Just 4.5% jobless during lockdowns? The unemployment rate is now meaningless
- Written by Jeff Borland, Professor of Economics, The University of Melbourne
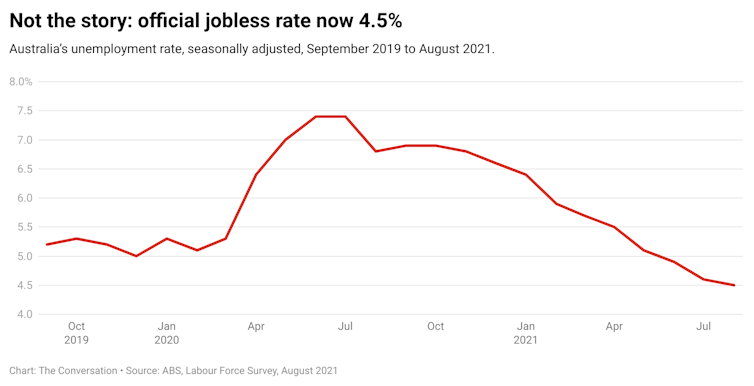
Australia’s labour force statistics for August again make the case for giving up on the rate of unemployment as an indicator of the state of the labour market.
In June the official unemployment rate dropped below 5%[1] for the first time since before the Global Financial Crisis of 2008. In July it dropped again, to 4.6%[2].
With major lockdowns across Australia since late July, the rate for August was widely expected to go up. Yet the Australian Bureau of Statistics’ figures show that while total hours worked were 5.6% down on their May peak, the jobless rate defied all predictions and fell again, to 4.5%
 CC BY-SA[3]
To understand why this has happened, we just need to follow the COVID-19 trail.
Employment fell
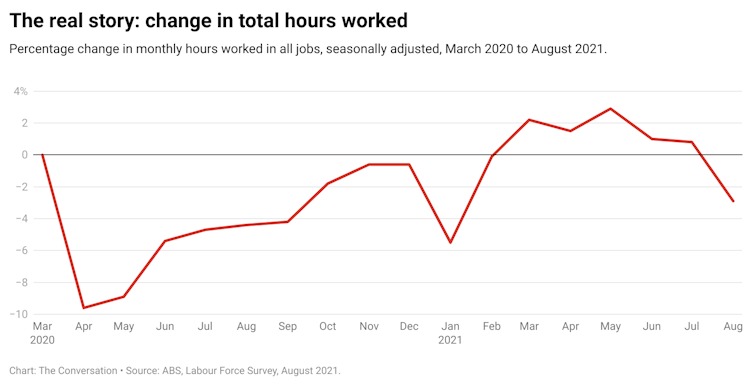
The re-emergence of COVID-19 in Victoria in June and NSW in July had already reduced hours of work. That trend accelerated in August with simultaneous lockdowns in NSW, Victoria, Queensland and the ACT.
Total hours worked in Australia declined by 3.8% in just one month, and are now back below their pre-COVID level in March 2020.
CC BY-SA[3]
To understand why this has happened, we just need to follow the COVID-19 trail.
Employment fell
The re-emergence of COVID-19 in Victoria in June and NSW in July had already reduced hours of work. That trend accelerated in August with simultaneous lockdowns in NSW, Victoria, Queensland and the ACT.
Total hours worked in Australia declined by 3.8% in just one month, and are now back below their pre-COVID level in March 2020.
 CC BY[4]
NSW has, unsurprisingly, been hardest hit. Hours worked there have fallen 11.8% since May. This is a more severe downturn than NSW experienced with the onset of COVID-19 in 2020, when hours worked decreased by 9.9%.
Until July, the re-emergence of COVID-19 brought decreases in hours worked but not in the number of people employed. That changed in August. Employment in NSW fell by 173,000, or 4.4%.
Other states in lockdown, Victoria and Queensland, have also gone backwards but to a lesser extent. Victoria in particular appears to have got away lightly in the month to August. Hours worked did fall by 2.8% but there was a slight increase in employment.
ABS payroll data[5] — a different measure to its monthly labour force survey — show much smaller decreases in jobs in Victoria than NSW in August across most industries.
This may reflect that Victoria’s latest lockdown started after NSW; or it may show that Victoria has managed to have its lockdown with less disruption to work. Data on employment for September will tell us more.
Hours worked fell more
Seeing larger falls in hours worked than employment tells us something important about how businesses adjust to needing less labour.
Rather than laying off their staff, at least in the initial stages of lockdown, businesses have chosen to reduce their hours of work.
This can be seen in the rise in the rate of underemployment between July and August, from 8.3% to 9.3%. Since May, the number of workers getting fewer hours than usual due to “no work, not enough work or stood down” rose about 490,000. Of those workers, about an extra 190,000 worked zero hours in the week of the survey.
People gave up looking for work
If employment fell between July and August, you might be thinking, doesn’t that mean more people unemployed, and a higher rate of unemployment?
Normally that’s what we’d expect to happen.
But it only happens if the people who lose their jobs stay in the labour market, looking for work.
In August, however, while employment decreased by 146,000, the number of people wanting to work — who the ABS counts as part of the labour force — declined even more, by 168,000. Thus unemployment fell by 22,000.
Withdrawals from the labour market were almost entirely concentrated in NSW. The state that saw the biggest decrease in hours worked also had the biggest decrease in people wanting to work — 3.8%.
Read more:
New finding: jobseekers subject to obligations take longer to find work[6]
So the lower rate of unemployment in August is not a sign of improving labour market conditions. Instead it shows many potential workers decided it wasn’t worth looking for a job.
Young people and women most affected
Those bearing the brunt of these latest lockdowns are same groups most adversely affected by the initial impact of COVID-19 in 2020.
Youth (aged 15 to 24 years) make up just 15% of the population but accounted for half of the decrease in employment in August. It’s likely this disproportionate impact is again due to younger people being more likely to work in the industries most affected by lockdowns – such as accommodation and food services.
Read more:
JobKeeper and JobMaker have left too many young people on the dole queue[7]
The story from 2020 is also repeating in the labour market impact of lockdowns by gender. From May to August, female employment fell by 90,000, compared with 25,000 for males. Women also withdraw from the labour force in much larger numbers than males, 119,000 to 80,000.
CC BY[4]
NSW has, unsurprisingly, been hardest hit. Hours worked there have fallen 11.8% since May. This is a more severe downturn than NSW experienced with the onset of COVID-19 in 2020, when hours worked decreased by 9.9%.
Until July, the re-emergence of COVID-19 brought decreases in hours worked but not in the number of people employed. That changed in August. Employment in NSW fell by 173,000, or 4.4%.
Other states in lockdown, Victoria and Queensland, have also gone backwards but to a lesser extent. Victoria in particular appears to have got away lightly in the month to August. Hours worked did fall by 2.8% but there was a slight increase in employment.
ABS payroll data[5] — a different measure to its monthly labour force survey — show much smaller decreases in jobs in Victoria than NSW in August across most industries.
This may reflect that Victoria’s latest lockdown started after NSW; or it may show that Victoria has managed to have its lockdown with less disruption to work. Data on employment for September will tell us more.
Hours worked fell more
Seeing larger falls in hours worked than employment tells us something important about how businesses adjust to needing less labour.
Rather than laying off their staff, at least in the initial stages of lockdown, businesses have chosen to reduce their hours of work.
This can be seen in the rise in the rate of underemployment between July and August, from 8.3% to 9.3%. Since May, the number of workers getting fewer hours than usual due to “no work, not enough work or stood down” rose about 490,000. Of those workers, about an extra 190,000 worked zero hours in the week of the survey.
People gave up looking for work
If employment fell between July and August, you might be thinking, doesn’t that mean more people unemployed, and a higher rate of unemployment?
Normally that’s what we’d expect to happen.
But it only happens if the people who lose their jobs stay in the labour market, looking for work.
In August, however, while employment decreased by 146,000, the number of people wanting to work — who the ABS counts as part of the labour force — declined even more, by 168,000. Thus unemployment fell by 22,000.
Withdrawals from the labour market were almost entirely concentrated in NSW. The state that saw the biggest decrease in hours worked also had the biggest decrease in people wanting to work — 3.8%.
Read more:
New finding: jobseekers subject to obligations take longer to find work[6]
So the lower rate of unemployment in August is not a sign of improving labour market conditions. Instead it shows many potential workers decided it wasn’t worth looking for a job.
Young people and women most affected
Those bearing the brunt of these latest lockdowns are same groups most adversely affected by the initial impact of COVID-19 in 2020.
Youth (aged 15 to 24 years) make up just 15% of the population but accounted for half of the decrease in employment in August. It’s likely this disproportionate impact is again due to younger people being more likely to work in the industries most affected by lockdowns – such as accommodation and food services.
Read more:
JobKeeper and JobMaker have left too many young people on the dole queue[7]
The story from 2020 is also repeating in the labour market impact of lockdowns by gender. From May to August, female employment fell by 90,000, compared with 25,000 for males. Women also withdraw from the labour force in much larger numbers than males, 119,000 to 80,000.
References
- ^ dropped below 5% (theconversation.com)
- ^ to 4.6% (theconversation.com)
- ^ CC BY-SA (creativecommons.org)
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
- ^ payroll data (www.abs.gov.au)
- ^ New finding: jobseekers subject to obligations take longer to find work (theconversation.com)
- ^ JobKeeper and JobMaker have left too many young people on the dole queue (theconversation.com)
Authors: Jeff Borland, Professor of Economics, The University of Melbourne













