As fall approaches rapidly, many are wondering if the race for a vaccine will bear fruit as early as January 2021.
I am a physician-scientist and infectious diseases specialist at the University of Virginia, where I care for patients and conduct research into COVID-19. I am occasionally asked how I can be sure that researchers will develop a successful vaccine to prevent COVID-19. After all, we still don’t have one for HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
Here is where the current research stands, where I think we will be in five months and why you can be optimistic about the delivery of a COVID-19 vaccine.
1. Human immune system cures COVID-19
In as many as 99% of all COVID-19 cases, the patient recovers from the infection, and the virus is cleared from the body.
Some of those who have had COVID-19 may have low levels of virus in the body for up to three months after infection. But in most cases these individuals can no longer transmit the virus to other people 10 days after first becoming sick.
It should therefore be much easier to make a vaccine for the new coronavirus than for infections such as HIV where the immune system fails to cure it naturally. SARS-CoV-2 doesn’t mutate the way that HIV does, making it a much easier target for the immune system to subdue or for a vaccine to control.
2. Antibodies targeting spike protein prevent infection
A vaccine will protect, in part, by inducing the production of antibodies against the spike protein on the surface of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
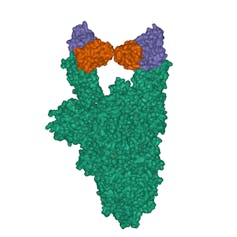
The virus needs the spike protein to attach to and enter human cells to reproduce. Researchers have shown that antibodies, like those made by the human immune system, bind to the spike protein, neutralize it and prevent the coronavirus from infecting cells in laboratory culture.
Vaccines in clinical trials have been shown to raise anti-spike antibodies that block virus infection in cells in the lab.
At least seven companies have developed monoclonal antibodies, laboratory-manufactured antibodies that recognize the spike protein. These antibodies are entering clinical trials to test their ability to prevent infection in those who are exposed, for example, through a household contact.
Monoclonal antibodies may also be effective for treatment. During an infection, a dose of these monoclonal antibodies could neutralize virus, giving the immune system a chance to catch up and manufacture its own antibodies to combat the pathogen.
3. Spike glycoprotein contains multiple targets
The spike protein has many locations where antibodies can bind to and neutralize the virus. That’s good news because with so many vulnerable spots, it will be difficult for the virus to mutate to avoid a vaccine.
Multiple parts of the spike would need to mutate to evade neutralizing anti-spike antibodies. Too many mutations to the spike protein would change its structure and render it incapable of binding to ACE2, which is key to infecting human cells.
4. We know how to make a safe vaccine
Safety of a new COVID-19 vaccine is improved by researchers’ understanding of potential vaccine side effects and how to avoid them.
One side effect seen in the past was antibody-dependent enhancement of infection. This occurs when antibodies don’t neutralize the virus but instead allow it to enter into cells via a receptor intended for antibodies. Researchers have found that by immunizing with the spike protein, high levels of neutralizing antibodies can be produced. This lessens the risk of enhancement.
A second potential problem posed by some vaccines is an allergic reaction that causes inflammation in the lung, as was seen in individuals who received a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine in the 1960s. This is dangerous because inflammation in the lung air spaces can make it difficult to breathe. However, researchers have now learned how to design vaccines to avoid this allergic response.
5. Several different vaccines in development
The U.S. government is supporting the development of several different vaccines via Operation Warp Speed.
The goal of Operation Warp Speed is to deliver 300 million doses of a safe and effective vaccine by January 2021.
The U.S. government is making a major investment, committing US$8 billion to seven different COVID-19 vaccines.
By supporting multiple COVID-19 vaccines, the government is hedging its bets. Only one of these vaccines needs to prove safe and effective in clinical trials for a COVID-19 vaccine to be made available to Americans in 2021.
[Get the best of The Conversation, every weekend. Sign up for our weekly newsletter.]
6. Vaccines passing through phase I and II trials
Phase I and phase II trials test if a vaccine is safe and induces an immune response. Already the results to date from three different vaccine trials are promising, triggering the production of anti-spike neutralizing antibodies levels that are two- to four-fold higher than those seen in people who have recovered from COVID-19.
Moderna, Oxford and Chinese company CanSino have all demonstrated the safety of their vaccines in phase I and phase II trials.
7. Phase III clinical trials are underway
During a phase III trial, the final step in vaccine development process, the vaccine is tested on tens of thousands of individuals to determine if it works to prevent infection with SARS-CoV-2, and that it is safe.
The vaccine produced by Moderna and NIH and the vaccine from Oxford-AstraZeneca began phase III trials in July. Other COVID-19 vaccines will be starting phase III within weeks.
8. Accelerating vaccine production and deployment
Operation Warp Speed is paying for the production of millions of doses of vaccines and supporting vaccine manufacturing at an industrial scale even before researchers have demonstrated vaccine efficacy and safety.
The advantage of this strategy is that once a vaccine is proven safe in phase III trials, a stockpile of it will already exist and it can be distributed immediately without compromising full assessment of safety and efficacy.
This is a more prudent approach than that of Russia, which is vaccinating the public with a vaccine before it has been shown to be safe and effective in phase III.
9. Vaccine distributors are being contracted now
McKesson Corp., the largest vaccine distributor in the U.S., has already been contracted by the CDC to distribute a COVID-19 vaccine to sites – including clinics and hospitals – where the vaccine will be administered.
I believe that it is realistic that we will know sometime in late 2020 whether some COVID-19 vaccines are safe, exactly how effective they are and which ones should be used to vaccinate the U.S. population in 2021.