'Homo' who? A new mystery human species has been discovered in Israel
- Written by Michelle Langley, Senior Research Fellow, Griffith University
An international group of archaeologists have discovered a missing piece in the story of human evolution.
Excavations at the Israeli site of Nesher Ramla have recovered a skull that may represent a late-surviving example of a distinct Homo population, which lived in and around modern-day Israel from about 420,000 to 120,000 years ago.
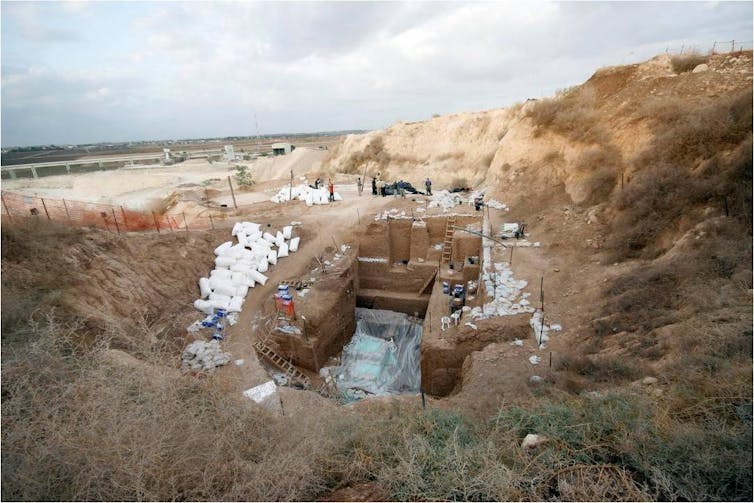 Aerial view of the Nesher Ramla sinkhole. The site of Nesher Ramla during excavation.
Yossi Zaidner
Aerial view of the Nesher Ramla sinkhole. The site of Nesher Ramla during excavation.
Yossi Zaidner
As researchers Israel Hershkovitz, Yossi Zaidner and colleagues detail in two companion studies published[1] today[2] in Science, this archaic human community traded both their culture and genes with nearby Homo sapiens groups for many thousands of years.
The new fossils
Pieces of a skull, including a right parietal (towards the back/side of the skull) and an almost complete mandible (jaw) were dated to 140,000–120,000 years old, with analysis finding the person it belonged to wasn’t fully H. sapiens.
 The Nesher Ramla mandible and skull.
Avi Levin and Ilan Theiler, Sackler / Tel Aviv University
The Nesher Ramla mandible and skull.
Avi Levin and Ilan Theiler, Sackler / Tel Aviv University
Nor were they Neanderthal, however, which was the only other type of human thought to have been living in the region at the time.
Instead, this individual falls right smack in the middle: a unique population of Homo never before recognised by science.
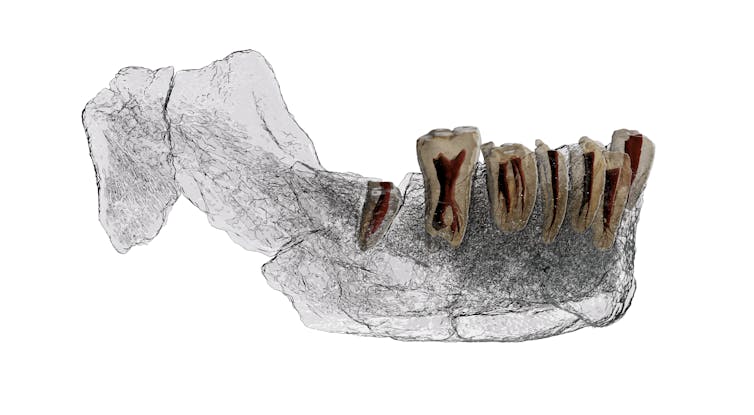 Imaging of the Nesher Ramla mandible and teeth.
Ariel Pokhojaev/Tel Aviv University
Imaging of the Nesher Ramla mandible and teeth.
Ariel Pokhojaev/Tel Aviv University
Through detailed comparison with many other fossil human skulls, the researchers found the parietal bone featured “archaic” traits that are substantially different from both early and recent H. sapiens. In addition, the bone is considerably thicker than those found in both Neanderthals and most early H. sapiens.
The jaw too displays archaic features, but also includes forms commonly seen in Neanderthals.
The bones together reveal a unique combination of archaic and Neanderthal features, distinct from both early H. sapiens and later Neanderthals.
Are there are more of these people?
The authors suggest fossils found at other Israeli sites, including the famous Lady of Tabun[3], might also be part of this new human population, in contrast to their previous Neanderthal or H. sapiens identification.
The “Lady of Tabun” (known to archaeologists as Tabun C1) was discovered in 1932 by pioneering archaeologist Yusra[4] and her field director, Dorothy Garrod.
Extensively studied, this important specimen taught us much about Neanderthal anatomy and behaviour in a time when very little was known about our enigmatic evolutionary cousins.
Read more: Ancient teenager the first known person with parents of two different species[5]
If Tabun C1 and others from the Qesem and Zuttiyeh Caves were indeed members of the Nasher Ramel Homo group, this reanalysis would explain some inconsistencies in their anatomy previously noted by researchers.
The mysterious Nesher Ramla Homo may even represent our most recent common ancestor with Neanderthals. Its mix of traits supports genetic evidence that early gene flow between H. sapiens and Neanderthals[6] occurred between 400,000 and 200,000 years ago. In other words, that interbreeding between the different Homo populations was more common than previously thought.
Even more puzzling, the team also found a collection of some 6,000 stone tools at the Nesher Ramla site.
 A flint scraper — one of the stone tools of Nesher Ramla Homo.
Tal Rogovski
A flint scraper — one of the stone tools of Nesher Ramla Homo.
Tal Rogovski
These tools were made the same way contemporaneous H. sapiens groups made their technology, with the similarity so strong it appears the two populations — Nesher Ramla Homo and H. sapiens — were hanging out on a regular basis. It seems they weren’t just exchanging genes, but also tips on tool-making.
And there was fire!
The site also produced bones of animals caught, butchered, and eaten on-site. These findings indicate Nesher Ramla Homo hunted a range of species, including tortoise, gazelle, aurochs, boar and ostrich.
Furthermore, they were using fire to cook their meals[7], evident through the uncovering of a campfire feature the same age as the fossils. Indeed, the Nesher Ramla Homo were not only collecting wood to make campfires and cook, but were also actively managing their fires as people do today.
 Exposure of animal bones and lithic artifacts in the layer with the Nesher Ramla Homo fossils.
Yossi Zaidner
Exposure of animal bones and lithic artifacts in the layer with the Nesher Ramla Homo fossils.
Yossi Zaidner
While the earliest indications of controlled use of fire is much older — perhaps one million years ago - the interesting thing about this particular campfire is the evidence that Nesher Ramla people tended to it as carefully as contemporary H. sapiens and Neanderthals did their own fires.
Most impressive is that the campfire feature survived, intact, outside of a protected cave environment for so long. It is now the oldest intact campfire ever found in the open air.
In sum, if we think of the story of human evolution like an Ikea bookcase that isn’t quite coming together, this discovery is effectively like finding the missing shelf buried at the bottom of the box. The new Nesher Ramla Homo allows for a better-fitting structure, although a few mysterious “extra” pieces remain to be pondered over.
For example, exactly how did the different Homo groups interact with each other? And what does it mean for the cultural and biological changes that were occurring for Homo populations in this period?
Continuing to work with these questions (the “extra pieces”) will help us build a better understanding of our human past.
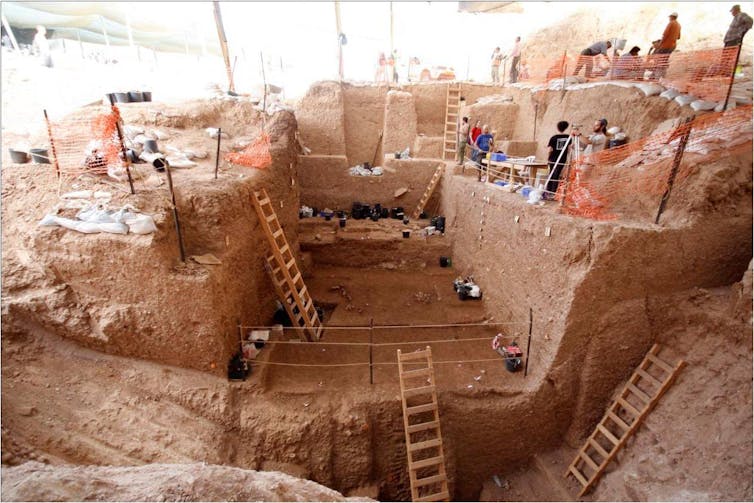 View of the deep section during excavation at Nesher Ramla, showing the deep.
archaeological sequence.
Yossi Zaidner
View of the deep section during excavation at Nesher Ramla, showing the deep.
archaeological sequence.
Yossi Zaidner
References
- ^ published (science.sciencemag.org)
- ^ today (science.sciencemag.org)
- ^ Lady of Tabun (humanorigins.si.edu)
- ^ Yusra (trowelblazers.com)
- ^ Ancient teenager the first known person with parents of two different species (theconversation.com)
- ^ gene flow between H. sapiens and Neanderthals (www.nature.com)
- ^ fire to cook their meals (www.youtube.com)

















