Fossil CO₂ emissions hit record high yet again in 2023
- Written by Pep Canadell, Chief Research Scientist, CSIRO Environment; Executive Director, Global Carbon Project, CSIRO
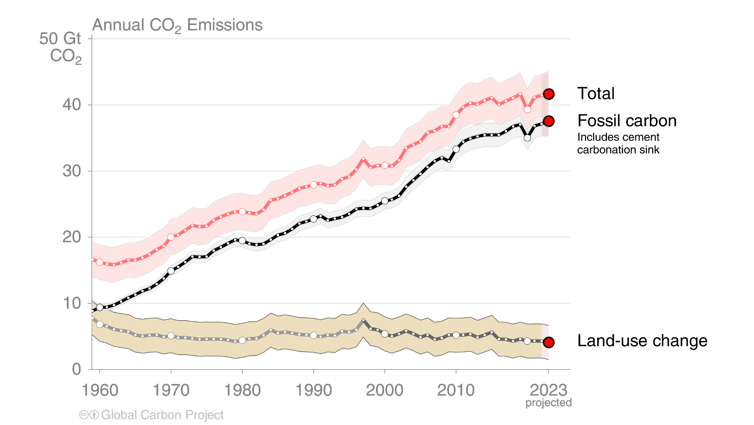
Global emissions of fossil carbon dioxide (CO₂), in yet another year of growth, will increase by 1.1% in 2023. These emissions will hit a record 36.8 billion tonnes. That’s the finding of the Global Carbon Project’s[1] 18th annual report card on the state of the global carbon budget[2], which we released today.
Fossil CO₂ includes emissions from the combustion and use of fossil fuels (coal, oil and gas) and cement production. Adding CO₂ emissions and removals from land-use change, such as deforestation and reforestation, human activities are projected to emit 40.9 billion tonnes of CO₂ in 2023.
The world’s vegetation and oceans continue to remove about half of all CO₂ emissions. The rest builds up in the atmosphere and is causing increasing warming of the planet.
At current emission levels, the remaining carbon budget for a one-in-two chance to limit warming to 1.5°C will likely be exceeded in seven years, and in 15 years for 1.7°C. The need to cut emissions has never been so urgent.
Emissions from every fossil source are up
Fossil CO₂ emissions now account for about 90% of all CO₂ emissions from human activities. Emissions from every single fossil source increased this year compared to 2022:
- coal (41% of global CO₂ emissions) up 1.1%
- oil (32%) up 1.5%
- natural gas (21%) up 0.5%
- cement (4%) up 0.8%.
Although global emissions have increased, the picture for individual countries is more diverse. There are some signs of progress towards decarbonisation.
China’s emissions (31% of the global total) increased by 4% with growth in all fossil fuel sources. The highest relative growth was from oil emissions. This was in part due to the transport sector’s recovery after COVID-19 pandemic shutdowns.
The United States’ emissions (14% of global) are down by 3%. The rapid retirement of coal-fired power plants drove most of this decline. US coal emissions are the lowest since 1903.
India’s emissions (8% of global) increased by 8.2%. Emissions for all fossil fuels grew by 5% or more, with coal the highest at 9.5%. India is now the world’s third-largest fossil CO₂ emitter.
European Union emissions (7% of global) are down by 7.4%. This decline was due to both high renewable energy penetration and the impacts on energy supply of the war in Ukraine.
During the decade of 2013-2022, 26 countries had declining fossil CO₂ emission trends while their economies continued to grow. The list includes Brazil, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Portugal, Romania, South African, United Kingdom and USA.
Total CO₂ emissions are near a peak
While fossil CO₂ emissions continue to increase, net emissions from land-use change, such as deforestation (CO₂ source), minus CO₂ removals, such as reforestation (CO₂ sink), appear to be falling. However, estimates of emissions from land-use change are highly uncertain and less accurate overall than for fossil fuel emissions.
Our preliminary estimate shows net emissions from land-use change were 4.1 billion tonnes of CO₂ in 2023. These emissions follow a small but relatively uncertain decline over the past two decades.
The declining trend was due to decreasing deforestation and a small increase in reforestation. The highest emitters are Brazil, Indonesia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. These three countries contribute 55% of net global CO₂ emissions from land-use change.
When we combine all CO₂ emissions from human activities (fossil and land use), we find very little trend in total emissions over the past decade. If confirmed, this would imply global CO₂ emissions from human activities are not growing further but remain at very high record levels.
Stable CO₂ emissions, at about 41 billion tonnes per year, will lead to continuing rapid CO₂ accumulation in the atmosphere and climate warming. To stabilise the climate, CO₂ emissions from human activities must reach net zero. This means any residual CO₂ emissions must be balanced by an equivalent CO₂ removal.
Nature’s a big help, with a little human help
Terrestrial vegetation and ocean absorb about half of all CO₂ emissions. This fraction has remained remarkably stable for six decades.
Besides the natural CO₂ sinks, humans are also removing CO₂ from the atmosphere through deliberate activities. We estimate permanent reforestation and afforestation over the past decade have removed about 1.9 billion tonnes of CO₂ per year.
This is equivalent to 5% of fossil fuel emissions per year.
Other non-vegetation strategies are in their infancy. They removed 0.01 million tonnes of CO₂.
Machines (direct air carbon capture and storage) pulled 0.007 million tonnes of CO₂ out of the atmosphere. Enhanced weathering projects, which accelerate natural weathering processes to increase the CO₂ uptake by spreading certain minerals, accounted for the other 0.004 million tonnes. This is more than a million times smaller than current fossil fuel emissions.
The remaining carbon budget
From January 2024, the remaining carbon budget for a one-in-two chance to limit global warming to 1.5°C has been reduced to 275 billion tonnes of CO₂. This budget will used up in seven years at 2023 emission levels.
The carbon budget for limiting warming to 1.7°C has been reduced to 625 billion tonnes of CO₂, with 15 years left at current emissions. The budget for staying below 2°C is 1,150 billion tonnes of CO₂ – 28 years at current emissions.
Reaching net zero by 2050 requires total anthropogenic CO₂ emissions to decrease on average by 1.5 billion tonnes of CO₂ per year. That’s comparable to the fall in 2020 emissions resulting from COVID-19 measures (-2.0 billion tonnes of CO₂).
Without additional negative emissions (CO₂ removal), a straight decreasing line of CO₂ emissions from today to 2050 (when many countries aspire to achieve net zero CO₂ or the more ambitious net zero for all greenhouse gases) would lead to a global mean surface temperature of 1.7°C, breaching the 1.5°C limit.
Renewable energy production is at a record high and growing fast. To limit climate change fossil and land-use change, CO₂ emissions must be cut much more quickly and ultimately reach net zero.
References
- ^ Global Carbon Project’s (www.globalcarbonproject.org)
- ^ global carbon budget (globalcarbonbudget.org)
- ^ Global Carbon Budget 2023/Global Carbon Project (www.globalcarbonproject.org)
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
- ^ Global Carbon Budget 2023/Global Carbon Project (www.globalcarbonproject.org)
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
Read more https://theconversation.com/fossil-co-emissions-hit-record-high-yet-again-in-2023-216436

















