here's how to make their loans cheaper
- Written by Isaac Gross, Lecturer in Economics, Monash University
The government has widely touted its support for small businesses – most notably the provision of loans subsidised by the Reserve Bank.
In its economic update on Friday the Reserve Bank talked up its low-cost Term Funding Facility[1]. Take-up was “increasing steadily[2]”.
The scheme gives banks ultra low-interest money[3] (0.25% per year for three years) on the understanding they will lend it to households and businesses that need it.
The first allocation was a proportion of each lenders’ loan book. The second was conditional on the the lender expanding lending to business.
Read more: More than a rate cut: behind the Reserve Bank's three point plan[4]
For every extra dollar the bank extended to large business, it would get one extra dollar of funding from the Reserve Bank. For every extra dollar it lent to a small or medium size business it would get an extra five dollars.
Yet the official figures suggest that the overwhelming bulk of the new money has gone to big businesses, those with turnovers of more than A$50 million per year.
Medium-sized businesses have barely got a look-in. Lending to small businesses has actually gone backwards.
Outstanding credit to businesses
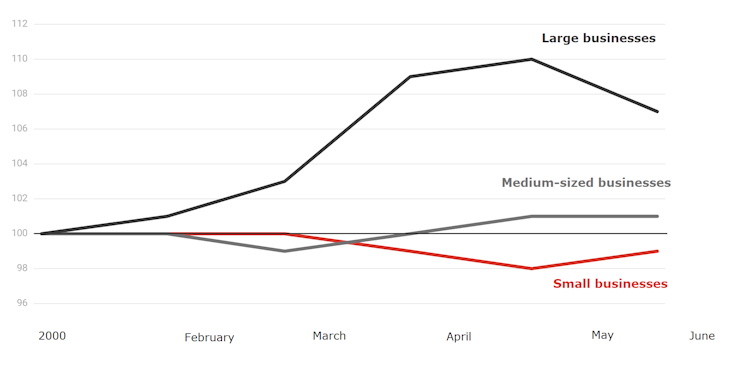 Index. 100 = January 1, 2020.
Reserve Bank of Australia[5]
Index. 100 = January 1, 2020.
Reserve Bank of Australia[5]
Loans outstanding for big businesses are 7.4% higher than at the start of the year, loans outstanding for medium-sized businesses are just 1.3% higher, and loans outstanding for small businesses are down 0.6%.
Not only have banks channelled the overwhelming bulk of their new lending to large businesses, they have also done so at lower interest rates.
Credit spread reductions for businesses
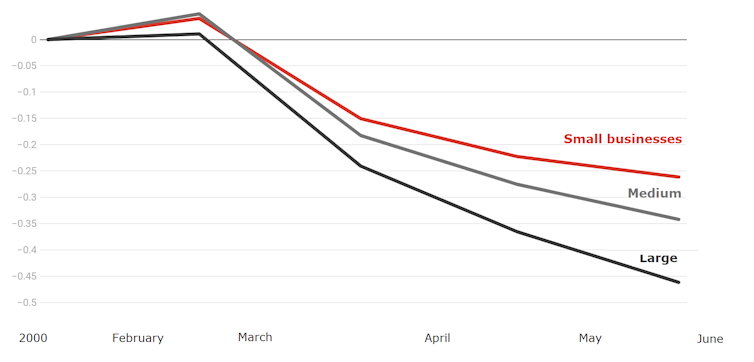 Percentage point change in spread between cash rate and rate charged from February 1, 2020.
APRA
Percentage point change in spread between cash rate and rate charged from February 1, 2020.
APRA
Why have small businesses missed out? One explanation might be that they are not interested in borrowing.
However, ask any economist, and she will tell you that demand for a good is usually a function of its price.
This ought to be also be true for business credit. The Reserve Bank says small businesses are being charged as much as 4.5%.
If the interest rate was lower there is a fair chance the amount borrowed would rise.
Banks don’t think they’re worth the risk
 Banks don’t like the risk.
Shutterstock
Banks don’t like the risk.
Shutterstock
Another explanation might be that banks don’t see much profit in lending to small businesses. Start ups are risky, even more so in a recession. But the Term Funding Facility was specifically set up to counter this.
Unfortunately it has proved inadequate to the task. The Reserve Bank’s offer of a three year loan fixed at 0.25% has not been generous enough to appeal to a banking sector whose cost of funding from traditional sources has also plunged.
What can it do to re-calibrate the Term Funding Facility? It is is due to expire in January and will need to be extended in one form or another.
They might if the money was free
One solution would be to take a leaf out of Europe’s book and make the interest rate on part of the next phase of the program negative, essentially free money.
The European Central Bank’s scheme offers loans at rates as low as -1% to banks that are willing to expand lending to small and medium-sized businesses.
This offer has helped drive the interest rate faced by small and medium-sized businesses as low as 2%, well below the 4.5% sometimes charged in Australia.
If the Reserve Bank offered part of the Term Funding Facility at a negative interest rate for banks that expanded lending to small businesses, it would likely see some expansion.
Read more: 'Yield curve control': the Reserve Bank's plan for when cash rate cuts no longer work[6]
It would both help stimulate the economy and increasing financial stability by making small business failures less likely.
Some might argue against this by saying that negative interest rates are unprecedented in Australia. But this argument does not hold water.
The times, and almost every proposed solution to our current problems, are unprecedented too.
References
- ^ Term Funding Facility (theconversation.com)
- ^ increasing steadily (www.rba.gov.au)
- ^ ultra low-interest money (www.rba.gov.au)
- ^ More than a rate cut: behind the Reserve Bank's three point plan (theconversation.com)
- ^ Reserve Bank of Australia (www.rba.gov.au)
- ^ 'Yield curve control': the Reserve Bank's plan for when cash rate cuts no longer work (theconversation.com)
Authors: Isaac Gross, Lecturer in Economics, Monash University














