It's hard to tell why China is targeting Australian wine. There are two possibilities
- Written by Markus Wagner, Associate Professor of Law, University of Wollongong
It’s on again. This time it’s Australia’s wine industry that’s under investigation[1] in China for allegedly violating anti-dumping rules.
The investigation has sent shock waves through the wine industry and beyond.
Broadly speaking, anti-dumping rules prohibit producers from selling anything for less than its market value.
The Chinese industry body claims[2] that the market share of Chinese wine has fallen from about 75% to just under 50% over the past four years.
It says this is due to the sale of Australian wine being dumped (sold at less than market prices) in China. It has asked for the imposition of an anti-dumping tariff of 202.70%, which would triple the price at which Australian wine is sold.
 The official complaint.
Ministry of Commerce[3]
The official complaint.
Ministry of Commerce[3]
Australian wine has enjoyed zero tariffs since 2019 under the China-Australia Free Trade Agreement[4].
In the past financial year, nearly 40%[5] of Australian wine exports (worth AU$1.1 billion) went to China.
The proposed duty would effectively exclude Australian wine from the Chinese market.
This comes after a highly publicised interview[6] in April in which China’s Ambassador to Australia Jingye Cheng said the Chinese public was “frustrated, dismayed and disappointed” at Australia’s stance on a number of issues and might boycott Australian goods and services.
Among those issues was Australia’s call for an investigation[7] into China’s handling of the coronavirus outbreak.
Other irritants include Australia’s criticism[8] of the new Hong Kong security law and its decision to ban[9] China’s Huawei from involvement in Australia’s 5G network.
Read more: China used anti-dumping rules against us because what goes around comes around[10]
Anti-dumping investigations turn on highly technical data, often obtainable only through the analysis of confidential business information.
This latest probe can be looked at in two ways:
1. Tit for tat
One is that it is just a tit for tat action following Australian anti-dumping measures[11] against Chinese electric cables, wind towers, glass, A4 copy paper, chemicals, herbicides and aluminium products and steel.
Australia has more anti-dumping measures in place against China[12] than it does against any other country.
Australian anti-dumping and countervailing measures by country, March 2020
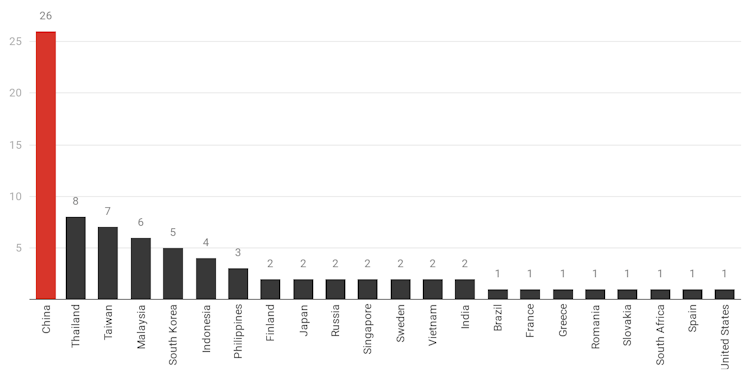 Anti-Dumping Commission, March 31, 2020[13]
China’s foreign ministry was quick to suggest its actions were a “normal anti-dumping investigation[14]”.
The ministry could find Australia’s wine industry is in a particular market situation[15], a technical term relating to government intervention and subsidies that Australia uses[16] when it imposes anti-dumping duties.
Standing in the way of such action is the presence of Chinese investors[17] in Australian wineries that sell directly to China via their own distribution networks. It would be difficult to design an anti-dumping penalty that didn’t also hit them.
2. Geo Economics
Another possibility is that China is trying to inflict economic pain to send a political message.
Using wine would be a shrewd move. China doesn’t need it for its economic growth. It has the added benefit of upsetting Australia’s powerful agricultural lobby which has the ear of governments.
The latest probe follows sanctions against Australian coal[18], barley[19] and beef[20].
Read more:
Vital Signs: Australian barley growers are the victims of weaponised trade rules[21]
The aim might be for the targeted industries, and their workers, to pressure the Australian government to be less confrontational with China.
A related strategy might be to portray Australia in a negative light. China (questionably) claimed that it stopped Australian coal and beef shipments for quality[22] and hygiene[23] reasons. Along with travel warnings[24], it is a way of turning the sentiment of Chinese citizens against Australia.
It’s hard to know which way to jump
It’s too early to tell whether China is simply expressing its dissatisfaction with Australian anti-dumping actions against it, or whether it is hoping to make Australia more politically malleable.
Each would require a different response.
The anti-dumping investigation might take up to 18 months[25], as did the investigation into Australian barley which resulted in extra tariffs.
Both countries stand to lose from a protracted battle.
Read more:
China might well refuse to take our barley, and there would be little we could do[26]
But China can get its coal, barley, beef and wine from elsewhere, although at potentially higher cost or lower quality. It is also trying to diversify its sources of iron ore[27].
The uncomfortable truth is that Australia’s economy relies on China far more[28] than China’s relies on Australia.
Anti-Dumping Commission, March 31, 2020[13]
China’s foreign ministry was quick to suggest its actions were a “normal anti-dumping investigation[14]”.
The ministry could find Australia’s wine industry is in a particular market situation[15], a technical term relating to government intervention and subsidies that Australia uses[16] when it imposes anti-dumping duties.
Standing in the way of such action is the presence of Chinese investors[17] in Australian wineries that sell directly to China via their own distribution networks. It would be difficult to design an anti-dumping penalty that didn’t also hit them.
2. Geo Economics
Another possibility is that China is trying to inflict economic pain to send a political message.
Using wine would be a shrewd move. China doesn’t need it for its economic growth. It has the added benefit of upsetting Australia’s powerful agricultural lobby which has the ear of governments.
The latest probe follows sanctions against Australian coal[18], barley[19] and beef[20].
Read more:
Vital Signs: Australian barley growers are the victims of weaponised trade rules[21]
The aim might be for the targeted industries, and their workers, to pressure the Australian government to be less confrontational with China.
A related strategy might be to portray Australia in a negative light. China (questionably) claimed that it stopped Australian coal and beef shipments for quality[22] and hygiene[23] reasons. Along with travel warnings[24], it is a way of turning the sentiment of Chinese citizens against Australia.
It’s hard to know which way to jump
It’s too early to tell whether China is simply expressing its dissatisfaction with Australian anti-dumping actions against it, or whether it is hoping to make Australia more politically malleable.
Each would require a different response.
The anti-dumping investigation might take up to 18 months[25], as did the investigation into Australian barley which resulted in extra tariffs.
Both countries stand to lose from a protracted battle.
Read more:
China might well refuse to take our barley, and there would be little we could do[26]
But China can get its coal, barley, beef and wine from elsewhere, although at potentially higher cost or lower quality. It is also trying to diversify its sources of iron ore[27].
The uncomfortable truth is that Australia’s economy relies on China far more[28] than China’s relies on Australia.
References
- ^ under investigation (www.mofcom.gov.cn)
- ^ industry body claims (images.mofcom.gov.cn)
- ^ Ministry of Commerce (images.mofcom.gov.cn)
- ^ China-Australia Free Trade Agreement (www.dfat.gov.au)
- ^ nearly 40% (www.wineaustralia.com)
- ^ highly publicised interview (au.china-embassy.org)
- ^ call for an investigation (www.foreignminister.gov.au)
- ^ Australia’s criticism (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ decision to ban (www.internationalaffairs.org.au)
- ^ China used anti-dumping rules against us because what goes around comes around (theconversation.com)
- ^ Australian anti-dumping measures (www.industry.gov.au)
- ^ against China (www.industry.gov.au)
- ^ Anti-Dumping Commission, March 31, 2020 (www.industry.gov.au)
- ^ normal anti-dumping investigation (www.washingtonpost.com)
- ^ particular market situation (www.springerprofessional.de)
- ^ Australia uses (www.dfat.gov.au)
- ^ Chinese investors (www.sbs.com.au)
- ^ coal (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ barley (www.afr.com)
- ^ beef (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ Vital Signs: Australian barley growers are the victims of weaponised trade rules (theconversation.com)
- ^ quality (www.news.com.au)
- ^ hygiene (www.smh.com.au)
- ^ travel warnings (www.abc.net.au)
- ^ 18 months (images.mofcom.gov.cn)
- ^ China might well refuse to take our barley, and there would be little we could do (theconversation.com)
- ^ iron ore (www.scmp.com)
- ^ far more (www.australiachinarelations.org)
Authors: Markus Wagner, Associate Professor of Law, University of Wollongong














