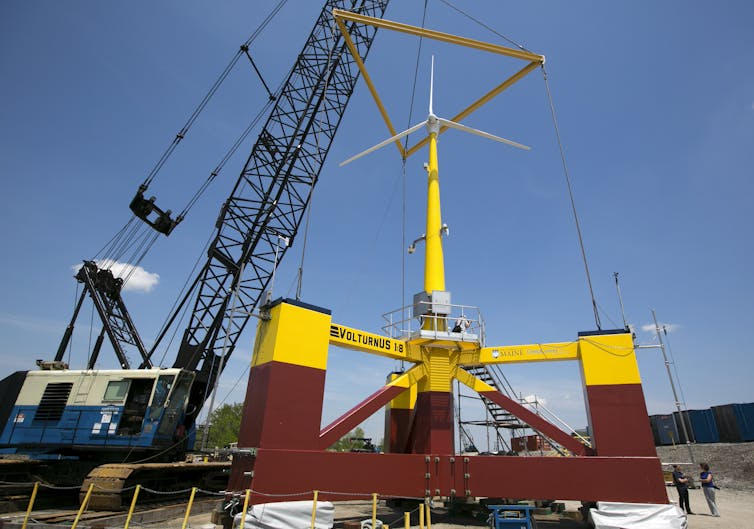 The University of Maine has been experimenting with a small floating wind turbine, about one-eighth scale, on a semi-submersible platform. It plans to launch a full-scale version with corporate partners in 2023.
AP Photo/Robert F. Bukaty[12]
The University of Maine has been experimenting with a small floating wind turbine, about one-eighth scale, on a semi-submersible platform. It plans to launch a full-scale version with corporate partners in 2023.
AP Photo/Robert F. Bukaty[12]
Floating platforms can support wind turbines that can produce 10 megawatts or more of power – that’s similar in size to other offshore wind turbines[13] and several times larger than the capacity of a typical onshore wind turbine you might see in a field.
Why do we need floating turbines?
Some of the strongest wind resources[14] are away from shore in locations with hundreds of feet of water below, such as off the U.S. West Coast, the Great Lakes, the Mediterranean Sea, and the coast of Japan.
In May 2021, Interior Secretary Deb Haaland and California Gov. Gavin Newsom announced plans to open up parts of the West Coast[15], off central California’s Morro Bay and near the Oregon state line, for offshore wind power. The water there gets deep quickly, so any wind farm that is even a few miles from shore will require floating turbines. Newsom said the area could initially provide 4.6 gigawatts of clean energy, enough to power 1.6 million homes. That’s more than 100 times the total U.S. offshore wind power today[16].
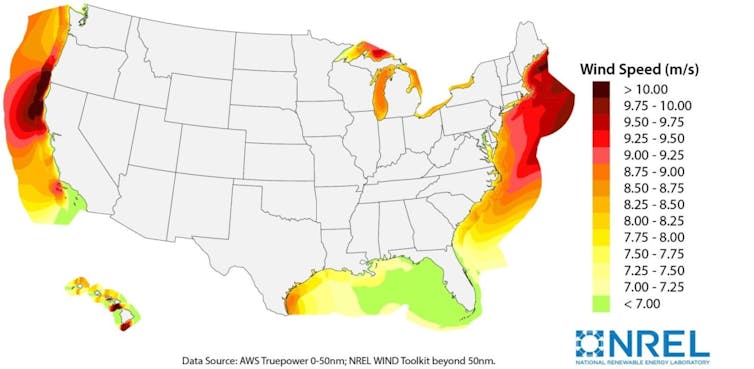 Some of the strongest offshore wind power potential in the U.S. is in areas where the water is too deep for fixed turbines, including off the West Coast and offshore from Maine.
NREL[17]
Some of the strongest offshore wind power potential in the U.S. is in areas where the water is too deep for fixed turbines, including off the West Coast and offshore from Maine.
NREL[17]
Globally, several full-scale demonstration projects are already operating in Europe and Asia. The Hywind Scotland project[18] became the first commercial-scale offshore floating wind farm in 2017, with five 6-megawatt turbines supported by spar buoys designed by the Norwegian energy company Equinor.
While floating offshore wind farms are becoming a commercial technology, there are still technical challenges that need to be solved. The platform motion may cause higher forces on the blades and tower, and more complicated and unsteady aerodynamics. Also, as water depths get very deep, the cost of the mooring lines, anchors, and electrical cabling may becomes very high, so cheaper but still reliable technologies will be needed.
Expect to see more offshore turbines supported by floating structures in the near future.
References
- ^ immense potential to produce clean energy (www.energy.gov)
- ^ drought is putting pressure (www.bloomberg.com)
- ^ fires have threatened (abc7.com)
- ^ moving forward on plans (www.gov.ca.gov)
- ^ works just like other wind turbines (www.energy.gov)
- ^ Josh Bauer/NREL (www.nrel.gov)
- ^ used by the oil and gas industry (www.rigzone.com)
- ^ experimenting with multiple turbines (www.maritime-executive.com)
- ^ lighter but more vulnerable (www.osti.gov)
- ^ far cheaper (www.osti.gov)
- ^ requires specialty boats (theconversation.com)
- ^ AP Photo/Robert F. Bukaty (newsroom.ap.org)
- ^ similar in size to other offshore wind turbines (doi.org)
- ^ strongest wind resources (www.energy.gov)
- ^ announced plans to open up parts of the West Coast (www.gov.ca.gov)
- ^ total U.S. offshore wind power today (us.orsted.com)
- ^ NREL (www.energy.gov)
- ^ Hywind Scotland project (us.orsted.com)

















