The surface of Venus is cracked and moves like ice floating on the ocean – likely due to tectonic activity
- Written by Paul K. Byrne, Associate Professor of Planetary Science, North Carolina State University
The Research Brief[1] is a short take about interesting academic work.
The big idea
Much of the brittle, upper crust of Venus is broken into fragments that jostle and move – and the slow churning of Venus’ mantle beneath the surface might be responsible. My colleagues and I arrived at this finding using decades-old radar data[2] to explore how the surface of Venus interacts with the interior of the planet. We describe it in a new study published[3] in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on June 21, 2021.
Planetary scientists like me[4] have long known that Venus has a plethora of tectonic landforms[5]. Some of these formations are long, thin belts where the crust has been pushed together to form ridges or pulled apart to form troughs and grooves. In many of these belts there’s evidence that pieces of the crust have moved side to side, too.
Our new study shows, for the first time, that these bands of ridges and troughs often mark the boundaries of flat, low-lying areas that themselves show relatively little deformation and are individual blocks of Venus’ crust that have shifted, rotated and slid past each other over time – and may have done so in the recent past. It’s a little like Earth’s plate tectonics[6] but on a smaller scale and more closely resembles pack ice that floats atop the ocean[7].
 Where ice chunks collide, the ice is thrust upwards to create ridges much like what researchers think happens on Venus.
Ben Holt and Susan Digby/WikimediaCommons[8]
Where ice chunks collide, the ice is thrust upwards to create ridges much like what researchers think happens on Venus.
Ben Holt and Susan Digby/WikimediaCommons[8]
 The crust of Venus is fractured into large pieces that behave more like chunks of ice floating on the ocean.
Endlisnis/WikimediaCommons, CC BY[9][10]
The crust of Venus is fractured into large pieces that behave more like chunks of ice floating on the ocean.
Endlisnis/WikimediaCommons, CC BY[9][10]
Researchers have hypothesized that – just like Earth’s mantle[11] – the mantle of Venus swirls with currents as it’s heated from below. My colleagues and I modeled the sluggish but powerful movement of Venus’ mantle and showed that it is sufficiently forceful to fragment the upper crust everywhere we’ve found these lowland blocks.
Why it matters
A major question about Venus is whether the planet has active volcanoes and tectonic faulting today. It’s essentially the same size, composition and age as Earth – so why wouldn’t it be geologically alive?
But no mission to Venus has yet conclusively shown the planet to be active. There’s tantalizing but ultimately inconclusive evidence that volcanic eruptions have taken place there in the geologically recent past[12] – and are perhaps even ongoing. The case for tectonic activity – the creaking, breaking and folding of the planet’s crust – is on even less solid ground.
Showing that Venus’ geological engine is still running would have huge implications for understanding the composition of the planet’s mantle, where and how volcanism might be taking place today and how the very crust itself is formed, destroyed and replaced. Because our study suggests that some of this jostling of the crust is geologically recent, we may have taken a big step forward in understanding if Venus really is active today.
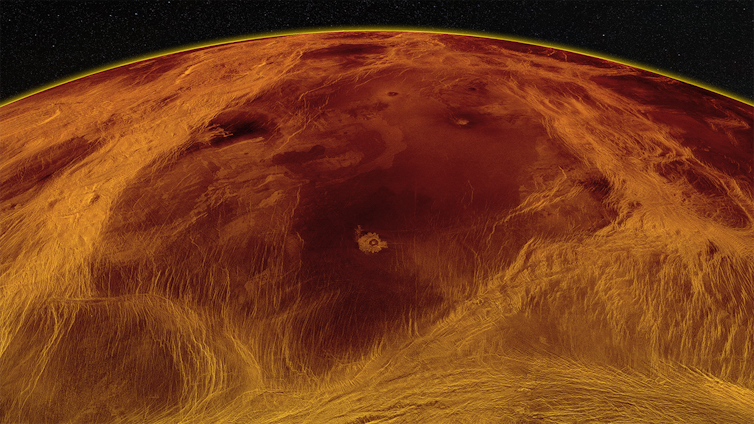 The largest block of lowlands the team found – the dark red shape in the center of this radar image – is about the size of Alaska and surrounded by ridges and deformations that show up as lighter colors.
Paul K. Byrne/NASA/USGS, CC BY-ND[13][14]
The largest block of lowlands the team found – the dark red shape in the center of this radar image – is about the size of Alaska and surrounded by ridges and deformations that show up as lighter colors.
Paul K. Byrne/NASA/USGS, CC BY-ND[13][14]
What still isn’t known
It’s not clear just how widespread these crustal fragments are. My colleagues and I have found 58 so far, but that’s almost certainly a low estimate.
We also don’t yet know when these crustal blocks first formed, nor how long they’ve been moving around on Venus. Determining when the crust’s fragmentation and jostling occurred is key – especially if planetary scientists want to understand this phenomenon in relation to the planet’s suspected recent volcanic activity. Figuring that out would give us vital information on how the planet’s surface features reflect the geological turmoil within.
What’s next
This initial study has allowed my colleagues and me to make our best guess yet about how Venus’ vast lowlands have been deformed, but we need much higher-resolution radar images and topographic data to build on this work. Luckily, that’s exactly what scientists are going to get[15] in the coming years, with NASA[16] and the European Space Agency[17] both recently announcing new missions bound for Venus later this decade. It’ll be worth the wait to get a better understanding of Earth’s enigmatic neighbor.
[The Conversation’s science, health and technology editors pick their favorite stories. Weekly on Wednesdays[18].]
References
- ^ Research Brief (theconversation.com)
- ^ decades-old radar data (astrogeology.usgs.gov)
- ^ new study published (doi.org)
- ^ Planetary scientists like me (scholar.google.com)
- ^ a plethora of tectonic landforms (arstechnica.com)
- ^ Earth’s plate tectonics (theconversation.com)
- ^ pack ice that floats atop the ocean (www.oceanpolaire.org)
- ^ Ben Holt and Susan Digby/WikimediaCommons (commons.wikimedia.org)
- ^ Endlisnis/WikimediaCommons (commons.wikimedia.org)
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
- ^ just like Earth’s mantle (people.earth.yale.edu)
- ^ volcanic eruptions have taken place there in the geologically recent past (www.esa.int)
- ^ Paul K. Byrne/NASA/USGS (astrogeology.usgs.gov)
- ^ CC BY-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ exactly what scientists are going to get (theconversation.com)
- ^ NASA (www.nasa.gov)
- ^ European Space Agency (www.esa.int)
- ^ Weekly on Wednesdays (theconversation.com)

















