People who lived in the UK in the 'mad cow disease' years may now be able to give blood. The risk of vCJD is tiny
- Written by Hamish McManus, Biostatistician, Kirby Institute, UNSW Sydney
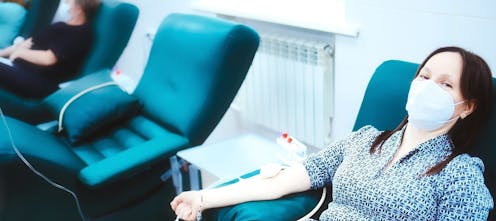
From today, eligible people who were in the United Kingdom in the 80s and 90s will be able to donate blood in Australia again.
That’s because the risk of acquiring variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) from blood transfusions in Australia is incredibly tiny.
We calculated that risk was about one in 1.4 billion, publishing our research[1] in the journal Vox Sanguinis.
The removal of restrictions, which have been in place for more than 20 years, means about 750,000 more Australians can now potentially donate blood.
This is at a time when there is a shortage of blood donations[2] due to donors sick with COVID or flu.
Remind me again, what is vCJD?
Researchers identified vCJD as a new and emerging fatal neurological disease in 1996[3]. It has since been associated with 233 cases worldwide[4], with 178 of those in the UK.
Once infected, people show no symptoms for many years. But when they do, there are psychiatric symptoms, such as depression. Then there are sensory symptoms, such as pain, followed by neurological abnormalities. People usually die about a year after symptoms start.
Transmission has been mainly via eating beef from cattle with bovine spongiform encephalitis (or BSE, commonly referred to as “mad cow disease”) in the UK during the 80s and 90s.
Mad cow disease had been spread by contaminated stock feed (cattle had been fed with contaminated beef products) before regulations were tightened and implemented, from 1996.
Over this time, an estimated 180,000[5] infected cattle had entered the UK human food chain.
Read more: Rare and deadly, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease remains a bit of a medical mystery[6]
How is this connected to giving blood?
There is no easy test for vCJD and infected people don’t know they have it until they have symptoms. This pre-symptomatic phase can be as long as several decades[7]. So there was speculation there could be unidentified people with vCJD, but exactly how many was unclear.
This is a potential public health issue as people who don’t know they have vCJD could transmit to others through blood, or tissue and organ donations.
This is why people who were in the UK between 1980 and 1996 for six months or more have been unable to give blood in Australia, since December 2000. Other countries had similar bans.
Read more: From animal experiments to saving lives: a history of blood transfusions[9]
So what’s changed?
Since the peak of the vCJD epidemic in 2000, when there were 28 deaths in the UK[10], there has been a rapid decline in recorded cases, with only two worldwide since 2015. These numbers are much lower than modelled predictions.
Because there have been no BSE or vCJD cases in Australia, lower-than-predicted vCJD case numbers generally, and the ongoing change in the proportion of people in Australia who were exposed to vCJD, we recently reassessed the risk of vCJD in Australian blood donors.
Read more: Australia’s ethnic face is changing, and so are our blood types[11]
The risk is tiny, the benefits large
We looked at a range of scenarios, including different assumptions about the numbers of people with vCJD, infectiousness and incubation periods.
Using modelling, we predicted a blood donation from an Australian with vCJD would occur once every 65 years, but this rate decreases over time.
If that donated blood was used in a transfusion today, there would be about a one in 1.4 billion chance of the recipient developing vCJD.
In other words, there is virtually no increased risk of vCJD transmission via transfusion (and this is decreasing). Lifting the ban on UK donors would increase the donor pool by 750,000 newly eligible people.
Assuming donation at the current rate, this would result in a gain of around 58,000 blood donations annually.
Our research was instrumental in supporting today’s opening up of blood donations, as approved[12] by the Therapeutic Goods Administration earlier this year and subsequently supported by Australian governments.
The Food and Drug Administration has also recommended[13] removing similar restrictions on blood donors in the United States.
The authors acknowledge the assistance of Veronica Hoad and Alison Gould from Lifeblood in drafting and reviewing the article.
Contact Lifeblood[14] to donate blood in Australia.
References
- ^ publishing our research (onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- ^ shortage of blood donations (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ in 1996 (pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- ^ worldwide (pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- ^ 180,000 (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- ^ Rare and deadly, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease remains a bit of a medical mystery (theconversation.com)
- ^ several decades (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- ^ Shutterstock (www.shutterstock.com)
- ^ From animal experiments to saving lives: a history of blood transfusions (theconversation.com)
- ^ 28 deaths in the UK (www.cjd.ed.ac.uk)
- ^ Australia’s ethnic face is changing, and so are our blood types (theconversation.com)
- ^ as approved (www.lifeblood.com.au)
- ^ recommended (www.fda.gov)
- ^ Lifeblood (www.lifeblood.com.au)

















