New evidence shows blood or plasma donations can reduce the PFAS 'forever chemicals' in our bodies
- Written by Mark Patrick Taylor, Chief Environmental Scientist, EPA Victoria; Honorary Professor, Macquarie University
You might have heard of PFAS, a synthetic chemical found in certain legacy firefighting foams, non-stick pans, carpets, clothes and stain- or water-resistant materials and paints.
PFAS stands for “per- and poly-fluorinated alkyl substances”. These molecules, made up of chains of carbon and fluorine atoms, are nicknamed “forever chemicals” because they don’t degrade in our bodies.
There is global concern[1] about PFAS because they have been used widely, are persistent in the environment and accumulate in our bodies over time.
There was no way to reduce the amount of PFAS found in the body – until now.
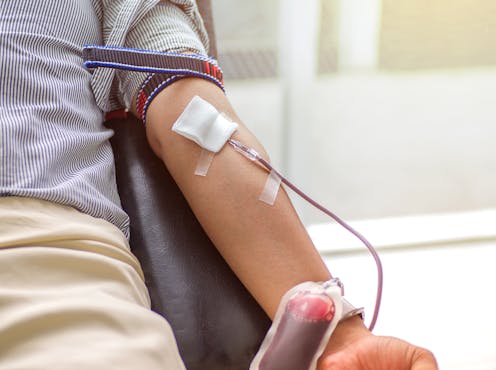
Our new randomised clinical trial, published in the journal JAMA Network Open[2], has found regularly donating blood or plasma can reduce blood PFAS levels.
Read more: PFAS 'forever chemicals' are widespread and threaten human health – here's a strategy for protecting the public[3]
What’s the concern about PFAS chemicals?
The science is unresolved around what levels of PFAS exposure, if any, are safe.
The historical use of some firefighting foams at fire stations[4], fire training bases[5], airports[6], military[7] and industrial facilities[8] has led to widespread environmental contamination across Australia[9], Europe[10] and the US.
Major environmental and health agencies, including the US Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry[11], US Environmental Protection Agency[12], and the Australian Department of Health[13] have noted PFAS exposure has been associated with adverse health effects.
But now, new research from Macquarie University and Fire Rescue Victoria has found that the concentration of PFAS in a person’s blood can be reduced if that person regularly donates blood or plasma.
Read more: Wearing shoes in the house is just plain gross. The verdict from scientists who study indoor contaminants[14]
How can PFAS in our bodies be reduced?
The trial aimed to find out whether plasma or blood removal are effective strategies for reducing serum PFAS concentrations. It was funded and supported by Fire Rescue Victoria to find a way to remove the PFAS from firefighters’ bodies.
The trial involved 285 Fire Rescue Victoria staff and contractors with elevated levels of PFOS, a common detected type of PFAS used in some firefighting foams.
They were randomly allocated to donate plasma every six weeks, to donate whole blood every 12 weeks, or to make no donations (the control group) for 12 months.
Their PFAS levels were measured at four intervals: at recruitment, the start of the trial, after 12 months of following their treatment plan, and again three months later to test if the results were sustained.
Both blood and plasma donation resulted in significantly lower PFAS chemicals than the control group, and these differences were maintained three months later.
Plasma donation was most effective, resulting in a roughly 30% decrease in average blood serum PFAS concentrations over the 12-month trial period.
Why would donating blood or plasma help?
Reductions in PFAS levels from blood or plasma donations may be because PFAS are bound to proteins primarily found in the serum; many other organic pollutants are bound to fats.
The finding that plasma was more effective than blood donation might be because firefighters in the plasma donation group donated blood every six weeks, whereas those in the blood donation group donated every 12 weeks.
In addition, each plasma donation can amount to as much as 800mL compared with 470mL for whole blood.
Plasma PFAS concentrations are also about two times higher than blood PFAS concentrations, which could make plasma donation more efficient at reducing the body burden of PFAS chemicals.
Still, plasma donation is more complex and can be more uncomfortable than blood donation. Indeed, the adherence to the study protocol was lower for the plasma group than the other groups.
Overall, the randomised clinical trial — which is the gold standard[15] for evaluating the effectiveness of intervention — had an exceptional 94% participant retention rate, with the 285 firefighters completing more than 1,000 blood tests and hundreds of blood and plasma donations.
This engagement from the Fire Rescue Victoria staff was a remarkable achievement because it spanned the Black Summer Bushfires as well as the extensive COVID-19 lockdowns in Melbourne.
It is a testament to their tenacity to support the discovery of an effective intervention to benefit others with substantial PFAS exposure.
Fire Rescue Victoria has replaced firefighting foams that contain PFAS and decontaminated fire trucks to eliminate or reduce ongoing occupational exposure to PFAS.
Still, because these chemicals accumulate in the body, many firefighters have elevated levels of PFAS because of historical exposures.
More research is needed to understand the ideal frequency and volumes of donations that will be effective for lowering PFAS, balancing the treatment efficacy with the obstacles to frequent donations.
It is also not clear whether reducing PFAS leads to improved health outcomes in the longer term. More research is needed to evaluate the clinical implications of the findings.
How can these findings be used in practice?
This study provides the first avenue for affected individuals to remove PFAS from their bodies and redress the effects of their PFAS exposure.
In future, more people with significant PFAS exposures may be encouraged to donate blood or plasma. According to the Australian Red Cross Lifeblood program, people who have been exposed to PFAS can still donate[16]. For recipients of donated blood components, no PFAS threshold has been identified as posing an increased risk. Our study didn’t investigate this risk, but blood authorities should continue to monitor the possible health effects of PFAS and consider any implications of elevated PFAS levels in blood donors.
In late March, a Senate joint standing committee[17] looking into PFAS recommended the government examine this research. For people with high PFAS levels who can’t donate blood or plasma – because, for example, of potential exposure to blood-borne illnesses – the committee recommended the government consider finding a way for them to make therapeutic donations.
The inquiry also recommended[18]:
that the Australian government provide funding for further longitudinal studies on potential adverse health effects for firefighters and members of PFAS-affected communities.
References
- ^ concern (www.epa.vic.gov.au)
- ^ JAMA Network Open (jamanetwork.com)
- ^ PFAS 'forever chemicals' are widespread and threaten human health – here's a strategy for protecting the public (theconversation.com)
- ^ fire stations (www.qfes.qld.gov.au)
- ^ fire training bases (www.parliament.vic.gov.au)
- ^ airports (www.airservicesaustralia.com)
- ^ military (defence.gov.au)
- ^ industrial facilities (www.industrialchemicals.gov.au)
- ^ Australia (pfas.australianmap.net)
- ^ Europe (www.eea.europa.eu)
- ^ US Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (www.atsdr.cdc.gov)
- ^ US Environmental Protection Agency (www.epa.gov)
- ^ Australian Department of Health (www1.health.gov.au)
- ^ Wearing shoes in the house is just plain gross. The verdict from scientists who study indoor contaminants (theconversation.com)
- ^ gold standard (doi.org)
- ^ can still donate (www.lifeblood.com.au)
- ^ joint standing committee (www.aph.gov.au)
- ^ recommended (www.aph.gov.au)

















