A quantum hack for microscopes can reveal the undiscovered details of life
- Written by Warwick Bowen, Professor of Quantum and Precision Technologies, The University of Queensland
You’ve probably seen images of scientists peering down a microscope, looking at objects invisible to the naked eye. Indeed, microscopes are indispensable to our understanding of life.
They are just as indispensable to biotechnology and medicine, for instance in our response to diseases such as COVID-19[1]. However, the best light microscopes have hit a fundamental barrier – the bright laser light used to illuminate tiny objects can also destroy them.
In research published in Nature today[2], our team of Australian and German researchers has shown that quantum technologies offer a solution. We built a quantum microscope that can more gently probe biological samples, which allowed us to observe biological structures that would otherwise be impossible to see.
Creating a damage-evading microscope like ours is a long-awaited milestone on international quantum technology roadmaps[3]. It represents a first step into an exciting new era for microscopy, and for sensing technologies more broadly.
The problem with laser microscopes
Microscopes have a long history. They are thought to have been first invented by the Dutch lens-maker Zacharias Janssen[4] around the turn of the seventeenth century. He may have used them to counterfeit coins. This chequered beginning led to the discovery of bacteria, cells and basically all microbiology as we now understand it.
The more recent invention of lasers provided an intense new kind of light. This made a whole new approach to microscopy possible. Laser microscopes allow us to see biology with truly exquisite detail, 10,000 times smaller than the thickness of a human hair. They were awarded the 2014 Nobel Prize in Chemistry[5], and have transformed our understanding of cells and of molecules like DNA within them.
However, laser microscopes face a major problem. The very quality that makes them successful – their intensity – is also their Achilles’ heel. The best laser microscopes use light billions of times brighter than sunlight on Earth. As you might imagine, this could cause serious sunburn!
In a laser microscope, biological samples can become sick or perish in seconds. You can see this happening in real time in the movie of a fibroblast cell below, taken by our team member Michael Taylor.
A cell getting uncomfortable and then dying under a laser microscope.Spooky action at a distance provide the solution
Our microscope evades this problem. It uses a property called quantum entanglement, which Albert Einstein described as “spooky action at a distance”.
 Our microscope uses pairs of ‘quantum correlated’ photons to achieve clarity that would be impossible with regular light sources.
Aleksandr Kakinen
Our microscope uses pairs of ‘quantum correlated’ photons to achieve clarity that would be impossible with regular light sources.
Aleksandr Kakinen
Entanglement is an unusual sort of correlation between particles, in our case between the photons that make up a laser beam. We use it to train the photons that leave the microscope to behave themselves, arriving at a detector in a very orderly fashion. This reduces noise.
Other microscopes need to increase the laser intensity to improve the clarity of images. By reducing noise, ours is able to improve the clarity without doing this. Alternatively, we can use a less intense laser to produce the same microscope performance.
Read more: Experiment shows Einstein's quantum 'spooky action' approaches the human scale[6]
A key challenge was to produce quantum entanglement that was bright enough for a laser microscope. We did this by concentrating the photons into laser pulses that were only a few billionths of a second long. This produced entanglement that was 1,000 billion times brighter than has previously been used in imaging.
When used in a microscope, our entangled laser light provided 35% better image clarity than was otherwise possible without destroying the sample. We used the microscope to image the vibrations of molecules within a living cell. This allowed us to see detailed structure that would have been invisible using traditional approaches.
The improvement can be seen in the images below. These images, taken with our microscope, show molecular vibrations within a portion of a yeast cell. The left image uses quantum entanglement, while the right image uses conventional laser light. As I hope you agree, the quantum image is clearer, with regions where fats are stored within the cell (the dark blobs) and the cell wall (the semi-circular structure) both more visible.
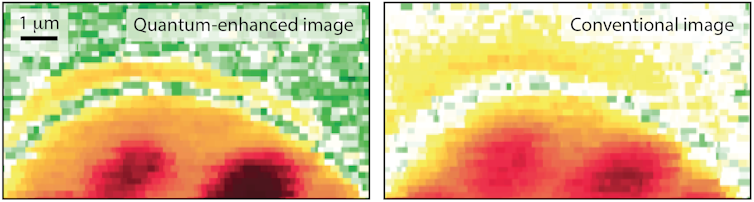 Example of quantum enhancement possible with our microscope.
Warwick Bowen
Example of quantum enhancement possible with our microscope.
Warwick Bowen
Towards applications of quantum sensing technologies
Quantum technologies are expected to have revolutionary applications in computing, communications and sensing. Australia’s Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) estimates[7] they will create an A$86 billion dollar global industry by 2040.
Quantum entanglement underpins many of these applications. A key challenge for quantum technology researchers is to show that it offers absolute advantages over current methods.
Entanglement is already used[8] by financial institutions and government agencies to communicate with guaranteed security. It is also at the heart of quantum computers, which Google[9] showed in 2019 can perform calculations that would be impossible with current conventional computers.
Quantum sensors are the last piece of this puzzle. They are predicted to improve pretty much every aspect of how we see the world, from better navigation to better health care and medical diagnostics.
About a year ago quantum entanglement was installed in kilometre-scale gravitational wave observatories[10]. This allows scientists to detect massive objects further away in space.
Our work shows that entanglement can provide an absolute sensing advantage at more normal size scales and in widespread technologies. This could have big ramifications – not only for microscopy, but also for many other applications such as global positioning[11], radar and navigation[12].
Read more: The 'second quantum revolution' is almost here. We need to make sure it benefits the many, not the few[13]
References
- ^ COVID-19 (micro.org.au)
- ^ published in Nature today (www.nature.com)
- ^ international quantum technology roadmaps (uknqt.ukri.org)
- ^ Zacharias Janssen (en.wikipedia.org)
- ^ 2014 Nobel Prize in Chemistry (www.nobelprize.org)
- ^ Experiment shows Einstein's quantum 'spooky action' approaches the human scale (theconversation.com)
- ^ estimates (www.csiro.au)
- ^ used (www.forbes.com)
- ^ Google (www.nature.com)
- ^ kilometre-scale gravitational wave observatories (arstechnica.com)
- ^ global positioning (phys.org)
- ^ radar and navigation (www.imperial.ac.uk)
- ^ The 'second quantum revolution' is almost here. We need to make sure it benefits the many, not the few (theconversation.com)

















