Yes, you can still get COVID after being vaccinated, but you're unlikely to get as sick
- Written by Lara Herrero, Research Leader in Virology and Infectious Disease, Griffith University
When a COVID cluster includes people who are vaccinated against the virus, we inevitably hear rumblings of complaint from people who wonder what the point is of vaccination.
But when you read past the headlines, you usually see the answer: in most cases, those who were vaccinated and contracted COVID-19 didn’t die, didn’t develop severe symptoms and didn’t need to be hospitalised.
For unvaccinated Australians in their later years, the chance of dying from COVID is high[1]. For unvaccinated people in their 80s, around 32% who contract COVID will die from it. For people in their 70s, it’s around 14%. (For unvaccinated people in their 60s, it drops to around 3%. And for under-50s, it’s less than 1%.)
The good news is both Pfizer and AstraZeneca are very effective at preventing severe disease and death from COVID-19, even from the more virulent Delta strain.
So how effective are our vaccines?
Preliminary data[2] from the United Kingdom shows after your first dose of either Pfizer or AstraZeneca, you’re 33% less likely than an unvaccinated person to contract the Delta variant.
Two weeks after your second dose, this rises to[3] 60% for AstraZeneca and 88% for Pfizer. This data is for any form of COVID-19, from mild to severe.
But when you look at how much the vaccines reduce your risk of developing severe illness that requires hospitalisation, the coverage is high for both. Pfizer and Astrazeneca vaccines are 96% and 92% effective[4] (respectively) in preventing Delta variant hospitalisations.
Why do some people still get COVID after being vaccinated?
Vaccines aren’t magic barriers. They don’t kill the virus or pathogen they target.
Rather, vaccines stimulate[5] a person’s immune system to create antibodies. These antibodies are specific against the virus or pathogen for the vaccine and allows the body to fight infection before it takes hold and causes severe disease.
However, some people won’t have a strong enough immune response to the vaccine and may still be susceptible to developing COVID-19 if exposed to the virus[6].
How a person responds to a vaccine is impacted by a number of host factors[7], including our age, gender, medications, diet, exercise, health and stress levels.
Read more: The symptoms of the Delta variant appear to differ from traditional COVID symptoms. Here's what to look out for[8]
It’s not easy to tell who hasn’t developed a strong enough immune response to the vaccine. Measuring a person’s immune response to a vaccine is not simple and requires detailed laboratory tests.
And while side effects from the vaccine indicate you’re having a response, the absence of symptoms doesn’t mean[9] you’re having a weak response.
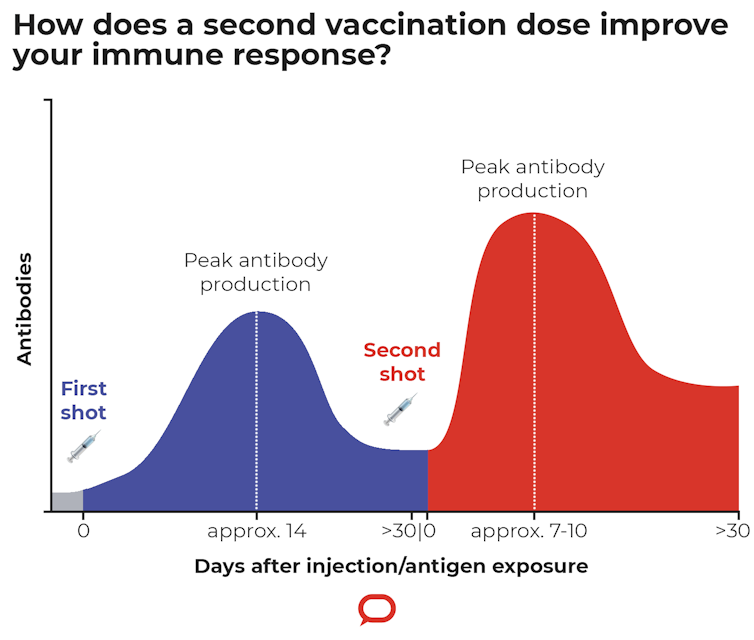
It also takes time for the immune system to respond to vaccines and produce antibodies. For most two-shot vaccines, antibody levels rise and then dip after the first dose[10]. These antibodies are then boosted after the second[11].
But you’re not optimally covered until your antibody levels rise after the second dose.
 The Conversation/ZOE COVID Symptom Study app, CC BY-ND[16][17]
Read more:
The symptoms of the Delta variant appear to differ from traditional COVID symptoms. Here's what to look out for[18]
There is always a chance a vaccinated person could pass the virus onto a non-vaccinated person without having symptoms themselves[19].
But vaccinated people who develop COVID-19 will likely have a lower viral load[20] than unvaccinated people, meaning they’re less likely to spread the virus.
One study estimated those who were vaccinated with either Pfizer or AstraZeneca were 50% less likely[21] to pass it on to an unvaccinated household contact than someone who wasn’t vaccinated. This transmission will likely reduce again if both household members are vaccinated.
But if you’re not vaccinated and contract COVID-19, you’re much more likely[22] to spread the virus.
What about future variants?
So far, the preliminary data[23] (some of which is ongoing and/or yet to be peer reviewed) shows our current vaccines are effective at protecting against circulating variants.
But as the virus mutates, there is increasing chance of viral escape[24]. This means there is a greater chance the virus will develop mutations that make it fitter against, or more easily able to evade, vaccinations.
Scientist are closely monitoring[25] to ensure our current and/or future vaccines are effective[26] against the circulating strains.
To help the fight against COVID-19 the best thing we can do is minimise the spread of the virus. This means get vaccinated when you can, ensure you maintain social distancing when required and get tested if you have any symptoms.
Read more:
No, vaccine side effects don't tell you how well your immune system will protect you from COVID-19[27]
The Conversation/ZOE COVID Symptom Study app, CC BY-ND[16][17]
Read more:
The symptoms of the Delta variant appear to differ from traditional COVID symptoms. Here's what to look out for[18]
There is always a chance a vaccinated person could pass the virus onto a non-vaccinated person without having symptoms themselves[19].
But vaccinated people who develop COVID-19 will likely have a lower viral load[20] than unvaccinated people, meaning they’re less likely to spread the virus.
One study estimated those who were vaccinated with either Pfizer or AstraZeneca were 50% less likely[21] to pass it on to an unvaccinated household contact than someone who wasn’t vaccinated. This transmission will likely reduce again if both household members are vaccinated.
But if you’re not vaccinated and contract COVID-19, you’re much more likely[22] to spread the virus.
What about future variants?
So far, the preliminary data[23] (some of which is ongoing and/or yet to be peer reviewed) shows our current vaccines are effective at protecting against circulating variants.
But as the virus mutates, there is increasing chance of viral escape[24]. This means there is a greater chance the virus will develop mutations that make it fitter against, or more easily able to evade, vaccinations.
Scientist are closely monitoring[25] to ensure our current and/or future vaccines are effective[26] against the circulating strains.
To help the fight against COVID-19 the best thing we can do is minimise the spread of the virus. This means get vaccinated when you can, ensure you maintain social distancing when required and get tested if you have any symptoms.
Read more:
No, vaccine side effects don't tell you how well your immune system will protect you from COVID-19[27]
References
- ^ is high (bmcmedresmethodol.biomedcentral.com)
- ^ Preliminary data (www.medrxiv.org)
- ^ rises to (www.medrxiv.org)
- ^ 96% and 92% effective (www.reuters.com)
- ^ stimulate (www.who.int)
- ^ if exposed to the virus (theconversation.com)
- ^ host factors (theconversation.com)
- ^ The symptoms of the Delta variant appear to differ from traditional COVID symptoms. Here's what to look out for (theconversation.com)
- ^ doesn’t mean (theconversation.com)
- ^ dip after the first dose (www.nature.com)
- ^ boosted after the second (theconversation.com)
- ^ The Conversation (adapted from Vaccine Immunology, Plotkin's Vaccines [Seventh Edition] 2018) (www.sciencedirect.com)
- ^ CC BY-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ report mild ones (covid.joinzoe.com)
- ^ shorter duration (www.nejm.org)
- ^ The Conversation/ZOE COVID Symptom Study app (covid.joinzoe.com)
- ^ CC BY-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ The symptoms of the Delta variant appear to differ from traditional COVID symptoms. Here's what to look out for (theconversation.com)
- ^ without having symptoms themselves (theconversation.com)
- ^ have a lower viral load (www.nature.com)
- ^ 50% less likely (www.nejm.org)
- ^ much more likely (www.thelancet.com)
- ^ preliminary data (www.forbes.com)
- ^ viral escape (science.sciencemag.org)
- ^ closely monitoring (www.nature.com)
- ^ effective (www.cuimc.columbia.edu)
- ^ No, vaccine side effects don't tell you how well your immune system will protect you from COVID-19 (theconversation.com)

















