Understanding Hair Loss in Men: Causes, Prevention, and Effective Care Routines
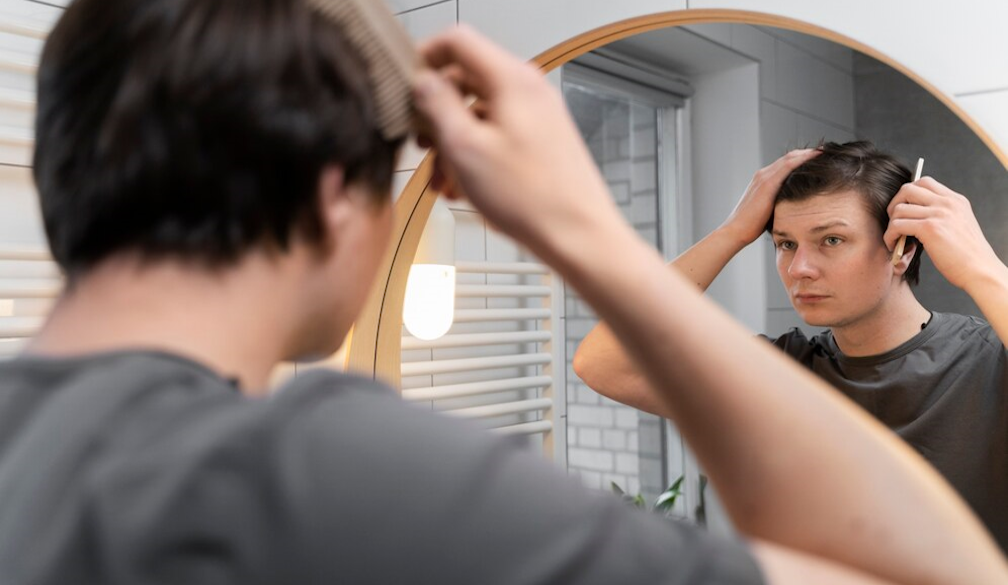

Most men suffer from hair loss, which is a common problem affecting millions of users worldwide and starts at various stages — Some may even have their hair thinning in the early 20s While others cannot observe any signs later on. No matter how it begins, the emotional baggage can stay with you for years to come and have an impact on your self-worth, confidence or freedom. Through identifying the causes, taking proactive preventive steps and practicing proper care, men can be able to control hair-loss better while preserving healthier-hair for a longer period of time.
We will explore the causes of hair loss in men, examine prevention strategies, and outline care routines that support a healthier scalp.
Causes of Hair Loss in Men
Identifying the underlying causes of hair loss in men is essential for determining effective treatment strategies. Below are some of the primary factors contributing to hair loss:
1. Androgenetic Alopecia (Male Pattern Baldness)
The leading cause of hair loss in men, male pattern baldness is a genetic condition and hormonal response to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It follows a predictable trajectory, starting with temporal hairline recession before thinning at the top of the scalp and can eventually lead to complete baldness.
2. Stress and Lifestyle Factors
One type of hair loss is telogen effluvium, a common temporary cause in which the follicles prematurely shift into the rest phase and then start to shed. Even more importantly, poor lifestyle choices like smoking and a lack of sleep or eating excessive diets can contribute greatly to hair loss.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies
Proper hair health depends on a balance of essential nutrients such as iron, zinc and biotin. Vitamin and mineral deficiency results in the weakening of hair follicles, making your strands brittle and prone to thinning or breaking.
4. Medical Conditions and Treatments
There are few medical conditions such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases and scalp infections that can be responsible for hair loss. In addition, certain medical treatments can cause the loss of hair -- but typically this is a temporary state referred to as shock shedding.
5. Hairstyling Practices
Over time, frequent use of tight hairstyles such as cornrows or dreadlocks, heat styling tools including flat irons and straighteners that damage the hair shaft at high temperatures when used daily to make your curls lay down more whilst also using chemical relaxers can all exerts stress on follicles causing traction alopecia. When the hair follicles are damaged for a long period of time, this predicament can aggravate permanent loss of scalp hairs if untreated.
Preventing Hair Loss in Men
Many types of hair loss cannot be prevented, but by taking practical steps can slow the process and throughout maintaining a healthier head.
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A good diet containing the following nutrients are well suited in order to have a healthy hair: Protein Iron Zinc Vitamin A and D Consuming foods such as leafy greens, eggs, fish nuts and fruits can nourish your scalp from inside.
2. Reduce Stress Levels
For one, chronic stress can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle. Consider trying mediation, yoga or regular exercise to reduce stress and keep a healthy environment on your scalp.
3. Be Gentle with Your Hair
Avoid any styles where the hair is being pulled, such as ponytails or cornrows. Use gentle shampoo, preferably one without sulfates and try not to wash too often as this can strip your scalp of its natural oils.
4. Avoid Heat and Chemical Damage
Using heat styling tools too often and exposing the hair to chemical treatments are some other factors that cause damage, resulting in weakened strands. Hair breakage can also be minimized by using blow dryers and straighteners less frequently, along aggressive hair coloring agents.
Effective Care Routines for Hair Loss in Men
Creating a daily hair care routine is necessary for controlling thinning and maintaining scalp health. Here is a practical approach with a few things to aim for on a daily/ weekly basis.
1. Use Topical Treatments
Minoxidil (Rogaine) is an FDA-approved topical treatment for male pattern baldness. It can be used twice daily, to stimulate hair follicles and slow down the process of losing hairs in particular on the top crown.
2. Explore Oral Medications
Finasteride, known by its brand name Propecia, is a medication approved by the FDA. It functions by inhibiting DHT, a hormone that contributes to the reduction of hair follicles. It is advisable to speak with your doctor to assess whether this medication is appropriate for your specific situation.
3. Incorporate Scalp Massages
Frequent scalp massages enhance blood circulation to hair follicles, which supports hair growth. You can stimulate the scalp by using your fingertips or a scalp massager for five to ten minutes each day.
4. Consider Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) is a non-invasive treatment that utilizes laser light to promote hair growth. This option is particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing the early stages of hair loss and can be effectively combined with topical or oral treatments.
5. Use Gentle Hair Products
Opt for hair care products specifically formulated for thinning hair. Seek out shampoos and conditioners that contain beneficial ingredients such as biotin, caffeine, and saw palmetto, as these may enhance hair health.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you notice a rapid thinning of your hairline or crown, or if you experience abrupt or severe hair loss, you should consult a dermatologist or trichologist. Preserving your hair and preventing additional loss require prompt action. A specialist will assess your particular ailment and recommend appropriate treatment options based on the root cause.
You might wish to think about more sophisticated options, such as hair transplant surgery or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, which provide longer-lasting effects, if conventional therapies like minoxidil or finasteride prove inadequate.