How a virtual placenta could help with early detection of at-risk babies
- Written by Alys Clark, Associate Professor in Bioengineering, University of Auckland

None of us would be here without our placenta, the remarkable fetal organ that nourished and sustained us before birth. But despite its importance, the placenta is among the least studied organs and we don’t fully understand how it grows and functions.
This is problematic, because in one in ten pregnancies, the placenta functions poorly, leading to pregnancy disorders[1] such as fetal growth restriction (FGR[2]), when a baby’s growth slows dramatically or stops. Across Australia[3] and New Zealand[4], this affects more than 30,000 pregnancies each year, and growth-restricted babies are four times more likely to be stillborn.
Modern ultrasound imaging tools and new technologies such as fetal DNA testing in maternal blood cannot yet predict which pregnancies are at risk of fetal growth restriction until after the baby’s growth slows down.
To help improve early detection and prediction of at-risk pregnancies, we have developed a virtual placenta – a computer-based representation of the organ – by piecing together a wide range of clinical and laboratory data from pregnancies that go well and those that don’t.
The placenta has several functions. It delivers nutrients and oxygen from the mother’s blood to the baby, removes wastes from the baby back to mum, and produces important hormones that adapt mum’s body to pregnancy. Māori have always understood its value, referring to the placenta as the whenua, which nourishes the baby as the whenua (land) nourishes the people.
Read more: How does a baby 'breathe' while inside its mom?[5]
We know there are some important factors, including smoking[6], that can affect a baby’s growth. But pregnancy disorders can occur in healthy women with no risk factors, and in a culture where mothers are often quick to blame themselves, it’s important for women to know that growth restriction hardly ever occurs because of something they did or did not do.
The most common way to estimate fetal growth is by a tape measure on mum’s stomach, but the technique is only 10% sensitive, and even less so in patients who carry more body fat. More than half of the babies struggling to grow well are not detected before delivery.
Virtual organs to detect health issues
We need to do better at detecting fetal growth issues. The earlier doctors know these babies are at risk, the better. While treatment options are currently limited, doctors can monitor the pregnancy more closely and make informed decisions about when to deliver.
This is not straightforward, as both the mother’s and baby’s physiology can change quickly in pregnancy, and we can’t ask pregnant mothers to have more tests, or ultrasounds, or to undergo procedures that might put the pregnancy at risk (like using radiation in a CT scan).
The virtual placenta allows us to look more closely at pregnancy without adding to the burden of tests an expectant mother needs to undergo, and without costing the healthcare system an excessive amount.
Read more: Research now backs routinely offering pregnant women the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine[7]
Virtual organs, or indeed virtual humans, are not a new concept[8]. For several decades scientists have been combining anatomical knowledge with the principles of physics to predict how changes in anatomy affect organ function. An example includes how changes in blood vessels affect how hard a heart has to pump to circulate blood around the body.
Simple virtual pregnancy models have guided interpretation of ultrasound[9] since the start of routine use in pregnancy in the 1980s.
Virtual clinical trials are also emerging where it is possible to experiment on a computer-based organ to predict outcomes before new treatments are trialled on real people. This reduces animal testing and the cost of clinical trials.
Earlier detection of problems
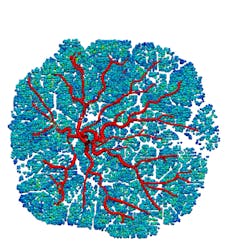 An illustration of a virtual placenta, with large arteries branching like a tree to deliver fetal blood to the site of exchange. Author provided
An illustration of a virtual placenta, with large arteries branching like a tree to deliver fetal blood to the site of exchange. Author provided
The placenta is like a dense forest of trees. The baby’s own blood vessels are inside the branches of these trees, while blood from mum’s uterus flows around the outside. How blood flows in both these circulations is critical for good exchange.
Only recently has technology allowed virtual placentas to include the detail of this blood flow and exchange[10], which can’t be measured directly. This is allowing scientists to make strides towards understanding how features of placentas that restrict a baby’s growth show up in imaging like ultrasound or MRI.
Finding cost-effective ways to predict and detect fetal growth restriction will go a long way to helping our smallest babies. Predicting which pregnancies are at risk in early pregnancy is especially important, as this is when the placenta is growing rapidly, and therapies delivered in early pregnancy are more likely to bolster placental function. For example, simple and safe therapies such as aspirin are effective at reducing fetal growth restriction, but only if started before 16 weeks of pregnancy.
As we cannot predict FGR in early pregnancy, much of what we know about restricted growth in utero comes from studies in late pregnancy, and assessment of placentas after delivery. Applying our anatomical understanding of earlier stages of placental development allows us to virtually “turn back the clock” and consider early contributors to poor placental function, and how we can measure these by ultrasound.
We hope to use this knowledge to develop new ways to predict at-risk pregnancies, so we can help prevent growth issues, and give all babies a better start to life.
References
- ^ pregnancy disorders (pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- ^ FGR (www.tommys.org)
- ^ Australia (www.aihw.gov.au)
- ^ New Zealand (www.hqsc.govt.nz)
- ^ How does a baby 'breathe' while inside its mom? (theconversation.com)
- ^ smoking (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- ^ Research now backs routinely offering pregnant women the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (theconversation.com)
- ^ not a new concept (physiomeproject.org)
- ^ interpretation of ultrasound (www.sciencedirect.com)
- ^ detail of this blood flow and exchange (wires.onlinelibrary.wiley.com)

















