why it's time to renew Australia's renewable energy policy
- Written by Tim Nelson, Associate Professor of Economics, Griffith University
This article is part of a series by The Conversation, Getting to Zero[1], examining Australia’s energy transition.
If Australia is to meet its commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions[2] to 43% below 2005 levels by 2030, we need to cut emissions faster. Even if all current government policy commitments are achieved – an unlikely outcome given delays in implementation – emissions are still projected to be only 40% below 2005 levels[3] by 2030.
Last year the federal government announced that 82% of all electricity production[4] would come from renewable energy by 2030. This was a crucial step. To have any chance of hitting our overall emission reduction targets, we must speed up the rollout of renewable energy.
Several experts, such as Tony Wood at the Grattan Institute[5] and the Clean Energy Council[6] are calling on governments to consider using the Renewable Energy Target (RET) to accelerate investment in new renewable supply. Why are these experts recommending the RET as a policy option?
Read more: Why Australia urgently needs a climate plan and a Net Zero National Cabinet Committee to implement it[7]
A brief history of renewable energy in Australia
At the turn of the century Australia had almost no wind or solar energy generation. In 2001, the Howard government recognised the potential benefits of renewables and introduced the RET[8]. The target, which was expanded and reformed by the Rudd and Abbott governments, has two elements:
the Large-Scale Renewable Energy Target[9], which requires retailers to buy a set percentage (currently about 15%) of their energy from renewable producers through the purchase of a Large-Scale Generation Certificate
the Small-Scale Renewable Energy Scheme[10], which provides an upfront subsidy to households and small businesses that install their own rooftop solar panels.
Over the past two decades, the RET has been by far the most effective of all Australia’s climate initiatives. It has led to an additional 40 gigawatts (the capacity of around 20 Liddell power stations[11]) of new solar and wind generation. It has lifted Australia’s renewable generation from almost nothing other than hydro (from Hydro Tasmania and Snowy Hydro) in 2000 to nearly 37% of all electricity today[12].
Read more: The human factor: why Australia's net zero transition risks failing unless it is fair[13]
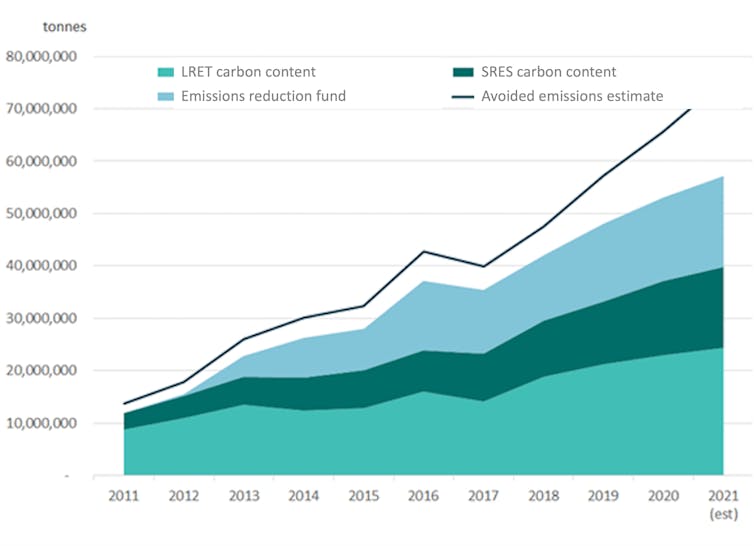
Between 2011 and 2021, the RET accounted for more than half of Australia’s greenhouse gas abatement, delivering by 2021 40 million metric tonnes (Mt) out of about 75 Mt. Over a decade that’s the equivalent of retiring two very large coal-fired power stations each year (see chart below).
The RET succeeded for two reasons. First, its targets extend all the way through to 2030, creating certainty for investors. Second, it created a market that encourages retailers to purchase the lowest-cost large-scale generation certificates. In purchasing a certificate, the retailer pays the difference between the cost of a project and what its generated power earns on the market.
That approach has diversified our renewable energy mix by making it easier to compare different technologies. For example, a wind farm might cost more to build than a solar farm but it can potentially earn more on the market by generating at the right time of day or night. A greater diversity of renewable energy sources means more reliable generation.
Why has the boom in renewables investment stalled?
The bad news is that while investment in small-scale solar photovoltaic continues to grow[15], investment in large-scale renewables has largely stalled[16]. There are two main reasons why.
First, Australia must build more transmission infrastructure. We have great renewable energy resources but we need new transmission lines to take that energy to homes and businesses. Governments have recognised this and are prioritising new Renewable Energy Zones[17], with the Commonwealth providing substantial funding through its Rewiring the Nation[18] package.
But the second reason for the stalled investment is less well known. The target of 33 terrawatt hours[20] under the Large-Scale Renewable Energy Target was largely achieved in 2020[21] and since then has not been increased. The current legislated target is about 15%, well below the government’s commitment to reach 82% by 2030. Why did governments pivot away from the successful RET policy?
In the late 2010s, the Commonwealth government was not interested in increasing renewable energy targets. So state governments keen to act on climate change moved away from using the RET and other market-based policies, instead creating their own policy frameworks, known as Contracts-for-Difference[22].
Under these frameworks, state governments hold reverse auctions and award solar and wind projects a contract for a guaranteed price for their energy for 15–20 years.
Government contracts-for-difference can be a useful tool to assist new technologies, such as offshore wind, to enter the market. But they have significant limitations[23] when they are used to deploy mature technologies such as solar and wind.
Read more: Too hard basket: why climate change is defeating our political system[24]
The most obvious problem is that, in contrast to a market framework such as the Large-Scale Renewable Energy Target, under contracts-for-difference the government becomes the only market for renewable energy. The government assumes the risk of any project, freeing operators from the need to efficiently locate and run their projects. If a project fails, the public pays the cost in higher power prices or taxes.
Moreover, when government is buying the power, it naturally often goes for the cheapest option, thereby usually favouring solar and narrowing our renewable energy mix. And a generator has no incentive to sell its electricity to households and businesses. The result is that investors hold off building new projects, waiting instead to be awarded a contract-for-difference.
This dynamic is stalling investment even as coal generators near the end of their useful lives and the market demand for both energy and firming capacity grows.
Governments working together to get investment flowing
But there is reason to be optimistic. The states and the Commonwealth all now agree on the need to rapidly decarbonise the electricity sector by deploying renewables, transmission and storage. Now the states have the opportunity to work with the Commonwealth to incorporate their different frameworks into a nationally consistent, market-based approach built on the Large-Scale Renewable Energy Target.
The simplest approach, which would create a pivot back to market-based frameworks, would be to legislate to increase that target each year to achieve a linear growth from current renewable energy levels to 82% in 2030.
Under that solution, history suggests[25] investors would rush to capture their share of the target. Investors and energy retailers would work together to find the right mix of technologies to deliver the lowest-cost power to consumers.
A national 82% renewable energy target also ensures that as other sectors use electrification[26] to decarbonise, they will have access to clean energy. Without a target, electrification may lead to use of high-emissions coal power.
Under our proposal, state governments could still pursue their own objectives, such as supporting projects in a particular region, but they could align their policy frameworks with the RET[28] by funding the cost of Large-Scale Generation Certificates rather than entire renewable energy projects.
Read more: The road is long and time is short, but Australia's pace towards net zero is quickening[29]
If the electricity sector does not reach 82% by 2030, other sectors will have to do more to deliver our legislated 43% reduction in emissions by 2030. This is likely to be more costly and unnecessarily increase pressure on our trade-exposed industries, which would be required to reduce emissions more quickly at higher cost.
No Australian emission reduction policy matches the success of the Renewable Energy Target. By working together and aligning their renewable energy policies with the target, Commonwealth and state governments can get Australia’s renewable energy investment back on track, providing us with a reliable, competitive and clean electricity system by 2030 and beyond.
References
- ^ Getting to Zero (theconversation.com)
- ^ commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions (www.dcceew.gov.au)
- ^ projected to be only 40% below 2005 levels (www.dcceew.gov.au)
- ^ 82% of all electricity production (www.energycouncil.com.au)
- ^ Tony Wood at the Grattan Institute (theconversation.com)
- ^ Clean Energy Council (www.cleanenergycouncil.org.au)
- ^ Why Australia urgently needs a climate plan and a Net Zero National Cabinet Committee to implement it (theconversation.com)
- ^ introduced the RET (www.aph.gov.au)
- ^ Large-Scale Renewable Energy Target (www.cleanenergyregulator.gov.au)
- ^ Small-Scale Renewable Energy Scheme (www.cleanenergyregulator.gov.au)
- ^ 20 Liddell power stations (www.agl.com.au)
- ^ 37% of all electricity today (opennem.org.au)
- ^ The human factor: why Australia's net zero transition risks failing unless it is fair (theconversation.com)
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
- ^ small-scale solar photovoltaic continues to grow (www.cleanenergycouncil.org.au)
- ^ large-scale renewables has largely stalled (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ Renewable Energy Zones (aemo.com.au)
- ^ Rewiring the Nation (www.dcceew.gov.au)
- ^ Lukas Coch/AAP (photos.aap.com.au)
- ^ target of 33 terrawatt hours (www.cleanenergyregulator.gov.au)
- ^ largely achieved in 2020 (en.wikipedia.org)
- ^ Contracts-for-Difference (www.energyco.nsw.gov.au)
- ^ significant limitations (ideas.repec.org)
- ^ Too hard basket: why climate change is defeating our political system (theconversation.com)
- ^ history suggests (www.sciencedirect.com)
- ^ sectors use electrification (www.climateworkscentre.org)
- ^ Diego Fedele/AAP (photos.aap.com.au)
- ^ align their policy frameworks with the RET (onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- ^ The road is long and time is short, but Australia's pace towards net zero is quickening (theconversation.com)

















