Novavax is absent from Australia's 2021 vaccination schedule. But it could be a useful booster later on
- Written by Cassandra Berry, Professor of Viral Immunology, Murdoch University
Novavax recently released excellent results from phase 3 clinical trials, finding its COVID-19 vaccine demonstrated 90.4% efficacy[1] overall after two doses given three weeks apart.
The results, from close to 30,000 people in the United States and Mexico, found the vaccine demonstrated 100% protection against moderate and severe COVID-19, and was highly protective against circulating variants of interest and concern. It also has a good safety profile.
It’s important to note these results came directly from Novavax in a press release, and we’re still waiting to see the data published in a peer-reviewed journal. Once this happens, it’s likely Novavax will apply for approval from medical regulators around the world.
But this process will take a few months. The Therapeutic Goods Administration[2] has said it doesn’t expect to receive the final data it needs to approve the vaccine until September. And in the COVID Vaccination Allocation Horizons[3], information the government released this week setting out vaccine allocation until the end of 2021, Novavax is not mentioned.
So by the time Australia is ready to deliver Novavax — the country has 51 million doses on order[4] — we may well have completed most of the vaccine rollout with the AstraZeneca, Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. The situation will be similar in other countries, such as the United States.
However, that doesn’t mean Novavax won’t play an important role in Australia’s fight against COVID-19.
How does Novavax work?
Novavax is designed using protein-based technology[5]. This is different[6] from the AstraZeneca vaccine, which is a viral vector vaccine, and Pfizer and Moderna, which use mRNA technology.
Novavax works by introducing a part of the SARS-CoV-2 virus — the spike protein — to the immune system. The spike protein used is made in insect cells and doesn’t contain any live components of the virus. It can’t replicate or cause COVID-19.
To help the vaccine generate a stronger protective response, it uses an adjuvant, which is a molecule that boosts the immune system. The adjuvant Novavax uses is based on saponin, a natural extract from the Chilean soapbark tree.
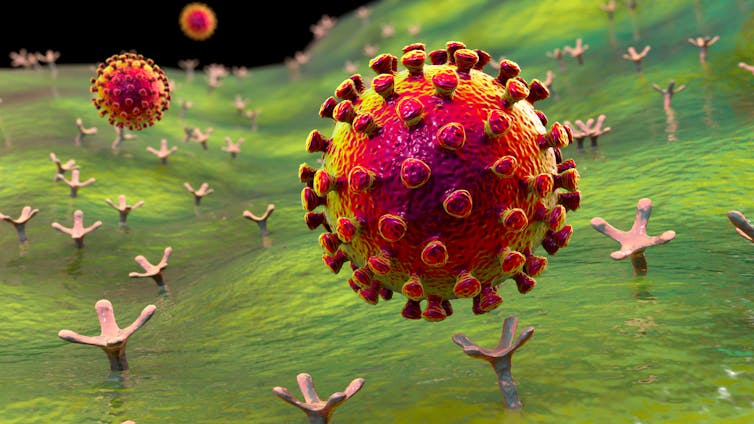 COVID-19 vaccines work by targeting the spike protein, a protein on the surface of SARS-CoV-2.
Shutterstock[7]
COVID-19 vaccines work by targeting the spike protein, a protein on the surface of SARS-CoV-2.
Shutterstock[7]
In some countries, Novavax could be used as an initial COVID vaccine. It will be relatively easy to distribute because it can be stored at regular fridge temperatures[8].
In other countries where most people will have already received two vaccine doses by the time Novavax becomes available, the vaccine could be used as an annual booster — on its own or as a supplement in formulated vaccines.
Read more: What is Novavax, Australia's third COVID vaccine option? And when will we get it?[9]
A potential booster
Let’s say you’re writing a book. You write your first draft — that’s the first dose of vaccine. Then you edit and refine the final draft — that’s the second dose. You could say annual booster vaccines are like updated editions. Perhaps the original book is also translated into different languages, just as boosters could cover viral variants around the world.
In slightly more scientific terms, after the first vaccine dose, certain cells in our immune system (normal B cells) are activated and produce a primary antibody response. After the second vaccine dose, a slightly different flavour of immune cells (memory B cells) mount a stronger antibody response more rapidly.
But this immune memory[10] can wane over time. Boosters may be needed to enhance immune memory responses to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in people who have previously been vaccinated against COVID-19.
Boosters could also be important as new variants emerge. Vaccines can often be reformulated to protect against new viral variants when original formulations aren’t working as well.
So even if Novavax isn’t the first or second COVID vaccine in our arms, it could be an important tool in our arsenal as we continue to navigate the pandemic.
 Novavax could potentially be used as a booster vaccine down the track.
Shutterstock[11]
Novavax could potentially be used as a booster vaccine down the track.
Shutterstock[11]
What about in combination with the flu shot?
Novavax has recently revealed[12] the efficacy of its COVID vaccine was roughly the same in a study where an influenza vaccine was administered simultaneously. This data, although yet to be peer-reviewed[13], signals Novavax could potentially be given alongside the annual flu shot.
In the future, we could even have the flu shot and Novavax combined in one vaccine[14]. Novavax has designed and is currently testing[15] a vaccine which combines SARS-CoV-2 and influenza spike proteins (called a multivalent vaccine).
Read more: Can I get AstraZeneca now and Pfizer later? Why mixing and matching COVID vaccines could help solve many rollout problems[16]
SARS-CoV-2 is rapidly evolving and we need to future-proof Australia against viral variants[17]. As our knowledge of COVID-19 builds, we must develop strategies for more robust protection.
Rather than a fast sprint, our immune systems likely need to be primed for an ultra-marathon. Thinking about vaccines beyond the “first wave” of vaccination will be key.
References
- ^ 90.4% efficacy (ir.novavax.com)
- ^ Therapeutic Goods Administration (www.smh.com.au)
- ^ COVID Vaccination Allocation Horizons (www.health.gov.au)
- ^ 51 million doses on order (www.smh.com.au)
- ^ protein-based technology (www.niaid.nih.gov)
- ^ is different (www.nature.com)
- ^ Shutterstock (www.shutterstock.com)
- ^ regular fridge temperatures (cdn.filestackcontent.com)
- ^ What is Novavax, Australia's third COVID vaccine option? And when will we get it? (theconversation.com)
- ^ immune memory (pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- ^ Shutterstock (www.shutterstock.com)
- ^ recently revealed (ir.novavax.com)
- ^ peer-reviewed (www.medrxiv.org)
- ^ combined in one vaccine (ir.novavax.com)
- ^ is currently testing (www.reuters.com)
- ^ Can I get AstraZeneca now and Pfizer later? Why mixing and matching COVID vaccines could help solve many rollout problems (theconversation.com)
- ^ viral variants (www.nature.com)

















