Chinese-Australians have a sense of dual 'belonging': Lowy poll
- Written by Michelle Grattan, Professorial Fellow, University of Canberra
A substantial minority of Chinese-Australians have experienced a backlash from the COVID-19 pandemic and the 2020 deterioration in bilateral relations, according to a survey from the Lowy Institute.
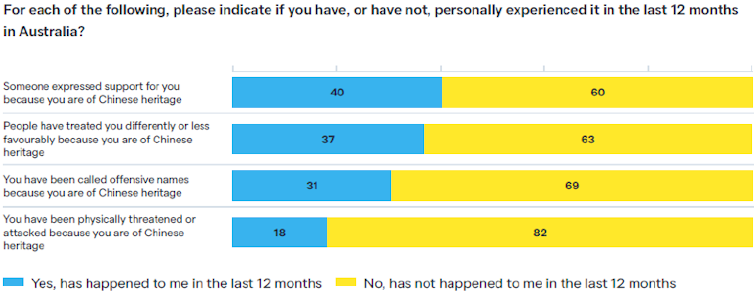
In the poll, 37% said they had been treated differently or less favourably in the past year because of their heritage and 31% had been called offensive names.
Nearly one in five (18%) said they had been physically threatened or attacked.
When those who’d had bad experiences were asked what they thought caused or contributed to that (COVID, Australia-China relations, other factors) 66% said COVID and 52% nominated the bilateral relationship, while 13% said other factors. Of the latter, 28% said racism.
On the positive side, 40% said someone had expressed support for them because of their heritage.
The Lowy report, Being Chinese in Australia, is based on a poll of 1040 who self-identify as of Chinese heritage. Australia has more than 1.2 million people of Chinese heritage. The poll, which received funding from the federal Department of Home Affairs, was done in November, in English and Mandarin.
 Lowy
It found some significant differences in attitudes and on policy issues between the Chinese-Australians and the general population.
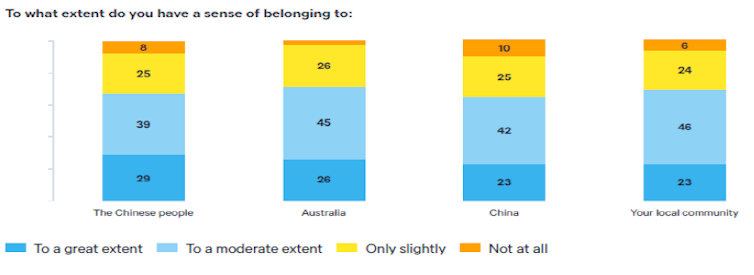
While most Chinese-Australians feel a sense of belonging in Australia (71%), they “also feel a sense of belonging to China, and that affects how they view that country,” according to the report authored by Natasha Kassam and Jennifer Hsu.
Lowy
It found some significant differences in attitudes and on policy issues between the Chinese-Australians and the general population.
While most Chinese-Australians feel a sense of belonging in Australia (71%), they “also feel a sense of belonging to China, and that affects how they view that country,” according to the report authored by Natasha Kassam and Jennifer Hsu.
 Lowy
The poll found 68% had a sense of belonging to the Chinese people, while 65% had a sense of belonging to China. This was stronger among recent migrants (those coming between 2010 and 2019) of whom more than eight in ten had a sense of belonging to China.
“Levels of trust in China are much higher in Chinese-Australian communities than in the broader Australian population,” the poll found.
“Chinese-Australians are more likely than other Australians to see China as an economic partner rather than as a security threat to Australia.
"They are divided in their views on China’s authoritarian system of government in light of COVID-19, and only a third say democracy is preferable to any other kind of government. In comparison, 71% of the broader Australian population express a preference for democracy. But Chinese-Australians’ perspectives on systems of government do not extend to all aspects of the Chinese system: many are critical of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP).
"For example, the majority of Chinese-Australians support sanctions on Chinese officials associated with human rights abuses, and want Australia to reduce its economic dependence on China.”
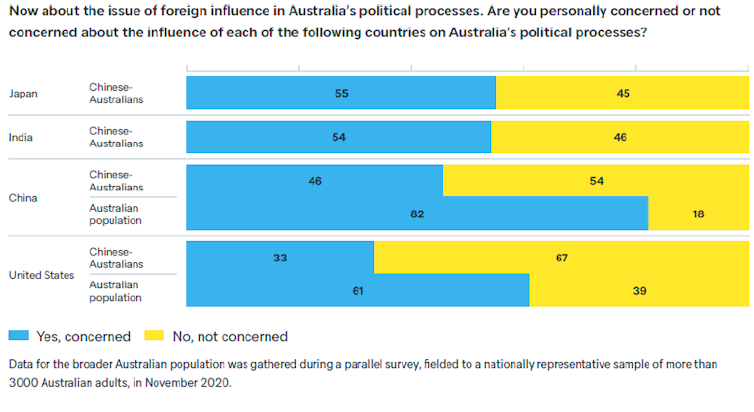
Less than half (46%) of the Chinese-Australians were concerned about China’s influence in Australian politics, while in a parallel national poll, 82% of the general population expressed concern about Chinese influence in Australia’s political processes.
The vast majority (84%) have almost no contact with the Chinese embassy or consulate and 75% say they have limited or no contact with Chinese community organisations.
Lowy
The poll found 68% had a sense of belonging to the Chinese people, while 65% had a sense of belonging to China. This was stronger among recent migrants (those coming between 2010 and 2019) of whom more than eight in ten had a sense of belonging to China.
“Levels of trust in China are much higher in Chinese-Australian communities than in the broader Australian population,” the poll found.
“Chinese-Australians are more likely than other Australians to see China as an economic partner rather than as a security threat to Australia.
"They are divided in their views on China’s authoritarian system of government in light of COVID-19, and only a third say democracy is preferable to any other kind of government. In comparison, 71% of the broader Australian population express a preference for democracy. But Chinese-Australians’ perspectives on systems of government do not extend to all aspects of the Chinese system: many are critical of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP).
"For example, the majority of Chinese-Australians support sanctions on Chinese officials associated with human rights abuses, and want Australia to reduce its economic dependence on China.”
Less than half (46%) of the Chinese-Australians were concerned about China’s influence in Australian politics, while in a parallel national poll, 82% of the general population expressed concern about Chinese influence in Australia’s political processes.
The vast majority (84%) have almost no contact with the Chinese embassy or consulate and 75% say they have limited or no contact with Chinese community organisations.
 Lowy
Reflecting the “dual ties” Chinese-Australians feel, 74% trust Australia to act responsibly in the world – and 72% trust China to do so. In contrast, the 2020 Lowy poll found only 23% of the general population trust China to act responsibly in the world.
“The majority of Chinese-Australians see China as a benign presence in the region, on a par with Japan , India and the United States.”
The divergence in views between the Chinese-Australians and the general community is particularly notable in relation to systems of government.
“A third of Chinese-Australians (36%) say ‘democracy is preferable to any other kind of government’, a far smaller proportion than the 71% of the broader Australian population expressing that view in the parallel survey.
"Four in ten Chinese-Australians (41%) say ‘in some circumstances, a non-democratic government can be preferable’ and 22% say ‘for someone like me, it doesn’t matter what kind of government we have’.
"These findings align with academic research indicating that migrants leaving authoritarian regimes to settle in a stable democracy do not see democracy as the only game in town’.”
Kassam says that “While the Chinese communist party seeks to collapse the diversity of Chinese-Australian communities into a unified whole, these poll results show the opposite.
"Depending on waves of migration, country of origin, visa status and age, Chinese-Australian have different perspectives on issues from foreign interference to China’s human rights record.”
Lowy
Reflecting the “dual ties” Chinese-Australians feel, 74% trust Australia to act responsibly in the world – and 72% trust China to do so. In contrast, the 2020 Lowy poll found only 23% of the general population trust China to act responsibly in the world.
“The majority of Chinese-Australians see China as a benign presence in the region, on a par with Japan , India and the United States.”
The divergence in views between the Chinese-Australians and the general community is particularly notable in relation to systems of government.
“A third of Chinese-Australians (36%) say ‘democracy is preferable to any other kind of government’, a far smaller proportion than the 71% of the broader Australian population expressing that view in the parallel survey.
"Four in ten Chinese-Australians (41%) say ‘in some circumstances, a non-democratic government can be preferable’ and 22% say ‘for someone like me, it doesn’t matter what kind of government we have’.
"These findings align with academic research indicating that migrants leaving authoritarian regimes to settle in a stable democracy do not see democracy as the only game in town’.”
Kassam says that “While the Chinese communist party seeks to collapse the diversity of Chinese-Australian communities into a unified whole, these poll results show the opposite.
"Depending on waves of migration, country of origin, visa status and age, Chinese-Australian have different perspectives on issues from foreign interference to China’s human rights record.”
Read more https://theconversation.com/chinese-australians-have-a-sense-of-dual-belonging-lowy-poll-156317

















