Tough carbon dioxide car emissions ceilings could get us well on the road to net-zero
- Written by Marion Terrill, Transport and Cities Program Director, Grattan Institute
The federal government’s mantra of “technology, not taxes[1]” has left it with few options to easily reduce carbon emissions.
In many sectors of the economy, it’s a recipe for disaster — a vague slogan that keeps us waiting.
But for all its flaws, relying on technology points us in the right direction in at least one field — reducing emissions from cars.
Light vehicles are responsible for 11% of Australia’s carbon emissions.
As it stands, Australia is way behind the pack. The lowest-emitting variants of the top-selling models in Australia are more emissions-intensive than the models available overseas.
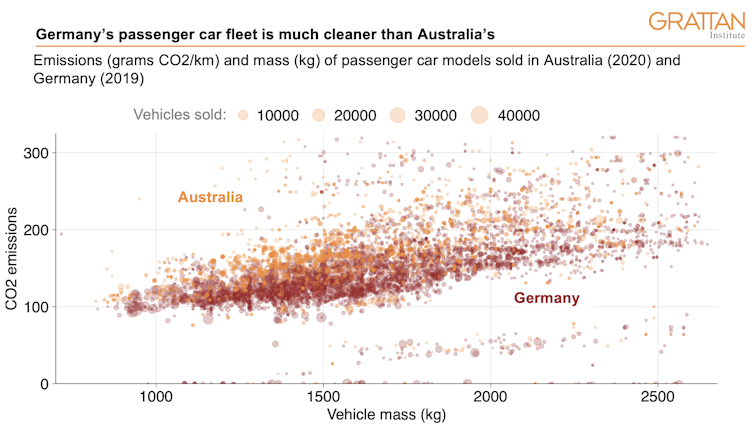
The average US passenger light vehicle is more than 100kg heavier than the average Australian light vehicle and has 30kW more power. Yet on average US vehicles emit 5 grams less carbon dioxide per kilometre travelled.
Emissions ceilings are common worldwide
A new Grattan Institute[2] report recommends Australia quickly move to catch up to mainstream international practice.
Eighty per cent of the world imposes a carbon dioxide emissions standard, or ceiling, on new light vehicles, applied across the offering of each manufacturer.
The US, the UK and Europe all have ceilings that tighten over time, bringing down average emissions. If manufacturers breach the ceiling, they face fines.
Read more: Top economists call for measures to speed the switch to electric cars[3]
Australia has no such standard, although it regulates other pollutants[4] including nitrogen oxides and particulate emissions, but to a weaker standard than much of the rest of the world because our petrol is of poorer quality.
Laboratory tests in 2015 found the average new vehicle sold in Australia emitted 184 grams of carbon dioxide per kilometre driven. More than five years on, little has changed – in 2020 the average new vehicle sold emitted 180 grams per kilometre driven.
That’s much higher than in comparable countries. New passenger cars sold in Germany, for example, are similar to Australia’s in weight, yet emit significantly less carbon dioxide per kilometre.

















