the final report mentions ‘equity’ 200 times, but can it boost access for underrepresented groups?
- Written by Sally Patfield, Lecturer, Teachers and Teaching Research Centre, School of Education, University of Newcastle
The federal government has released the final report on a Universities Accord. Taking more than a year to prepare, it is billed as a “blueprint” for reform for the next decade and beyond. It contains 47 recommendations across student fees, wellbeing, funding, teaching, research and university governance. You can find the rest of our accord coverage here[1].
Equity has been an ongoing theme in Australian higher education policy for decades. Beginning with the Whitlam government in 1972, equity has often been viewed as a major challenge or “wicked problem[2]” that needs solving.
It’s also been at the forefront of discussions about the Universities Accord, with “access and opportunity” for underrepresented groups highlighted in the review’s terms of reference[3].
So it’s not surprising to see equity feature prominently in the final report. In fact, “equity” is mentioned more than 200 times. But does it live up to its promise to improve access to education for all Australians?
Read more: 'I would like to go to university': flexi school students share their goals in Australia-first survey[4]
What do we mean by equity?
The accord report continues the tradition of many previous federal government policies[5] by defining equity as “parity” or “proportional representation”. This means the major goal is for the university student population to reflect more closely the demographic composition of Australian society.
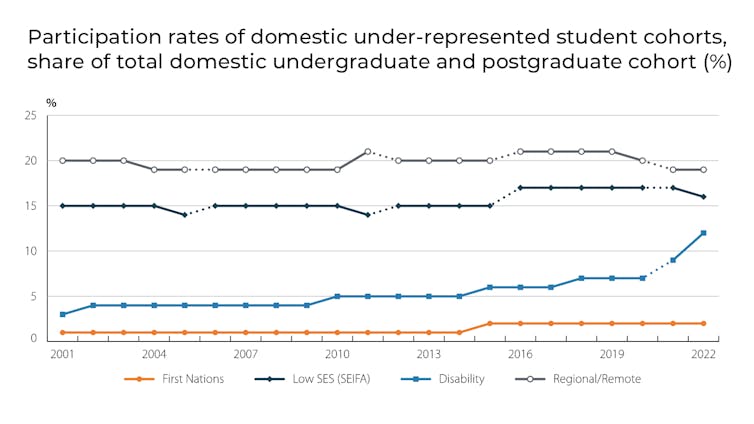
For example, Australians from low socio-economic status backgrounds currently make up around 17% of enrolments in higher education but 25% of the broader Australian population. So the aim here would be to have participation rates closer to, if not at, 25%. The other key target groups are First Nations peoples, people living in regional and remote areas, and people with a disability.
At face value, this a noble pursuit. Expanding access to higher education helps expand opportunities for all Australians and can lead to more diverse voices in professions and public life.
But this is not necessarily the accord’s rationale. The report notes we need to increase enrolments from underrepresented groups to increase the number of skilled workers. As such, we end up with phrases in the final report such as “growth through equity” and “skills through equity”.
So it downplays the importance of equity as a genuine concern in its own right.
‘Lack of aspiration’ isn’t a problem
Both sides of Australians politics have long used the language of “aspiration[8]” to suggest anybody can have a good life, as long as they just “get on with things[9]” and try hard enough.
In 2008, the Bradley Review[10] (the previous broad review of higher education in Australia) similarly argued one of the main barriers to increasing the enrolment of underrepresented groups was a lack of aspiration.
There is a large body of Australian research[11] demonstrating aspiration is not the problem it has been made out to be – many young people from all different kinds of backgrounds aspire to go to university. Nevertheless, the accord continues to talk about “increasing aspiration” and “building aspiration” as a strategy for facilitating access to higher education.
The accord proposes access to higher education can be improved, in part, by strengthening careers advice in schools and enhancing familiarity with university through outreach programs.
These are important for students who are the first in their family[12] to go to university, as they are often complete “newcomers” to higher education. But we need to move beyond seeing aspiration as a problem to be fixed.
Read more: 'Why would you go to uni?' A new study looks at what young Australians do after school[13]
What can make a difference?
Despite these limitations, the accord does propose a “whole of student” approach to raising university attainment levels (from how students learn to how they are financially supported), noting it’s not enough simply to enrol disadvantaged students “hoping they succeed”.
A number of practical recommendations likely to make a positive difference to students at various stages in their university journey include:
a significant increase in the availability of fee-free places in preparation or enabling programs[14], which prepare students for university study
government financial support for compulsory work placements[15] in teaching, nursing and other care-related fields
a new national “Jobs Broker” to help students find appropriate part-time employment during their studies
abolishing the Job-Ready Graduates scheme for fees, so student contributions are based on potential lifetime earnings.
Read more: These 5 equity ideas should be at the heart of the Universities Accord[18]
Beyond ‘bums on seats’
While these measures are welcome, we know there are longstanding challenges[19] to getting underrepresented groups into university, including improving academic outcomes during school. Cost-of-living pressures may also continue to make university study a challenge, despite increases in government help.
But even if targets are reached, achieving parity for underrepresented groups does not necessarily make higher education equitable.
Equity is much more than physical presence or getting bums on seats. We also need to think about what students are accessing, how they are supported, and how universities ultimately value and include them.
References
- ^ here (theconversation.com)
- ^ wicked problem (theconversation.com)
- ^ terms of reference (www.education.gov.au)
- ^ 'I would like to go to university': flexi school students share their goals in Australia-first survey (theconversation.com)
- ^ previous federal government policies (www.voced.edu.au)
- ^ Department of Education (www.education.gov.au)
- ^ CC BY-SA (creativecommons.org)
- ^ aspiration (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ get on with things (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ the Bradley Review (www.voced.edu.au)
- ^ large body of Australian research (www.newcastle.edu.au)
- ^ students who are the first in their family (link.springer.com)
- ^ 'Why would you go to uni?' A new study looks at what young Australians do after school (theconversation.com)
- ^ enabling programs (theconversation.com)
- ^ compulsory work placements (theconversation.com)
- ^ Nathan Dumlao/ Unsplash (unsplash.com)
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
- ^ These 5 equity ideas should be at the heart of the Universities Accord (theconversation.com)
- ^ longstanding challenges (andrewnorton.net.au)
















