Were it not for JobKeeper, unemployment would be 11.7%, up from 5.2% in one month. Here's how the numbers pan out
- Written by Jeff Borland, Professor of Economics, University of Melbourne
After all the forecasts and speculation, now we know the worst.
Today’s numbers from the Australian Bureau of Statistics[1] lay out the catastrophic impact of COVID-19 on the Australian labour market.
Total hours worked fell 9.2% – in just one month, between March and April.
Percentage fall in hours worked
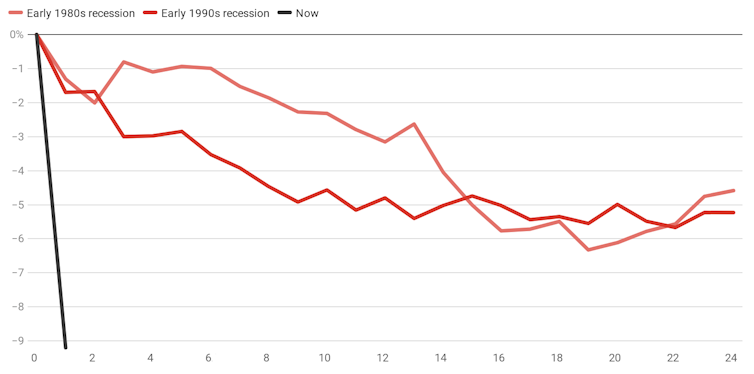 Months from start of recession.
Author's calculations from ABS 6202.0[2]
Months from start of recession.
Author's calculations from ABS 6202.0[2]
The scale and speed are difficult to comprehend.
By comparison, in the major recessions of the 1980s and 1990s, hours worked fell by 6% – but after 18 months.
Women have been hurt more than men, losing 11.5% of the hours worked in March, compared to men who lost 7.5%.
Queensland and NSW have so far fared better than other states.
Percentage fall in hours worked by state
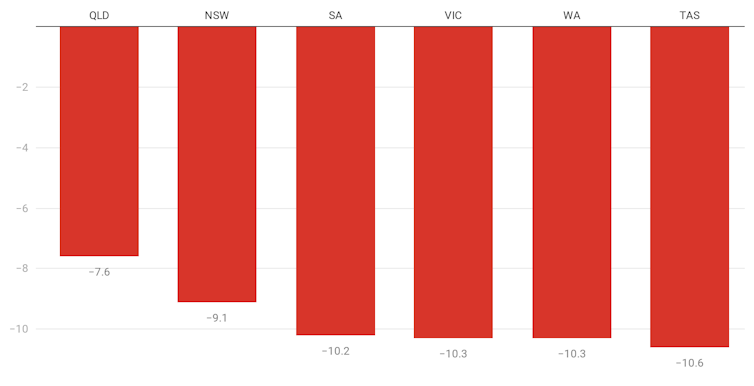 ABS 6202.0[3]
Predictions of much bigger job losses for the young than the old have been proved correct.
Workers aged 15 to 24 losing about 11% of employment compared to 3.4% for those aged 25 to 54, and 4.3% for the over 55s.
The official rate of unemployment in April 2020 rose to 6.2%. This is the highest rate since July 2015.
Read more:
What'll happen when the money's snatched back? Our looming coronavirus support cliff[4]
It doesn’t seem a big rise amid talk of a new great depression, but this is one of those times when you need to read the fine print.
To calculate its official rate the Australian Bureau of Statistics follows International Labor Organisation conventions in classifying employment and unemployment.
These classify as employed anyone who worked zero hours but was still being paid or who believed they had a job to go back to.
This is important because the JobKeeper scheme means many workers in Australia fit these categories. It makes a difference.
For this reason, the bureau has provided an adjusted[5] rate of unemployment which counts these workers as unemployed.
It puts our unemployment rate at 11.7% in April, up from 5.2% in March.
It is more in line with what we have been seeing in Canada and the United States.
Unemployment rates, January 2019 to April 2020
ABS 6202.0[3]
Predictions of much bigger job losses for the young than the old have been proved correct.
Workers aged 15 to 24 losing about 11% of employment compared to 3.4% for those aged 25 to 54, and 4.3% for the over 55s.
The official rate of unemployment in April 2020 rose to 6.2%. This is the highest rate since July 2015.
Read more:
What'll happen when the money's snatched back? Our looming coronavirus support cliff[4]
It doesn’t seem a big rise amid talk of a new great depression, but this is one of those times when you need to read the fine print.
To calculate its official rate the Australian Bureau of Statistics follows International Labor Organisation conventions in classifying employment and unemployment.
These classify as employed anyone who worked zero hours but was still being paid or who believed they had a job to go back to.
This is important because the JobKeeper scheme means many workers in Australia fit these categories. It makes a difference.
For this reason, the bureau has provided an adjusted[5] rate of unemployment which counts these workers as unemployed.
It puts our unemployment rate at 11.7% in April, up from 5.2% in March.
It is more in line with what we have been seeing in Canada and the United States.
Unemployment rates, January 2019 to April 2020
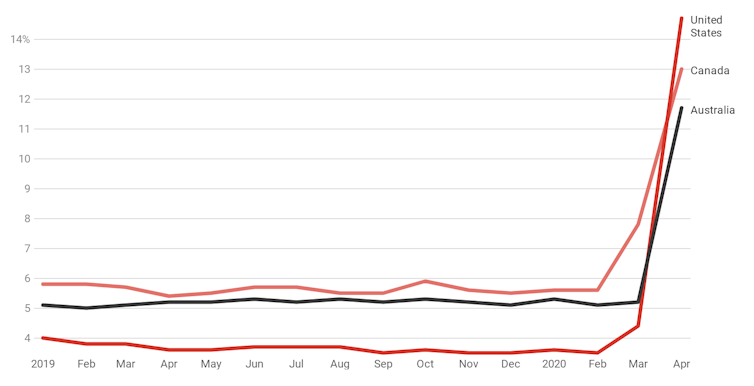 ABS 6202.0 and Canndian and US statistical agencies[6]
Under-employment is also an important part of the story. Workers who kept their jobs are now much less likely to be working the hours they want.
Between March and April the rate of underemployment (working fewer hours than wanted) jumped from 9.8% to 13.7%.
Read more:
The attacks are misguided: in a time of crisis the Bureau of Statistics is serving us well[7]
And many workers have also withdrawn completely from looking for work.
In the past month the labour force participation rate fell by 2.5 percentage points.
Again, women have been hurt more than men, with an extra 2.9% of women out of the labour force compared to an extra 2.1% for men.
Statistically, these people have vanished. They are not employed, but they are not counted as unemployed because they say they are no longer available for work.
ABS 6202.0 and Canndian and US statistical agencies[6]
Under-employment is also an important part of the story. Workers who kept their jobs are now much less likely to be working the hours they want.
Between March and April the rate of underemployment (working fewer hours than wanted) jumped from 9.8% to 13.7%.
Read more:
The attacks are misguided: in a time of crisis the Bureau of Statistics is serving us well[7]
And many workers have also withdrawn completely from looking for work.
In the past month the labour force participation rate fell by 2.5 percentage points.
Again, women have been hurt more than men, with an extra 2.9% of women out of the labour force compared to an extra 2.1% for men.
Statistically, these people have vanished. They are not employed, but they are not counted as unemployed because they say they are no longer available for work.
References
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics (www.abs.gov.au)
- ^ Author's calculations from ABS 6202.0 (www.abs.gov.au)
- ^ ABS 6202.0 (www.abs.gov.au)
- ^ What'll happen when the money's snatched back? Our looming coronavirus support cliff (theconversation.com)
- ^ adjusted (www.abs.gov.au)
- ^ ABS 6202.0 and Canndian and US statistical agencies (www.abs.gov.au)
- ^ The attacks are misguided: in a time of crisis the Bureau of Statistics is serving us well (theconversation.com)
Authors: Jeff Borland, Professor of Economics, University of Melbourne














