Now that Australia's inflation rate is 3.8%, is it time to worry?
- Written by John Hawkins, Senior Lecturer, Canberra School of Politics, Economics and Society and NATSEM, University of Canberra
Suddenly, Australia’s annual inflation rate is 3.8%, having jumped from 1.1% for the twelve months to March.
The June quarter jump follows a jump in the United States to 5.4%[1] and a jump in New Zealand to 3.3[2]%, sparking a debate between leading pundits such as former US treasury secretary Larry Summers[3] and Nobel Prize winner Paul Krugman[4] about whether high inflation is on the way back, after years of playing dead.
Annual inflation, Australia
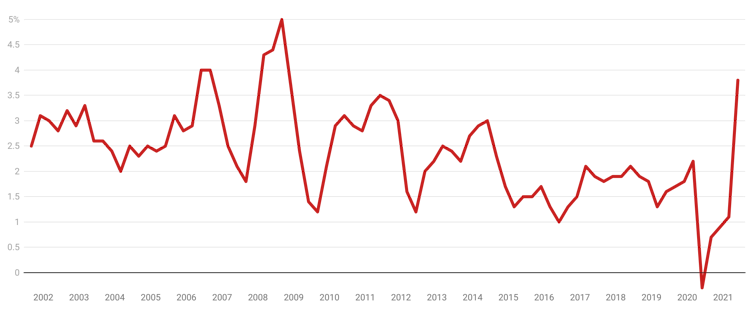 Australian Bureau of Statistics[5]
The best advice is not to worry. Most of the jump is only temporary, the result of several one-offs.
As the Reserve Bank told us back in May[6], a main cause is that in the depths of COVID lockdowns last year, the government heavily subsidised child care, pushing the effective price to near zero.
With removal of those subsidies the price has bounced back. This is a one-off — it can’t be repeated.
Reasons to not worry
Petrol prices[7] also collapsed as cities locked down last year, and have since returned to pre-COVID levels. This is another one-off that won’t be repeated.
There were also big jumps in the prices of some fruit and some vegetables due to a shortage of pickers and heavy rainfall. They are also best seen as one-offs.
The “trimmed mean[8]” measure of so-called underlying inflation used by the Reserve Bank to see through transient influences was only 1.6%. It’s a better guide to what is going on.
Australian Bureau of Statistics[5]
The best advice is not to worry. Most of the jump is only temporary, the result of several one-offs.
As the Reserve Bank told us back in May[6], a main cause is that in the depths of COVID lockdowns last year, the government heavily subsidised child care, pushing the effective price to near zero.
With removal of those subsidies the price has bounced back. This is a one-off — it can’t be repeated.
Reasons to not worry
Petrol prices[7] also collapsed as cities locked down last year, and have since returned to pre-COVID levels. This is another one-off that won’t be repeated.
There were also big jumps in the prices of some fruit and some vegetables due to a shortage of pickers and heavy rainfall. They are also best seen as one-offs.
The “trimmed mean[8]” measure of so-called underlying inflation used by the Reserve Bank to see through transient influences was only 1.6%. It’s a better guide to what is going on.
 Reserve Bank Governor Lowe.
This also true in other countries. The Bank for International Settlements concluded[9] this month that a common thread in recent increases in inflation was that they were “likely to be temporary”.
The Reserve Bank is expecting inflation back below 2%[10] by the end of the year. The bank forecasts consumer prices to rise by 1.5% through 2022.
Most economists broadly agree. The average forecast from The Conversation’s panel was an inflation rate of 2.1%[11] in 2022.
What about the traders in financial markets, whose pay depends on trying to guess inflation right?
The traders’ average forecast can be derived from what they will pay for inflation-indexed compared to non-indexed bonds.
Over the next ten years, they expect inflation to average 2%[12].
But isn’t too much money being printed?
Yes, there have indeed been such claims[13], often by people trying to talk up the value of cryptocurrencies through internet memes[14].
It is true that as the Reserve Bank sought to steady the economy last year, there was a period of rapid monetary growth. In times of uncertainty, people tend to want to hoard some money.
But the same thing happened during the global financial crisis in 2008. It didn’t end up leading to high inflation then. It is unlikely to do so now.
Concerns have also been expressed[15] that central banks have been buying too many government bonds — so-called “quantitative easing”. These fears were expressed internationally during the global financial crisis. They proved unfounded.
What else might push up inflation?
There are some longer-run structural changes. After the global financial crisis, the effective supply of workers[16] in the global economy grew due to demographic factors and the re-engagement of China.
Some of the demographic factors may be reversing, but the effect will be gradual.
It is also true that many economies, including Australia’s, rebounded from last year’s COVID lockdowns faster than expected. This has led some commentators to talk about overheating[17].
Read more:
What's in the CPI and what does it actually measure?[18]
But now the emergence of the more contagious Delta strain[19] has seen a new round of lockdowns. The Australian economy is likely to contract[20] in the September quarter, making our recovery look W-shaped rather than V-shaped as it did.
Reserve Bank Governor Lowe.
This also true in other countries. The Bank for International Settlements concluded[9] this month that a common thread in recent increases in inflation was that they were “likely to be temporary”.
The Reserve Bank is expecting inflation back below 2%[10] by the end of the year. The bank forecasts consumer prices to rise by 1.5% through 2022.
Most economists broadly agree. The average forecast from The Conversation’s panel was an inflation rate of 2.1%[11] in 2022.
What about the traders in financial markets, whose pay depends on trying to guess inflation right?
The traders’ average forecast can be derived from what they will pay for inflation-indexed compared to non-indexed bonds.
Over the next ten years, they expect inflation to average 2%[12].
But isn’t too much money being printed?
Yes, there have indeed been such claims[13], often by people trying to talk up the value of cryptocurrencies through internet memes[14].
It is true that as the Reserve Bank sought to steady the economy last year, there was a period of rapid monetary growth. In times of uncertainty, people tend to want to hoard some money.
But the same thing happened during the global financial crisis in 2008. It didn’t end up leading to high inflation then. It is unlikely to do so now.
Concerns have also been expressed[15] that central banks have been buying too many government bonds — so-called “quantitative easing”. These fears were expressed internationally during the global financial crisis. They proved unfounded.
What else might push up inflation?
There are some longer-run structural changes. After the global financial crisis, the effective supply of workers[16] in the global economy grew due to demographic factors and the re-engagement of China.
Some of the demographic factors may be reversing, but the effect will be gradual.
It is also true that many economies, including Australia’s, rebounded from last year’s COVID lockdowns faster than expected. This has led some commentators to talk about overheating[17].
Read more:
What's in the CPI and what does it actually measure?[18]
But now the emergence of the more contagious Delta strain[19] has seen a new round of lockdowns. The Australian economy is likely to contract[20] in the September quarter, making our recovery look W-shaped rather than V-shaped as it did.
 The Conversation, June 2 2021[21]
A big rise in inflation is unlikely unless wages grow strongly. There is no sign of this. Australia’s wage price index[22] is climbing by just 1.5%.
But what if the experts are wrong?
Contrary to some claims[23], the Reserve Bank has not promised to keep interest rates on hold at 0.1% until 2024.
As the bank’s governor has made clear[24], if inflation accelerates into its target band it will raise interest rates earlier.
Since the Reserve Bank introduced its 2-3% target, inflation has averaged 2.4%. There is no reason to think it won’t continue to act to keep it moderate.
But if I still fear inflation, what should I do?
You should look for a good “inflation hedge”, an asset that will increase in price with inflation.
It is possible to buy indexed government bonds[25].
Rents and dividends also tend to rise with inflation, meaning houses and shares have proved reasonable inflation hedges in the past.
Assets with no returns, such as gold and cryptocurrencies, are less reliable. The price of Bitcoin has more than halved in two of the past seven years, so beware.
The Conversation, June 2 2021[21]
A big rise in inflation is unlikely unless wages grow strongly. There is no sign of this. Australia’s wage price index[22] is climbing by just 1.5%.
But what if the experts are wrong?
Contrary to some claims[23], the Reserve Bank has not promised to keep interest rates on hold at 0.1% until 2024.
As the bank’s governor has made clear[24], if inflation accelerates into its target band it will raise interest rates earlier.
Since the Reserve Bank introduced its 2-3% target, inflation has averaged 2.4%. There is no reason to think it won’t continue to act to keep it moderate.
But if I still fear inflation, what should I do?
You should look for a good “inflation hedge”, an asset that will increase in price with inflation.
It is possible to buy indexed government bonds[25].
Rents and dividends also tend to rise with inflation, meaning houses and shares have proved reasonable inflation hedges in the past.
Assets with no returns, such as gold and cryptocurrencies, are less reliable. The price of Bitcoin has more than halved in two of the past seven years, so beware.
References
- ^ 5.4% (www.bls.gov)
- ^ 3.3 (www.stats.govt.nz)
- ^ Larry Summers (larrysummers.com)
- ^ Paul Krugman (www.nytimes.com)
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics (www.abs.gov.au)
- ^ Reserve Bank told us back in May (www.rba.gov.au)
- ^ Petrol prices (www.accc.gov.au)
- ^ trimmed mean (www.rba.gov.au)
- ^ concluded (www.bis.org)
- ^ below 2% (www.rba.gov.au)
- ^ 2.1% (theconversation.com)
- ^ 2% (www.rba.gov.au)
- ^ claims (www.afr.com)
- ^ internet memes (www.youtube.com)
- ^ expressed (theconversation.com)
- ^ workers (www.imf.org)
- ^ overheating (larrysummers.com)
- ^ What's in the CPI and what does it actually measure? (theconversation.com)
- ^ more contagious Delta strain (theconversation.com)
- ^ contract (www.reuters.com)
- ^ The Conversation, June 2 2021 (theconversation.com)
- ^ wage price index (www.abs.gov.au)
- ^ some claims (www.afr.com)
- ^ made clear (parlinfo.aph.gov.au)
- ^ indexed government bonds (www.australiangovernmentbonds.gov.au)
Read more https://theconversation.com/now-that-australias-inflation-rate-is-3-8-is-it-time-to-worry-165098
















