Australia's economy can withstand the proposed European Union carbon tariff — here's what we find
- Written by Philip Adams, Professor at the Centre of Policy Studie, Victoria University
The European Union has committed to very significant emission cuts — 55% on 1990 levels by 2030, and zero net emissions by 2050.
To help it get there without too much disruption, the president of the European Commission proposed a carbon tariff – known as the carbon border adjustment mechanism, or CBAM.
The details will be tabled in the European Parliament later this year.
A carbon tariff is a tax on imports based on the carbon dioxide emissions involved in making them. Its purpose is to level the playing field with the domestic producers who will be made to pay a carbon price based on their emissions.
At the Victoria University Centre of Policy Studies we have modelled the effect on Australia’s economy.
Initially, we find it will reduce demand for Australian exports of coal, and steel and other emissions-intensive commodities, lowering both export prices and volumes.
But then a range of second round effects will kick in.
Less coal, lower dollar
Lower export income will lower the Australian dollar, pushing up prices for Australian households, particularly the price of imports.
The lower dollar will also make exporters not directly affected by CBAM more attractive to customers overseas.
How big will these effects be?
We have used simulations from the Victoria University Regional Model to run the numbers taking into account emissions intensities, the importance of the EU as a destination for individual Australian exports and the extent to which Australian producers are able to divert each export from the EU to other markets.
Increase in price of exports to EU under carbon border adjustment mechanism
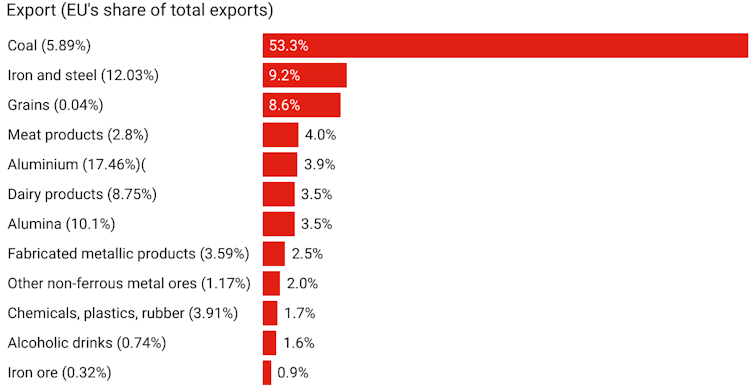 Assumes an EU carbon price of 60 euro per tonne, which is roughly today’s price; assumies the CBAM covers CO2 emissions including fugitive emissions involved in production other than direct combustion emissions that are priced already by the EU Emissions Trading Scheme.
Assumes an EU carbon price of 60 euro per tonne, which is roughly today’s price; assumies the CBAM covers CO2 emissions including fugitive emissions involved in production other than direct combustion emissions that are priced already by the EU Emissions Trading Scheme.
We find that some of the price effects are big (especially for coal) but, with a few exceptions, the EU isn’t an important market for Australian exports.
The exceptions are steel, alumina and aluminium where the EU accounts for between 10% and 20% of Australia’s exports.
Our simulations suggest that for the most part that the projected impacts on the Australian economy are small.
A week’s worth of economic growth
The long-run projected loss in gross domestic product is 0.05%, which is equivalent to a fall in weekly income of less than $1 per person or about one weeks’ worth of normal growth.
At an industry level, most industries slightly increase production, the fall in EU demand being more than compensated for by the weaker exchange rate.
Following a temporary increase in unemployment, job losses in declining industries are offset by expansion in other industries.
Change in industry output under carbon border adjustment mechanism
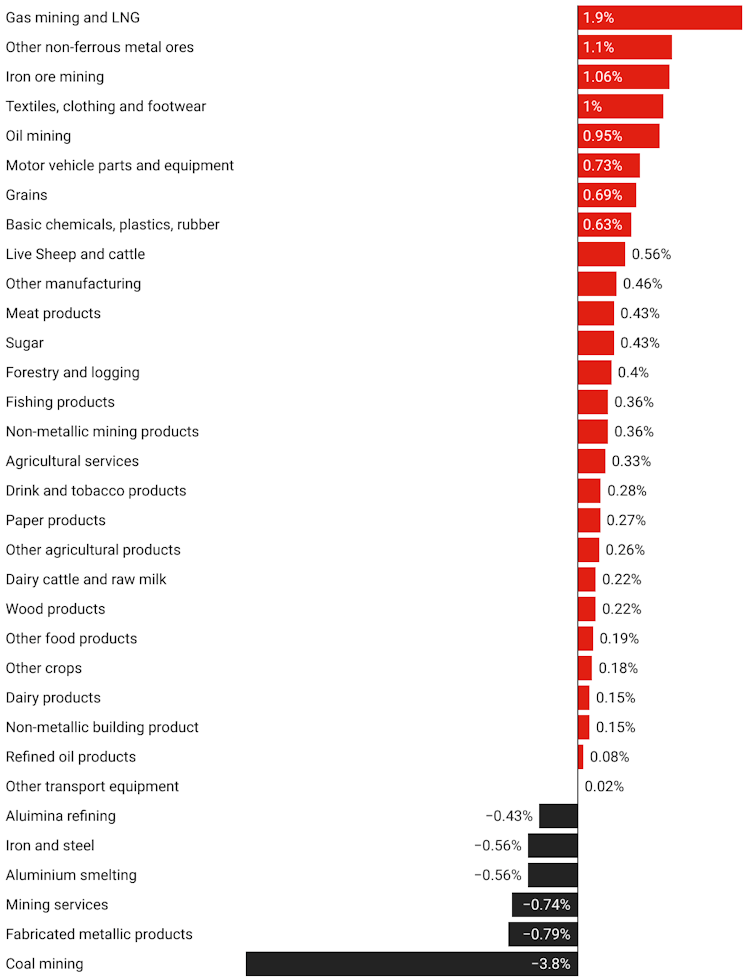 The main loser is coal mining. The carbon border adjustment mechanism has the potential to increase the landed duty-paid price of Australian-produced coal in the EU by more than half, effectively excluding it from the EU market.
Overall, it is projected to cut Australian coal production by 3.8% relative to where it would have been with the loss of about 3,000 jobs.
Jobs lost, jobs gained
The mechanism is projected to increase the buying price of iron and steel in the EU by almost 10%. While the EU is an important export market for Australian iron and steel, most of it is sold within Australia, meaning total production should fall by only 0.6%.
The decline in production should be relatively small, costing around 200 jobs.
Read more:
The EU is considering carbon tariffs on Australian exports. Is that legal?[1]
The job losses in mining and metal industries would be offset by the gains in the other industries which are able to take advantage of the lower exchange rate, including agriculture, some parts of manufacturing, tourism and education.
A temporary increase in unemployment as workers transition out of affected industries could be eased by training and other support for displaced workers.
The main loser is coal mining. The carbon border adjustment mechanism has the potential to increase the landed duty-paid price of Australian-produced coal in the EU by more than half, effectively excluding it from the EU market.
Overall, it is projected to cut Australian coal production by 3.8% relative to where it would have been with the loss of about 3,000 jobs.
Jobs lost, jobs gained
The mechanism is projected to increase the buying price of iron and steel in the EU by almost 10%. While the EU is an important export market for Australian iron and steel, most of it is sold within Australia, meaning total production should fall by only 0.6%.
The decline in production should be relatively small, costing around 200 jobs.
Read more:
The EU is considering carbon tariffs on Australian exports. Is that legal?[1]
The job losses in mining and metal industries would be offset by the gains in the other industries which are able to take advantage of the lower exchange rate, including agriculture, some parts of manufacturing, tourism and education.
A temporary increase in unemployment as workers transition out of affected industries could be eased by training and other support for displaced workers.
References
- ^ The EU is considering carbon tariffs on Australian exports. Is that legal? (theconversation.com)
Authors: Philip Adams, Professor at the Centre of Policy Studie, Victoria University














