'What is my IP address?' Explaining one of the world's most Googled questions
- Written by Paul Haskell-Dowland, Associate Dean (Computing and Security), Edith Cowan University
What is my IP? It’s an odd question in most people’s minds, yet it’s one of the top ten most-searched[1] questions on Google.
Those who know what an IP address is will already know most of these searches are coming from people who understand what they’re searching for. But for the rest of us a more relevant question might be: what is an IP address?
Across the globe there are billions of computing devices that connect to the internet. To communicate, each device needs an address, just like our homes.
Our home address is typically structured along the lines of “number, street, city, postcode, country”. And our entire postal delivery network is based on this system.
Our digital world is similar, and has an address system that allows network traffic to move around the internet. So, an IP (internet protocol) address — which also has its own implicit structure — is fundamentally a numeric address for an endpoint on the internet.
An online content delivery system
Akin to postal addresses, IP addresses are assigned to each recipient in a worldwide infrastructure. The recipient could be a single device such as a laptop, phone, tablet or even your air-conditioner controller — but could also be a network entry point to a large organisation.
Since its inception, IP was designed with simplicity and efficiency in mind. That’s why it has remained effective at handling internet traffic, starting on a network with four nodes in the late 1960s, to billions of devices today.
An IP address is a number in binary format, which means it has 32 digits (or bits) comprising 1s and 0s. The address is typically grouped as four 8-bit numbers, so each number is eight digits that are either a 1 or 0.
But we usually view IP addresses in a decimal format, wherein the value between 00000000-11111111 becomes a number between 0 and 255. So the complete IP address space ranges from 0.0.0.0 through to 255.255.255.255.
See an example below, using the IP address of one of the servers that hosts theconversation.com.
 Examples of the same IP address in three different notations.
Author provided
Examples of the same IP address in three different notations.
Author provided
IP addresses are centrally managed by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority[2], which delegates to one of five regional registries: Africa, America, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Europe-West/Central Asia.
Not all addresses are available for use by anyone. Many are reserved[3] for specific purposes. For example, three ranges of addresses (10.0.0.0—10.255.255.255, 192.168.0.0—192.168.255.255 and 172.16.0.0—172.31.255.255) are reserved for private networks such as your home.
 For an IT geek, there’s no place like your local loopback address.
Author provided
For an IT geek, there’s no place like your local loopback address.
Author provided
Other large blocks of addresses are assigned to specific organisations[4]. The US Department of Defense “owns” the “6” prefix (6.x.y.z), as well as 11 others.
IPv6: a new frontier
IPv4 (version 4) is the most widely used version of IP in the world right now. Dating back to the 1980s[5], it has a capacity of more than four billion unique addresses — which was considered enough back then.
But a combination of wasteful use (such as organisations being allocated larger IP address spaces than they need), and the exponential increase of users, is causing this space to run out.
For now, IPv4 is still here. But its demise has long been predicted[6] and it will eventually no longer be fit for purpose. There are technical solutions, however.
The most useful ones are Network Address Translation (more on this later) and a newer version of IP: version 6. Although IPv6 is newer than IPv4, it isn’t really “new”. It was originally proposed some 25 years ago[7].
Read more: Here's why the internet will always have enough space for all our devices[8]
The shift to IPv6 brings a range of benefits, even if they are basically transparent as far as consumers are concerned. The most significant change with IPv6 is the increase in the size of IP addresses from 32 bits to 128 bits.
Version 6 also boosts the total number of unique IP addresses on offer, up to some 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456. Even with the rapid rise in device usage, this address pool should last us a long time[9].
 While IPv6 contains an unimaginable number of assignable addresses, as technology evolves we may well reach address exhaustion again!
xkcd
While IPv6 contains an unimaginable number of assignable addresses, as technology evolves we may well reach address exhaustion again!
xkcd
Making efficient use of addresses
As mentioned above, private addresses can be used for individual devices inside an organisation (or home). But private addresses can’t be used on the internet, so these devices “hide” behind one public/external IP address.
This public address is capable of supporting up to hundreds of thousands of devices for a large organisation. But a router is needed to connect the network to the internet. The router translates the many internal private addresses which are hiding behind the public IP address (or several of them).
 Private address spaces often use the 192.168 prefix. You cannot trace an address to this network remotely!
xkcd
Private address spaces often use the 192.168 prefix. You cannot trace an address to this network remotely!
xkcd
When data is delivered to a private organisation or home network, the router forwards the traffic to a specific internal computer using that computer’s private IP address.
The process of routing many devices through a single IP address is called “nesting” networks. And the technique it uses is referred to as Network Address Translation (NAT).
IP and download speeds
You probably won’t be using IP addresses in your daily life. But in order to access a website our computers need to “look up” the IP address for that site. This all happens in the background.
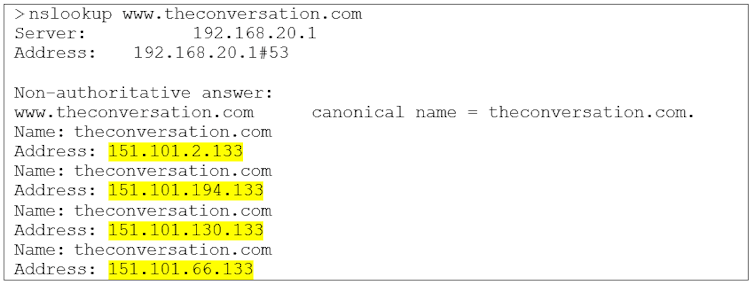 An example DNS lookup, the web address ‘www.theconversation.com’ is converted to the shorter form ‘theconversation.com’ and returns four distinct IP addresses.
Author provided
An example DNS lookup, the web address ‘www.theconversation.com’ is converted to the shorter form ‘theconversation.com’ and returns four distinct IP addresses.
Author provided
Once our computer has retrieved the website’s IP address, our browser will connect to the address, request the website data from the server and load the page.
In the image above, you’ll notice four different addresses. This allows the servers delivering the content to distribute the workload between four servers. Some websites go further and use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
Read more: Fastly global internet outage: why did so many sites go down — and what is a CDN, anyway?[10]
CDNs host copies of web content in servers around the globe. This means the content requested can be delivered from a location that is geographically closer to the user trying to access it. This reduces the time it takes to load the page.
The future of IP
IPv6 may be slowly rolling out in ISP networks and large organisations, but home users and smaller companies will still be using IPv4 for the foreseeable future.
The increased number of devices connected to the internet will certainly test our home routers – with predictions of 25 billion[11] devices expected globally within the next decade. Fortunately, even with this predicted explosion, IPv4 at home will be able to cope.
In the meantime, if you want to know your public IP address, simply search “what is my IP address[12]” and Google (as well as several other search engines) will deliver your public IP address. If you want to check your private IP address, this will take a little more effort[13].
References
- ^ top ten most-searched (www.semrush.com)
- ^ Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (www.iana.org)
- ^ reserved (www.arin.net)
- ^ assigned to specific organisations (www.pingdom.com)
- ^ back to the 1980s (datatracker.ietf.org)
- ^ predicted (www.theatlantic.com)
- ^ 25 years ago (datatracker.ietf.org)
- ^ Here's why the internet will always have enough space for all our devices (theconversation.com)
- ^ last us a long time (theconversation.com)
- ^ Fastly global internet outage: why did so many sites go down — and what is a CDN, anyway? (theconversation.com)
- ^ 25 billion (www.statista.com)
- ^ what is my IP address (www.google.com)
- ^ little more effort (www.howtogeek.com)

















