Where did the ingredients in that sandwich come from? Our global nutrient tracker tells a complex story
- Written by Nick William Smith, Research Officer, Riddet Institute, Massey University
Have you ever looked down at your breakfast, lunch or dinner and considered where the various ingredients travelled from to reach your plate?
A basic sandwich in New Zealand can easily represent five countries: an Australian wheat and Indian sesame seed roll, Danish salami, local lettuce and cheese, seasoned with Vietnamese pepper.
And because your food travels a long way to reach you, so does your nutrition.
Research on global food trade – particularly trade in cereals – has a long history. More recently, researchers have begun considering the nutrients – energy, protein, vitamins, minerals – that move around the world within traded food.
As we learn more about the global trade in nutrients we can build a better picture of how these key dietary ingredients are distributed, and how they affect global population health.
Read more: Five ways to reboot the global food economy to make it healthier for all[1]
Mapping global nutrient trade
The Sustainable Nutrition Initiative[2] undertakes modelling research on the links between global food production and the nutrition of the global population.
Working with researchers at the University of São Paulo and State University of Campinas in Brazil, we have now published a broader analysis[3] of global nutrient trade over time and its impact on health.
It shows the variation in nutrient trade between countries with differing wealth, and some positive links between nutrient trade and health.
Read more: What does a healthy diet look like for me and the planet? It depends where you live[4]
Our team built a large data set of all flows of food for human consumption between 254 countries from 1986 to 2020. From this, we worked out the flows of 48 essential nutrients over that period.
As this is too much information for a single scientific paper, the team built an interactive app[5] to let anyone explore the data.
The paper itself focused on a few key nutrients: protein, calcium, iron and vitamins A and B12. These are often used in analyses of food security (having reliable access to enough affordable, nutritious food) because of their importance to human health.
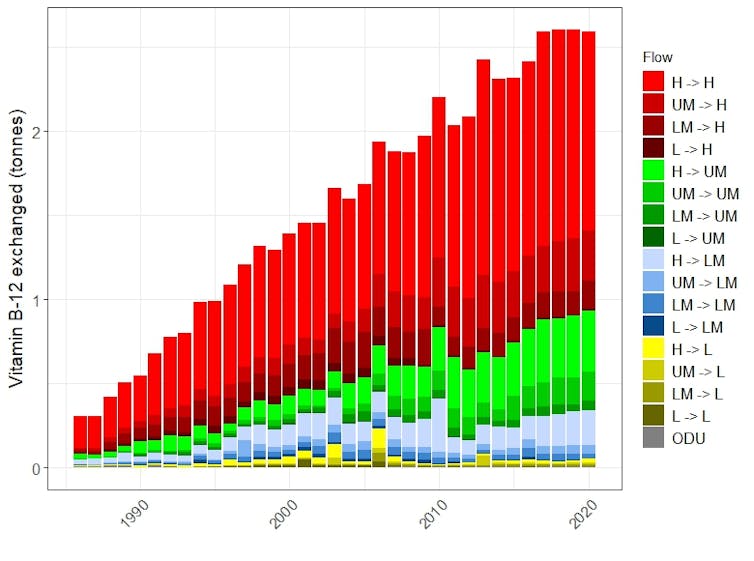
Some of these nutrients are under-supplied in many parts of the world, particularly low-income countries. At the same time, nutrient trade over the 35 years we analysed has grown rapidly, as shown in the chart below for vitamin B12.
The wealth and nutrient gap
High-income countries were the biggest importers of vitamin B12, but also the other nutrients analysed, largely from trade with other high-income countries. This is despite those countries having only around 15% of the global population.
In contrast, low-income countries have little involvement in global trade of any nutrients. This limits their ability to improve dietary diversity and quality through food from outside their borders.
Most of New Zealand’s trading partners are in the higher-income brackets. Milk and meat dominate New Zealand protein exports, with China the major partner (see chart below).
The quantity of protein exported would meet the needs of nearly seven times New Zealand’s own population. In a country like China, of course, this is only a small fraction of the population.
In contrast, nearly 60% of New Zealand’s protein imports comes from Australia, largely in wheat and wheat products. And New Zealand imports enough protein to meet around half its population’s need.
We also analysed the socioeconomic, demographic and health outcome data potentially associated with food consumption patterns and nutrient trade.
The findings suggest higher involvement in nutrient trade networks was significantly associated with improvements in infant mortality rates, lower prevalence of anaemia in women of reproductive age, and greater life expectancy.
Read more: Hunger is increasing worldwide but women bear the brunt of food insecurity[8]
Food security and nutrition
It is concerning to see the low involvement of low-income countries in nutrient trade, particularly given the benefits it can bring for population health.
Our research provides context for how important traded nutrients are in meeting national population requirements. This knowledge can be used to identify weaknesses in the global food system, and which shocks (climatic, political or biological) might have the greatest consequences for nutrition.
These data can then be combined with other knowledge and modelling of food production, distribution and consumption at national levels to give a more complete view of food systems.
Food trade plays a key role in fostering food security and good nutrition. The trade has grown rapidly in both quantity and economic value over the past 35 years. Understanding its importance for healthy nutrition is essential.
References
- ^ Five ways to reboot the global food economy to make it healthier for all (theconversation.com)
- ^ Sustainable Nutrition Initiative (sustainablenutritioninitiative.com)
- ^ broader analysis (doi.org)
- ^ What does a healthy diet look like for me and the planet? It depends where you live (theconversation.com)
- ^ interactive app (sustainablenutritioninitiative.com)
- ^ CC BY-SA (creativecommons.org)
- ^ CC BY-SA (creativecommons.org)
- ^ Hunger is increasing worldwide but women bear the brunt of food insecurity (theconversation.com)

















