Folded diamond has been discovered in a rare type of meteorite. How is this possible?
- Written by Andrew Tomkins, Geologist, Monash University
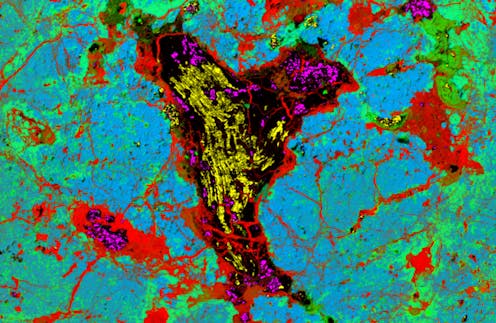
A “folded diamond” doesn’t sound entirely plausible. But that’s exactly what we’ve found inside a rare group of meteorites known as ureilites, which likely came from the mantle of a dwarf planet[1] or very large asteroid that was destroyed 4.56 billion years ago in a giant collision.
Within these space rocks, we found layered diamonds with distinctive fold patterns. Our discovery is published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences[2].
Now of course, everyone knows diamond is the hardest naturally occurring material[3], so the obvious question was – how on Earth (or in space!) could a folded diamond possibly form?!
This was exactly the sort of curiosity-piquing observation that sends scientists diving down rabbit holes for months on end.
A new analysis technique
Carbon, one of the most abundant elements in the universe, can form all kinds of structures. Among the more familiar ones are graphite and, of course, diamond. But there’s also an unusual hexagonal form of diamond known as lonsdaleite, which has been suggested to be even harder than standard cubic diamonds.
Our team includes a bunch of people who drive development of advanced analysis techniques. At CSIRO, Nick Wilson, Colin MacRae and Aaron Torpy developed a new approach in electron microscopy to map the distribution of diamond, graphite and lonsdaleite in the meteorites.
When our mapping suggested the folded diamond might actually be lonsdaleite, we – Dougal McCulloch, Alan Salek and Matthew Field at RMIT – performed a more detailed investigation via a method called high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM[5]).
The results were exciting: we had found some of the largest lonsdaleite crystallites (microscopic crystals) ever discovered, about 1 micrometre across. So, those intriguing fold shapes were composed of polycrystalline lonsdaleite, meaning they were made from numerous tiny crystals.
Reconstructing the cataclysm
And there was even more. We found the lonsdaleite had been partially converted to diamond and graphite, giving us clues to the sequence of events that had happened in the meteorites. Follow-up work at the Australian Synchrotron by Helen Brand confirmed this result.
By comparing the diamond, graphite and lonsdaleite across 18 different ureilite meteorites, we started to form a picture of what probably happened to produce the folded structures we found. At the first stage, graphite crystals folded deep inside the mantle of the asteroid thanks to high temperatures causing the other surrounding minerals to grow, pushing aside the graphite crystals. (You can see this in the schematic below.)
The second stage happened in the aftermath of the gigantic collision that catastrophically disrupted the ureilite parent asteroid. Evidence in the meteorites[6] suggested the disruption event produced a rich mix of fluids and gases as it progressed.
This mix then caused lonsdaleite to form by replacement of the folded graphite crystals, almost perfectly preserving the intricate textures of the graphite. Of course, it’s not actually possible to fold lonsdaleite or diamond – it formed by replacement of pre-existing shapes.
We think this was driven by the hot fluid mix as pressure and temperature dropped immediately after the cataclysm. Then, shortly after, diamond and graphite partially replaced the lonsdaleite as the fluid further decompressed and cooled to form a gas mixture.
Read more: How rare minerals form when meteorites slam into Earth[7]
Manufacturing clues from nature
The process is quite similar to a process used to manufacture diamonds known as chemical vapour deposition[8]. These manufactured diamonds are widely used in industry today, particularly for cutting and grinding because diamond is so hard. The difference is that we think the lonsdaleite replaced the shaped graphite at moderately higher pressures than those normally used to grow diamonds, from a supercritical fluid[9] rather than a gas.
So, nature appears to have given us clues on how to make shaped ultra-hard micro machine parts! If we can find a way to replicate the process preserved in the meteorites, we can make these machine parts by replacement of pre-shaped graphite with lonsdaleite.
Being able to study these weird folded diamonds was possible because lead author Andrew Tomkins had time to follow his nose – we call this type of research “curiosity-driven science”. However, although curiosity-driven science produces important breakthroughs[10], it isn’t normally funded by major funding agencies. They like to see well thought-out details for grand projects that already have a solid foundation of prior research.
We think a good way to boost Australia’s innovation would be to provide recognised science innovators a small grant annually to spend on research as they see fit; no questions asked, no justification or follow-up required.
For curiosity-driven research like our project, scientists need a small amount of time (and money) that can be spent with complete freedom; this produces the creativity[11] that drives innovation. You never know what else we might find out there.
Read more: We created diamonds in mere minutes, without heat — by mimicking the force of an asteroid collision[12]
References
- ^ dwarf planet (en.wikipedia.org)
- ^ Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (www.pnas.org)
- ^ the hardest naturally occurring material (pursuit.unimelb.edu.au)
- ^ Nick Wilson (www.eurekalert.org)
- ^ TEM (en.wikipedia.org)
- ^ Evidence in the meteorites (onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- ^ How rare minerals form when meteorites slam into Earth (theconversation.com)
- ^ chemical vapour deposition (www.youtube.com)
- ^ supercritical fluid (en.wikipedia.org)
- ^ curiosity-driven science produces important breakthroughs (news.harvard.edu)
- ^ the creativity (theconversation.com)
- ^ We created diamonds in mere minutes, without heat — by mimicking the force of an asteroid collision (theconversation.com)

















