Anyone can save a life, including kids. Here's why they should learn CPR and basic life support
- Written by Janet Bray, Associate Professor, Monash University
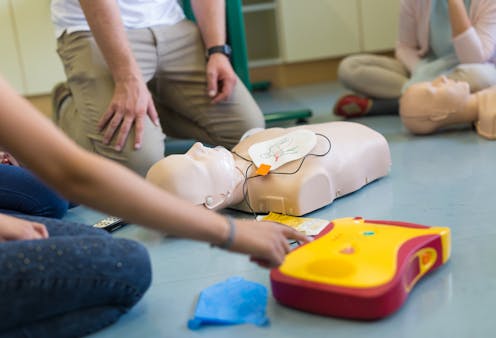
With over 26,000 cardiac arrests[1] occurring every year in Australia and over 76% of them occurring in the home[2], some of our youngest Australians are learning how to help.
But why kids? It’s simple. Anyone can learn to save a life.
Basic life support includes cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and using a portable defibrillator (AED) if required. These emergency procedures aim to save the lives of people in cardiac arrest.
What is a cardiac arrest?
A cardiac arrest[3] occurs when the heart stops beating. This means the heart stops acting like a pump, which stops oxygen getting to the brain. When this happens, the person quickly becomes unconscious and stops breathing. Without immediate CPR, the person is likely to die.
Performing CPR[4] involves pushing down on the chest, which mimics the pumping action of the heart and pushes blood and oxygen around the body and, importantly, to the brain.
An AED[5] works by analysing the person’s heart rhythm and delivering an electric shock, if necessary, to restore a normal heartbeat. AEDs are designed to be used by the public, and typically provide recorded audio instruction and visual prompts to guide users through the process.
Read more: How Australians Die: cause #1 – heart diseases and stroke[6]
Anyone can perform these life-saving skills, and the quicker they are performed the more likely the person will survive. The Australian Resuscitation Council[7], of which we are both members, believes teaching basic life support skills, CPR and how to use an AED in schools is the best way to reach and train whole generations how to save a life.
A patchy approach in schools
The current Australian curriculum supports basic life support education in some years. But schools vary in its implementation. Some schools have organisations come in to teach students, like the Red Cross or St John Ambulance, but teachers are also well placed to provide this education.
The Aussie Kids Save Lives program[9], an initiative being run by the Australian Resuscitation Council and partners, is aiming to provide teachers with the resources to be able to teach high school students.
A pilot study is currently underway in Victoria. Teachers are guided in instruction and students are practising skills using Ambulance Victoria’s Call, Push, Shock[10] kits that instruct young people how to call for help, perform push (compressions) and deliver lifesaving shocks with a defibrillator.
So far, more than 550 Victorian Year 7 and 8 students have been taught in the pilot, with more than 3,000 expected to be taught in 2023. Early data from the ongoing evaluation of this program is encouraging, with teachers and students finding the materials engaging and effective.
The Australian Resuscitation Council plans to use a report of the evaluation to lobby the federal government to introduce two hours of mandatory training in every year of school.
How young is too young?
The World Health Organization[11] has endorsed two hours of teaching CPR to children every year from the age of 12. However, this isn’t to say younger children shouldn’t be taught how to respond to emergencies.
Children as young as four years[12] of age can be taught how to recognise an emergency and how to call an ambulance.
Progressive annual learning can help children of all ages learn how to save a life. Initial learning should use simplified methods of instruction, such as Call, Push Shock[13]. Older students can be taught the more technical DRSABCD[14] acronym that guides them to look for danger and responses, send for help, and check airways and breathing before starting CPR and defibrillation.
There is an added bonus in teaching children, as they can be encouraged to pass their learning on to their family, perhaps as homework. This increases community awareness of basic life support skills.
Read more: In cases of cardiac arrest, time is everything. Community responders can save lives[17]
Intervention is vital
Data[18] reported by the Australasian Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium[19] shows that even though CPR instructions are given in 000 calls and the person is asked if there is an AED available, only 38% of Australians in cardiac arrest receive bystander CPR and less than 2% receive an AED shock.
Research listening to emergency calls has uncovered this often happens because the caller lacks confidence[20] in their ability to perform CPR skills. Most callers do not know[21] what a defibrillator is.
But areas of Australia with higher rates of trained community members have higher rates[22] of bystander CPR.
Help at home
We encourage parents to advocate for basic life support training in their children’s schools and even teach their children simple CPR themselves using online videos.
Former Yellow Wiggle Greg Page teaches kids about CPR and calling Triple Zero (000).While it may take some time, it is vital to have every Australian know what to do if they find someone collapsed in cardiac arrest, including our youngest. Without any intervention, the person is likely to die. Any attempt is better than nothing.
Read more: When is it OK to call an ambulance?[23]
References
- ^ 26,000 cardiac arrests (www.resuscitationjournal.com)
- ^ over 76% of them occurring in the home (www.resuscitationjournal.com)
- ^ cardiac arrest (www.heartfoundation.org.au)
- ^ CPR (www.healthdirect.gov.au)
- ^ AED (www.healthdirect.gov.au)
- ^ How Australians Die: cause #1 – heart diseases and stroke (theconversation.com)
- ^ Australian Resuscitation Council (resus.org.au)
- ^ Shutterstock (www.shutterstock.com)
- ^ Aussie Kids Save Lives program (onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- ^ Call, Push, Shock (www.ambulance.vic.gov.au)
- ^ World Health Organization (www.resuscitationjournal.com)
- ^ four years (bmjopen.bmj.com)
- ^ Call, Push Shock (www.ambulance.vic.gov.au)
- ^ DRSABCD (www.healthdirect.gov.au)
- ^ Unsplash (unsplash.com)
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
- ^ In cases of cardiac arrest, time is everything. Community responders can save lives (theconversation.com)
- ^ Data (www.resuscitationjournal.com)
- ^ Australasian Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium (www.ausroc.org.au)
- ^ lacks confidence (www.resuscitationjournal.com)
- ^ callers do not know (www.sciencedirect.com)
- ^ higher rates (pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- ^ When is it OK to call an ambulance? (theconversation.com)

















