Third-largest diamond found in June, then a bigger one days later. What's behind the monster gem boom?
- Written by Jodie Bradby, Professor of Physics, Australian National University
A mega diamond of a staggering 1,174 carats was recently recovered[1] from the Karowe mine in Botswana, making it one of the largest natural diamonds ever recovered.
More remarkably, the stone was found alongside several other similar diamonds weighing 471, 218 and 159 carats[2] — suggesting the original diamond could have had a weight of more than 2,000 carats when it first formed.
The latest discovery is hot on the heels of another mega diamond[3] of more than 1,000 carats which was recovered from the Jwaneng mine, also in Botswana, only a few weeks ago.
Why are we seeing a sudden rush in the recovery of these mammoth gems?
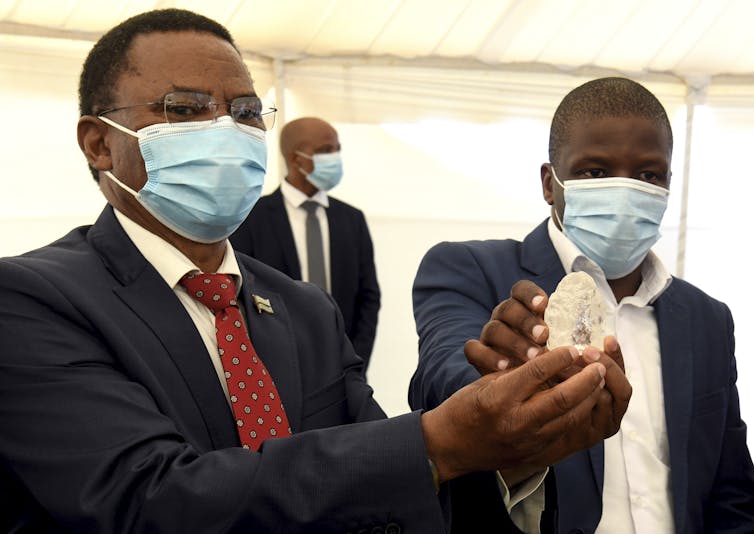 Botswana Vice President Slumber Tsogwane, on the left, holds the 1098 carat diamond unearthed in Botswana in June. This one has now been replaced by a larger one.
EPA
Botswana Vice President Slumber Tsogwane, on the left, holds the 1098 carat diamond unearthed in Botswana in June. This one has now been replaced by a larger one.
EPA
Are diamonds really ‘rare’ as they’re said to be?
In 2020, global diamond production amounted to 111 million carats[4] or just over 20 tonnes of diamond. However, a small proportion of this production is of high-quality gemstones. The vast majority of diamonds are small, at less than one carat.
Australia’s Argyle mine, famous for its pink diamonds (and once the world’s largest diamond mine by volume) ceased its operations late last year since it was no longer economically viable[5]. This is because most of the diamonds extracted were small, and therefore only useful for industrial applications.
These small diamonds are so common that a diamond-tipped scribe tool[6] can be purchased for less than the price of a tank of petrol.
Large gemstone-quality diamonds, on the other hand, are extremely rare. To understand why, we need to look at how diamonds are formed, as well as how they are mined.
Read more: We created diamonds in mere minutes, without heat — by mimicking the force of an asteroid collision[7]
How are natural diamonds formed?
Natural diamonds are billions of years old. They’re formed deep in the Earth where temperatures and pressures are high enough to squash carbon atoms into a dense, crystalline structure.
Some scientists have suggested[8] there are vast quantities of diamonds hundreds of kilometres deep. But as the deepest hole ever drilled is about 12km[9], we will never be able to mine these deep-earth diamonds.
So we have to make do with the relatively tiny fraction that make it to the surface. Diamonds near the ground’s surface are typically thought to have hitched a ride via a deep-source volcanic eruption.
These violent events need to be fast enough to deliver the diamonds to the surface and, at the same time, the diamonds can’t be exposed to extreme heat, shock or oxygen. It’s a narrow Goldilocks scenario.
Most diamonds are found within igneous rocks called Kimberlite. Kimberlite “pipes” are carrot-shaped columns of rock, often just tens of metres across, at the very top of deep-source volcanoes.
But only a small percentage of all known Kimberlite deposits contain diamonds. And only a handful of these are rich enough with diamonds to warrant being mined.
The ideal conditions are very difficult to find[10]. Only particular regions of a continent can host diamonds as the crust has to be thick enough to have hosted a deep volcanic event. It also needs to be stable and ancient — characteristics which are common in parts of Australia and Africa.
Moreover, despite its reputation for being indestructible, diamond is a brittle material. This is a property that must be taken into account when polishing diamonds into gems. At regular atmospheric pressures, diamond is not even the most stable arrangement[11] of carbon atoms.
A crushing task
Large natural diamonds that manage to survive the tortuous path to the surface often get destroyed by the very process of us finding them. In most diamond mines, ore is blasted with explosives and then crushed into fragments to search for diamonds.
But new technologies are allowing mines to process ore with the aid of X-ray ore-sorting technology. This is specifically targeted for “mega diamond recovery”.
Although the diamond world is notoriously secretive about specifics, we do know the latest diamond from the Karowe mine was recovered using these newer techniques[12]. And it’s likely more of these mega stones will be discovered in the future.
Advances in diamond mining techniques, coupled with the inherent rarity of mega diamonds, is a boon for Botswana, where diamonds constitute a significant portion of the country’s GDP.
Diamonds in the lab
Diamonds are getting bigger in the laboratory too. For decades, artificial diamonds were manufactured using high-pressure equipment that mimics the extreme physical conditions deep in the earth.
Now, new technology employing low-pressure conditions and carefully controlled chemistry can make perfect diamond discs as large as a dinner plate.
This chemical approach is being used commercially to manufacture gem-quality stones for jewellery. But making diamonds in this way requires patience. To grow one millimetre of diamond takes the best part of a day[13], meaning mining will likely play a key role in the diamond industry for some time.
Read more: More than just a sparkling gem: what you didn't know about diamonds[14]
References
- ^ recovered (lucaradiamond.com)
- ^ 471, 218 and 159 carats (twitter.com)
- ^ another mega diamond (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ 111 million carats (www.bain.com)
- ^ late last year since it was no longer economically viable (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ diamond-tipped scribe tool (www.tdiinternational.com)
- ^ We created diamonds in mere minutes, without heat — by mimicking the force of an asteroid collision (theconversation.com)
- ^ Some scientists have suggested (agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- ^ deepest hole ever drilled is about 12km (www.bbc.com)
- ^ difficult to find (physicsworld.com)
- ^ the most stable arrangement (www.nationalgeographic.org)
- ^ techniques (lucaradiamond.com)
- ^ the best part of a day (www.sciencedirect.com)
- ^ More than just a sparkling gem: what you didn't know about diamonds (theconversation.com)

















